

Blogs/ LA VIE APRES LA MORT (Sources) Smart Drugs. Drugs. Drugs.jpg (JPEG Image, 1053x588 pixels) - Scaled (95%) Amphetamine. Pseudoephedrine. Pseudoephedrine (/ˌsjuːdoʊ.ɨˈfɛdrɪn/ or /ˌsjuːdoʊˈɛfɨdriːn/; PSE) is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.
EDMA. Methylenedioxyethylamphetamine. MDEA (3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine; MDE, "Eve") is a psychedelic and entactogenic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.
Like MDA, MDEA acts as a serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine releasing agent.[1][2][3] Adderall. While concerns have been raised over side effects and rare, serious complications, Adderall is generally well-tolerated and effective.[3] The most common side effects are cardiovascular, such as fast or irregular heartbeat, and psychological, such as anxiety.
Adderall is a common drug of abuse. [citation needed] However, abuse or dependence is very unlikely to develop in those who use it as prescribed. [citation needed] Uses[edit] Medical[edit] Adderall is generally used for the treatment of ADHD and narcolepsy, the two conditions for which the United States Food and Drug Administration has approved its use.[4] However, it is sometimes prescribed off-label for other conditions such as depression. Methylenedioxyethylamphetamine. 94. Methcathinone. Methcathinone (α-methylamino-propiophenone or ephedrone) (sometimes called "cat" or "jeff") is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone.
It is used as a recreational drug and considered to be addictive.[1] It is usually snorted, but can be smoked, injected, or taken orally. Methcathinone is listed as a Schedule I controlled substance by the Convention on Psychotropic Substances and the United States' Controlled Substances Act. History[edit] Methcathinone was first synthesized in 1928 in the United States[2] and was patented by Parke Davis in 1957.[3] It was used in the Soviet Union during the 1930s and 1940s as an anti-depressant (under the name Эфедрон—ephedrone). Methcathinone has long been used as a drug of abuse in the Soviet Union and Russia. Circa 1994, the United States government recommended to the UN Secretary-General that methcathinone should be listed as a Schedule I controlled substance in the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.[4] MDMA. MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine) is an empathogenic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes of drugs.
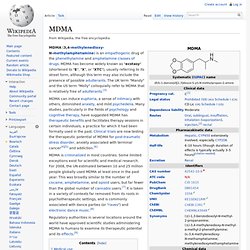
MDMA has become widely known as "ecstasy" (shortened to "E", "X", or "XTC"), usually referring to its street form, although this term may also include the presence of possible adulterants. The UK term "Mandy" and the US term "Molly" colloquially refer to MDMA that is relatively free of adulterants.[3] MDMA can induce euphoria, a sense of intimacy with others, diminished anxiety, and mild psychedelia. Many studies, particularly in the fields of psychology and cognitive therapy, have suggested MDMA has therapeutic benefits and facilitates therapy sessions in certain individuals, a practice for which it had been formally used in the past.
Clinical trials are now testing the therapeutic potential of MDMA for post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety associated with terminal cancer[4][5] and addiction.[6] Dimethoxyamphetamine. DMA, or dimethoxyamphetamine, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs similar in structure to amphetamine and to trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA).
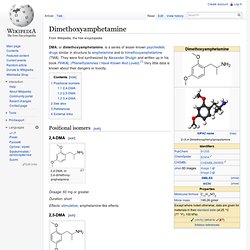
They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and written up in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known And Loved).[1] Very little data is known about their dangers or toxicity. Positional isomers[edit] 2,4-DMA[edit] Cathinone. Cathinone /ˈkæθɨnoʊn/, benzoylethanamine, or β-ketone-amphetamine also known as hagigat (Hebrew: חגיגת) in Israel,[2] is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines.
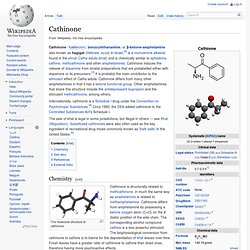
Cathinone induces the release of dopamine from striatal preparations that are prelabelled either with dopamine or its precursors.[3] It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other amphetamines that share this structure include the antidepressant bupropion and the stimulant methcathinone, among others. Internationally, cathinone is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.[4] Circa 1993, the DEA added cathinone to the Controlled Substances Act's Schedule I.
Chemistry[edit] The molecular structure of cathinone. 3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine. Medical use[edit] There are no currently accepted medical uses for MDA.
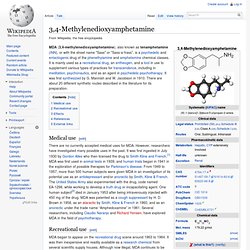
However, researchers have investigated many possible uses in the past. It was first ingested in July 1930 by Gordon Alles who then licensed the drug to Smith Kline and French.[1] MDA was first used in animal tests in 1939, and human trials began in 1941 in the exploration of possible therapies for Parkinson's disease. From 1949 to 1957, more than 500 human subjects were given MDA in an investigation of its potential use as an antidepressant and/or anorectic by Smith, Kline & French. Methylbenzodioxolylbutanamine. 1,3-Benzodioxolyl-N-methylbutanamine (N-methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine, MBDB) is an entactogen of the phenethylamine chemical class.
It is known by the street names Eden and Methyl-J.[1] MBDB is a closely related chemical analogue of MDMA, with the only difference between the two molecules being an ethyl group instead of a methyl group attached to the alpha carbon. Yohimbine. Yohimbine is a mild MAOI with stimulant and aphrodisiac effects.
It is sold as prescription medicine in pure form for the treatment of sexual dysfunction. Yohimbine was explored as a remedy for type 2 diabetes in animal and human models carrying polymorphisms of the α2A-adrenergic receptor gene.[2] Prescription Drugs - Information, Interactions & Side Effects. LY-503,430. Armodafinil. Although they have similar half lives, armodafinil reaches its peak concentration in the blood later after administration than modafinil does, which may make it more effective at improving wakefulness in patients with excessive daytime sleepiness.[5] Mechanism of action[edit] The mechanism of action of armodafinil is poorly understood, but it has been shown to act as both an indirect dopamine receptor agonist and a dopamine reuptake inhibitor.[2] Medical uses[edit]
Modafinil. Modafinil is a wakefulness-promoting agent[3] (or eugeroic) that is approved by the United States' Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of wakefulness disorders such as narcolepsy, shift work sleep disorder,[4][5] and excessive daytime sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnea.[6] In English-speaking countries it is sold under the brand names: Alertec (CA), Modavigil (AU, NZ), and Provigil (IE, ZA, UK, US). Medical uses[edit] Approved uses[edit] In 1998, modafinil was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration[7] for the treatment of narcolepsy and in 2003 for shift work sleep disorder and obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea[8] even though caffeine and amphetamine were shown to be more wakefulness promoting on the Stanford Sleepiness Test Score than modafinil.[9] EEG studies indicate caffeine, amphetamine, and modafinil to all be theta wave reducing but only modafinil to be Alpha wave promoting during wakefulness as well as theta wave increasing during sleep.[10]
Effect of pharmacological enhancement on the cognit... [Ann Surg. 2012. LY-404,187. LY-404,187 (or LY404187) is an ampakine (or "AMPA receptor potentiator") developed by Eli Lilly and Company.[1] It is a member of the biarylpropylsulfonamide class of ampakines.[2] LY-404,187 has been demonstrated to enhance cognitive function in animal studies, and has also shown effects suggesting antidepressant action as well as having possible application in the treatment of schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease and ADHD. These effects appear to be mediated through multiple mechanisms of action secondary to AMPA receptor potentiation, with a prominent effect seen in research being increased levels of BDNF in the brain.[3] It may therefore be continued on to human trials, although Eli Lilly has developed a whole family of biarylpropylsulfonamide derivatives and it is unclear at this stage which compound is most likely to be selected for further development.[4][5]
CX717. CX717 is an ampakine compound created by Christopher Marrs and Gary Rogers in 1996[1] at Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It affects the neurotransmitter glutamate, with trials showing the drug improves cognitive functioning and memory.[2] Approval process[edit] Also, in 2005, the United States Department of Defense funded a study to look into CX717 and the physiological effects of sleepiness. The study found that rhesus monkeys performed faster and better after receiving the drug, and it counteracted the effects of sleep deprivation. Farampator. Farampator (CX-691, Org 24448) is an ampakine drug. It was developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals, and licensed to Organon BioSciences for commercial development.
Following the purchase of Organon by Schering-Plough in 2007, the development license to farampator has been transferred, and development is continuing. Farampator has been investigated for its effect on AMPA receptors and researched for potential use in the treatment of schizophrenia and Alzheimer's Disease. CX-546. CX-546 is an ampakine drug developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It has been proposed as a treatment for schizophrenia.[1] CX-546 was the second drug of note to come out of the Cortex research program, after CX-516, but while it was an improvement over its predecessor in some respects, it still has problems with limited oral bioavailability. However CX-546 still represented a significant advance that led on to the development of newer compounds such as CX-614 and CX-717 with superior properties over the earlier drugs.
CX-516. Racetam. Racetams are a class of drugs that share a pyrrolidone nucleus.[1] Many, such as piracetam, but not all, are considered nootropics. Some such as oxiracetam and phenylpiracetam are also stimulants. Others such as levetiracetam and seletracetam are anticonvulsants. Phenethylamine. Occurrence[edit] Nicotine. In smaller doses (an average cigarette yields about 1 mg of absorbed nicotine), the substance acts as a stimulant in mammals, while high amounts (50–100 mg) can be harmful.[5][6][7] This stimulant effect is likely to be a major contributing factor to the dependence-forming properties of tobacco smoking, nicotine patches, nicotine gum, nicotine inhalers and liquid nicotine vaporizers.
[citation needed] According to the American Heart Association, nicotine addiction has historically been one of the hardest addictions to break, while the pharmacological and behavioral characteristics that determine nicotine addiction are similar to those determining addiction to heroin and cocaine. The nicotine content of popular American-brand cigarettes has slowly increased over the years, and one study found that there was an average increase of 1.78% per year between the years of 1998 and 2005. Crack cocaine. Crack cocaine ‘rocks’. Appearance and characteristics In purer forms, crack rocks appear as off-white nuggets with jagged edges,[3] with a slightly higher density than candle wax.
Purer forms of crack resemble a hard brittle plastic, in crystalline form[3] (snaps when broken). Modafinil Occupies Dopamine and Norepinephrine Transporters in Vivo and Modulates the Transporters and Trace Amine Activity in Vitro. Adrafinil. Adrafinil is a prodrug; it is primarily metabolized in vivo to modafinil, resulting in nearly identical pharmacological effects. Unlike modafinil, however, it takes time for the metabolite to accumulate to active levels in the bloodstream. Effects usually are apparent within 45–60 minutes when taken orally on an empty stomach. IDRA-21. IDRA-21 is an ampakine drug and a benzothiadiazine derivative. Cocaine. Caffeine. Methamphetamine. Substituted amphetamine.
Ephedrine. Dextroamphetamine. Ampakine. CX717. CX717. Stimulant. Methylphenidate. Provigil (Modafinil) Drug Information: Clinical Pharmacology. Drugs Homepage: a huge online resource of drug information, help and advice including cannabis, cocaine, heroin, ecstasy, solvents, ketamine and more. Why Intelligent People Use More Drugs. Drugs World. Recovery Humor At It's Darkest. The Internet Drug Index for prescription drugs, medications and pill identifier. CX614. List of drug films. NME’s 50 Druggiest Albums Ever. Illegal drug trade. New York's Worst Drug Sites - Persistent Markets of Death. Get Your Musical Fix Here: 21 Songs About Addiction. Top Ten - Top 10 Heroin-Inspired Songs - Top 10 - Drug Songs - Dead Flowers - Rolling Stones Lyrics - Little Susie - Brown Heroin - Fire and Rain - James Taylor Lyrics - JT - Running to Stand Still - U2 - Mr. Brownstone - Under the Bridge - Red Hot Chili.
Erowid. Bluelight. Drugs Forum. How to Deal With the Police. The Internet Drug Index for prescription drugs, medications and pill identifier. Prescription Drugs - Information, Interactions & Side Effects. The Great Big Narcotics Cookbook. Pot Tips. RateADrug.com - User Scores and Evaluations on over 8000 Rx medications and alternative therapies. Mapping Mexico's drug war.