

Raising the prospects for quantum levitation. An eerie quantum force may one day help separate the surfaces in tiny machines for frictionless movement.
More than half-a-century ago, the Dutch theoretical physicist Hendrik Casimir calculated that two mirrors placed facing each other in a vacuum would attract. How to treat heat like light: New approach using nanoparticle alloys allows heat to be focused or reflected just like electromagnetic waves. An MIT researcher has developed a technique that provides a new way of manipulating heat, allowing it to be controlled much as light waves can be manipulated by lenses and mirrors.
The approach relies on engineered materials consisting of nanostructured semiconductor alloy crystals. Heat is a vibration of matter -- technically, a vibration of the atomic lattice of a material -- just as sound is. Such vibrations can also be thought of as a stream of phonons -- a kind of "virtual particle" that is analogous to the photons that carry light. The new approach is similar to recently developed photonic crystals that can control the passage of light, and phononic crystals that can do the same for sound.
"It's a completely new way to manipulate heat," Maldovan says. A temperature below absolute zero: Atoms at negative absolute temperature are the hottest systems in the world. What is normal to most people in winter has so far been impossible in physics: a minus temperature.
On the Celsius scale minus temperatures are only surprising in summer. On the absolute temperature scale, which is used by physicists and is also called the Kelvin scale, it is not possible to go below zero – at least not in the sense of getting colder than zero kelvin. According to the physical meaning of temperature, the temperature of a gas is determined by the chaotic movement of its particles – the colder the gas, the slower the particles. At zero kelvin (minus 273 degrees Celsius) the particles stop moving and all disorder disappears. Thus, nothing can be colder than absolute zero on the Kelvin scale. In order to bring water to the boil, energy needs to be added. “The inverted Boltzmann distribution is the hallmark of negative absolute temperature; and this is what we have achieved,” says Ulrich Schneider.
At negative temperatures an engine can do more work. Quantum Theory Demonstrated: Observation Affects Reality. From universities, journals, and other organizations Date: February 27, 1998 Source:
Daya Bay: Discovery of new kind of neutrino transformation. The Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment, a multinational collaboration operating in the south of China, has just reported the first results of its search for the last, most elusive piece of a long-standing puzzle: how is it that neutrinos can appear to vanish as they travel?
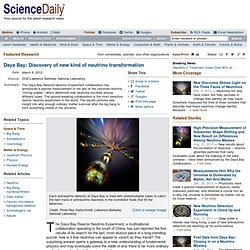
The surprising answer opens a gateway to a new understanding of fundamental physics and may eventually solve the riddle of why there is far more ordinary matter than antimatter in the universe today. Traveling at close to the speed of light, the three basic neutrino "flavors" -- electron, muon, and tau neutrinos, as well as their corresponding antineutrinos -- mix together and oscillate (transform), but this activity is extremely difficult to detect. Neutrinos, “más veloces que la luz”, amenazan teoría de Einstein. Ginebra.- Científicos dijeron que el descubrimiento de unas partículas subatómicas que parecen viajar más rápido que la luz podrían obligar a replantear las teorías sobre el origen del universo, pero que primero hay que confirmar los hallazgos de forma independiente, informó Jeff Forshaw, profesor de física de partículas en británica de Manchester, dijo que de confirmarse, los resultados supondrían que en teoría es posible enviar información al pasado.

En otras palabras, viajar en el tiempo sería posible (...) Higgs boson announcement live: Cern scientists discover subatomic particle. 7.17am: Good morning all.
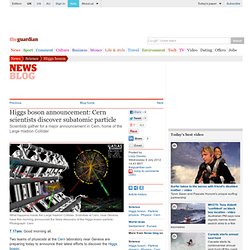
Two teams of physicists at the Cern laboratory near Geneva are preparing today to announce their latest efforts to discover the Higgs boson. Participants take a rest early before the opening of the seminar. Photograph: Denis Balibouse/AFP/Getty Images The elusive "God particle" has become the most sought-after particle in modern science. Its discovery would be proof of an invisible energy field that fills the vacuum of space, and excitement in the scientific community is at fever pitch.
Peter Higgs, the Edinburgh University physicist who proposed the idea of the particle in 1964, is flying in to Geneva, as are two other men who published similar theories at around the same time: François Englert, professor emeritus at the Free University of Brussels (ULB) in Belgium, and Tom Kibble, professor emeritus at Imperial College London. The Guardian's Ian Sample has flown to Geneva and I'll be live-blogging this potentially historic morning on this page. Antimatter Detonation & Von Neumann Machines.
Sam Hughes, LiveScience Contributor | January 12, 2012 08:45am ET.
The Coolest Little Particles in Nature. Vacuum energy. Vacuum energy is an underlying background energy that exists in space throughout the entire Universe.
One contribution to the vacuum energy may be from virtual particles which are thought to be particle pairs that blink into existence and then annihilate in a timespan too short to observe. They are expected to do this everywhere, throughout the Universe. Their behavior is codified in Heisenberg's energy–time uncertainty principle.