

Celiac.com. Celiac Disease Foundation. MayoClinic-Celiac Disease. Overview Celiac disease Your small intestine is lined with tiny hair-like projections called villi, which work to absorb vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from the food you eat.
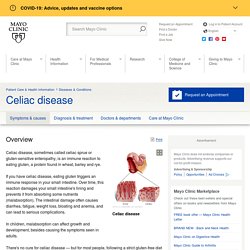
Celiac disease damages the villi, leaving your body unable to absorb nutrients necessary for health and growth. Celiac disease, sometimes called celiac sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is an immune reaction to eating gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. If you have celiac disease, eating gluten triggers an immune response in your small intestine. In children, malabsorption can affect growth and development, besides causing the symptoms seen in adults. There's no cure for celiac disease — but for most people, following a strict gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms and promote intestinal healing. Symptoms The signs and symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly and differ in children and adults. Diarrhea Fatigue Weight loss Bloating and gas Abdominal pain Nausea and vomiting Constipation.
National Foundation for Celiac Awareness. Celiac disease is an autoimmune digestive disease that damages the villi of the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food.

What does this mean? Essentially the body is attacking itself every time a person with celiac consumes gluten. Do you have celiac disease? Take our celiac disease symptoms checklist » Celiac disease is triggered by consumption of the protein called gluten, which is found in wheat, barley and rye. NDDIC: Celiac Disease. On this page: What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten, a protein in wheat, rye, and barley.
Gluten is found mainly in foods but may also be found in everyday products such as medicines, vitamins, and lip balms. The small intestine is shaded above. When people with celiac disease eat foods or use products containing gluten, their immune system responds by damaging or destroying villi—the tiny, fingerlike protrusions lining the small intestine. Villi on the lining of the small intestine help absorb nutrients.
Celiac disease is both a disease of malabsorption—meaning nutrients are not absorbed properly—and an abnormal immune reaction to gluten. [Top] What are the symptoms of celiac disease? Symptoms of celiac disease vary from person to person. Irritability is another common symptom in children. How common is celiac disease? 2Ibid. PubMed Health: Celiac Disease.
The University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center. Wikipedia: Celiac Disease. Coeliac disease, also spelled celiac disease, is an autoimmune disorder affecting primarily the small intestine that occurs in people who are genetically predisposed.[1] Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally.
This often begins between six months and two years of age.[2] Non-classic symptoms are the most common, especially in people older than two years.[3][4][5] There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms.[2] Coeliac disease was first described in childhood;[3][6] however, it may develop at any age.[2][3] It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as diabetes mellitus type 1 and thyroiditis, among others.[6] Signs and symptoms[edit] Gastrointestinal[edit] Malabsorption-related[edit] Miscellaneous[edit] Cause[edit] Other grains[edit] Risk modifiers[edit]