

Rainforest Animals. Dangerous Animals. The Amazon Rainforest is one of the world’s fascinating places.
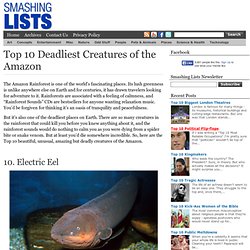
Its lush greenness is unlike anywhere else on Earth and for centuries, it has drawn travelers looking for adventure to it. Rainforests are associated with a feeling of calmness, and “Rainforest Sounds” CDs are bestsellers for anyone wanting relaxation music. You’d be forgiven for thinking it’s an oasis of tranquility and peacefulness. But it’s also one of the deadliest places on Earth. There are so many creatures in the rainforest that could kill you before you knew anything about it, and the rainforest sounds would do nothing to calm you as you were dying from a spider bite or snake venom. 10. Let’s start with one that’s not deadly to humans, though it would deliver a bit of a shock. Electric eels are rarely found in zoos and collections, because the built-in shock system makes it very difficult for them to be caught. 9. This handsome fellow is one of the biggest freshwater fishes in the world, at over 100kg and 2m long.
How Many Species of Animals Live in the Rainforest. Animals Often Seen. Advertisement.
EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site. As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.Click here to learn more. (Already a member? Click here.) Rainforests are tremendously rich in animal life. How Animals Help. Anamils in the Rain Forest. Interestiring Facts. Rainforest Bugs. Medical Plants. Rainforest Remedies Daniel Mowrey, Ph.D.

Flowers. Cool Trees. A giant in the rainforests, the kapok tree can reach up to 200 feet in height, sometimes growing as much as 13 feet per year.
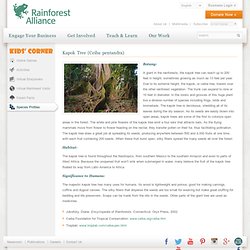
Due to its extreme height, the kapok, or ceiba tree, towers over the other rainforest vegetation. The trunk can expand to nine or 10 feet in diameter. In the nooks and grooves of this huge plant live a diverse number of species including frogs, birds and bromeliads. Facts For Kids. Climate. Worldwide zones of Tropical rainforest climate (Af).
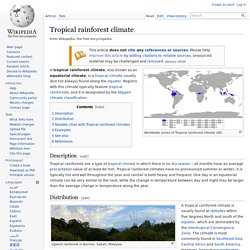
A tropical rainforest climate, also known as an equatorial climate, is a tropical climate usually (but not always) found along the equator. Regions with this climate typically feature tropical rainforests, and it is designated by the Köppen climate classification. Description[edit] Distribution[edit] Climate changes. Do Trees Grow on Money?

Rainforests are back on the global agenda in a big way. Governments now recognise the importance of protecting tropical forests in order to avoid dangerous climate change, and there is now much debate. As governments try to thrash out the details of a new international agreement, possibly to be signed at the end of 2010, they are discussing how best to include measures to save rainforests, and thereby address one of the major causes of climate change. Worldwide, forest destruction generates more greenhouse gas emissions each year than do all the trains, planes and cars on the planet. So if we are to tackle global warming, there is an urgent need to find ways to reduce the 14% or so of global greenhouse gas emissions caused by forest destruction each year, and to keep the remaining forests standing.
To date, most of the talk has focused on how to pay for reducing deforestation, rather than on how to actually go about doing it. Warm Tempetures. Cold Tempetures. Updated January 11, 2009.
Normal Weather. Avarage Weather. The tropical rain forest is a forest of tall trees in a region of year-round warmth.

An average of 50 to 260 inches (125 to 660 cm.) of rain falls yearly. Rain forests belong to the tropical wet climate group. The temperature in a rain forest rarely gets higher than 93 °F (34 °C) or drops below 68 °F (20 °C); average humidity is between 77 and 88%; rainfall is often more than 100 inches a year. Rainforest Plants. A tropical greenhouse More than two thirds of the world's plant species are found in the tropical rainforests: plants that provide shelter and food for rainforest animals as well as taking part in the gas exchanges which provide much of the world's oxygen supply.
Rainforest plants live in a warm humid environment that allows an enormous variation rare in more temperate climates: some like the orchids have beautiful flowers adapted to attract the profusion of forest insects. Competition at ground level for light and food has lead to evolution of plants which live on the branches of other plants, or even strangle large trees to fight for survival.
Types of Plants in Tropical Rainforest. Dangerous Plants. Helpful Plants. Tropical Rainforest Resources Edible Rainforest Plants Allspice: (Pimenta dioica) Berries-- shaped like peppercorns-- of an evergreen tree which can grow up to 100' in height in height in the Latin American Rainforest.

The small, aromatic fruits have a subtle flavor like a mixture of clove, cinnamon, and nutmeg, hence the name "allspice. " Banana: (Musa paradisiaca) This is the most common Musa, but there are 21 species and subspecies which are edible. Black Pepper: (Piper nigrum) A vine native to the East Indies. Caspicum annum: Cayenne pepper, sweet pepper, paprika, and jalapenos are just four of the many cultivars of this plant.
Cardamom: (Elleteria cardamom) Native to India, the third most expensive spice after saffron and vanilla. Cashews: (Anarcardium occidental) Originally from Tropical America, a valuable nut and vitamin rich fruit from the tree. Chocolate/Cocoa: (Theobroma cacao) Native to lowland tropical America, probably first domesticated in Mexico. Rare Plant. Ten Amazing Rainforest Plants. Our surroundings are sometimes taken for granted. Even something as unique as the rainforest is forgotten. It seems a little bit of knowledge and a shove in the right direction can get people to appreciate the environment. So, why not start with the wonder that is the rainforest? Even though rainforests only cover less than two percent of the Earth’s entire surface area, they are home to 50 percent of the plants and animals.
They are also found on every continent, except Antarctica. You’re probably thinking “I know all there is to know about bananas; I eat them for breakfast and can make delicious banana bread.” Habitation: Found in Central America, South America, Africa, Southeast Asia and non-tropical regions like the United States thanks to modern agricultural technologies.