

JoAnn Kuchera-Morin: Tour the AlloSphere, a stunning new way to see scientific data. This is onformative a studio for generative design. Arc Clock. Processing-Arc-Clock/arc_clock.pde at master · jain7th/Processing-Arc-Clock. Claudius Ptolemäus. Claudius Ptolemäus (griechisch Κλαύδιος Πτολεμαῖος Klaúdios Ptolemaíos, lateinisch Claudius Ptolomaeus; * um 100, möglicherweise in Ptolemais Hermeiou, Ägypten; † nach 160, vermutlich in Alexandria)[1] war ein griechischer Mathematiker, Geograf, Astronom, Astrologe, Musiktheoretiker und Philosoph.
Insbesondere seine drei Werke zur Astronomie, Geografie und Astrologie galten in Europa bis in die frühe Neuzeit als wichtige umfangreiche Datensammlungen und wissenschaftliche Standardwerke. Damit verwarf er wie der größte Teil seiner Zeitgenossen das von Aristarchos von Samos und Seleukos von Seleukia vertretene heliozentrische Weltbild, das erst 1300 Jahre später durch Nikolaus Kopernikus, Johannes Kepler und Galileo Galilei in Europa durchgesetzt werden sollte. Astronomie[Bearbeiten] Ptolemäisches Weltbild[Bearbeiten] Gottorfer Riesenglobus. Der Gottorfer Riesenglobus, Neubau von 2005 Das Globushaus im Neuwerkgarten[Bearbeiten] Altes Globushaus, Rekonstruktion, Modellbau von Felix Lühning Das neue Globushaus im Neuwerkgarten Wahrscheinlich war Adam Olearius der Architekt des Globushauses.
Es stand nord-südlich ausgerichtet im Scheitelpunkt einer Mauer, die den halbkreisförmigen sogenannten 'Globusgarten' nördlich des Herkulesteiches einfriedete. Das Raumkonzept des Gebäudes sah zwei übereinander liegende, niedrige Kellergeschosse vor, darüber das Hauptgeschoss mit dem Globussaal und schließlich das Obergeschoss mit zwei Schlafkammern, Kabinett und einem größeren Saal nach Süden.
Über die Nutzung des Globushauses ist wenig überliefert, obgleich Grabungsfunde von ausgedehnten Mahlzeiten im Gebäude zeugen. Der Globus[Bearbeiten] Rekonstruktion des Globusantriebs (Zeichnung: Felix Lühning) Transport nach St. Ein Besuch im Globushaus[Bearbeiten] §33. §33.
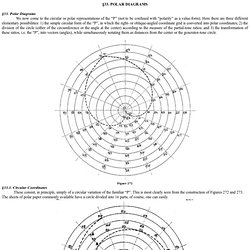
Polar Diagrams We now come to the circular or polar representations of the “P” (not to be confused with “polarity” as a value-form). Here there are three different elementary possibilities: 1) the simple circular form of the “P”, in which the right- or oblique-angled coordinate grid is converted into polar coordinates; 2) the division of the circle (either of the circumference or the angle at the center) according to the measure of the partial-tone ratios; and 3) the transformation of these ratios, i.e. the “P”, into vectors (angles), while simultaneously notating them as distances from the center or the generator-tone circle. Figure 272. Стив Блэйк. Системы полярных координат и астрология местоположения. © Стив Блэйк.

Евроазиатский филиал NCGR, 1997. © Перевод Ю. Олешко, Е. Гайдуковой. Гороскоп местоположения (Local Space Horoscope) — это тот же гороскоп, рассчитанный на определенный момент времени для определенной точки на Земле, но спроецированный на горизонт урожденного. Это статический гороскоп, полностью подобный геоцентрическому гороскопу, который используется большинством астрологов. Я намерен тщательно обосновывать все свои доводы в дальнейшем, но прежде всего следовало бы несколько вернуться назад и рассказать об Астрологии Местоположения в собственном ее смысле и в свете основных астрологических понятий. Geocentric model. Figure of the heavenly bodies — An illustration of the Ptolemaic geocentric system by Portuguese cosmographer and cartographer Bartolomeu Velho, 1568 (Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris) In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies.
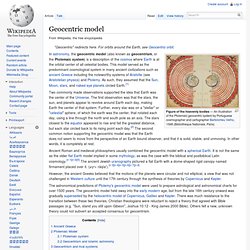
This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they assumed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.[1] Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. Heliocentrism. Andreas Cellarius's illustration of the Copernican system, from the Harmonia Macrocosmica (1660).
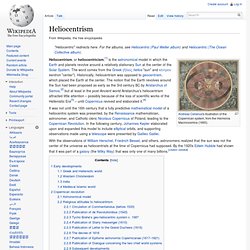
Heliocentrism, or heliocentricism,[1] is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around a relatively stationary Sun at the center of the Solar System. House (astrology) Most horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number (usually twelve) of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date.
In Hindu astrological tradition these are known as Bhāvas. God the Geometer.jpg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Circle. A circle can be defined as the curve traced out by a point that moves so that its distance from a given point is constant.
Terminology[edit] History[edit] Circular piece of silk with Mongol images The circle has been known since before the beginning of recorded history. Natural circles would have been observed, such as the Moon, Sun, and a short plant stalk blowing in the wind on sand, which forms a circle shape in the sand. Early science, particularly geometry and astrology and astronomy, was connected to the divine for most medieval scholars, and many believed that there was something intrinsically "divine" or "perfect" that could be found in circles.[2][3] Файл:Oceanic.Stripe.Magnetic.Anomalies.Scheme.gif — Википедия. Файл:Plasma magnet saturn.jpg — Википедия. Solar System. Discovery and exploration.
Astrology. People who study Astrology are called an astrologer, astrologist or a mathematicus.

Astrology is considered as a form of divination and is different from the study of astronomy. The word Astrology stems from the Greek. The belief in astrology is that the positions of certain celestial bodies either influence or correlate with a persons personality trait.