

Pancreas. Structure[edit] 1.
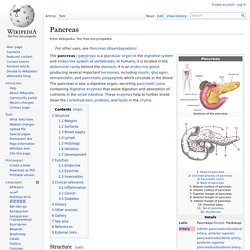
Bile ducts: 2. Intrahepatic bile ducts, 3. Left and right hepatic ducts, 4. Common hepatic duct, 5. The pancreas is an endocrine organ that lies in the abdomen, specifically the upper left abdomen. Anatomically, the pancreas is divided into a head, which rests within the concavity of the duodenum, a body lying behind the base of the stomach, and a tail, which ends abutting the spleen. The pancreas is a secretory structure with a internal hormonal role (endocrine) and an external digestive role (exocrine). Margins[edit] The superior margin of pancreas is blunt and flat to the right; narrow and sharp to the left, near the tail. It commences on the right in the tuber omentale, and is in relation with the celiac artery, from which the hepatic artery courses to the right just above the gland, while the lienal artery runs toward the left in a groove along this border. Surfaces[edit] The anterior surface of the pancreas faces the front of the abdomen.
Blood supply[edit] Gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis (abbreviated GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, glucogenic amino acids, and fatty acids (both even-chain[1] and odd-chain).
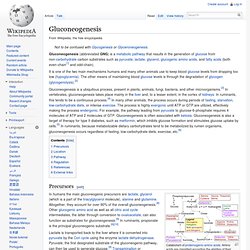
It is one of the two main mechanisms humans and many other animals use to keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia). The other means of maintaining blood glucose levels is through the degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis).[2] Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.[3] In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of kidneys. In ruminants, this tends to be a continuous process.[4] In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. Precursors[edit] Catabolism of proteinogenic amino acids. Location[edit] Pathway[edit] . Endocrine system. In addition to the specialised endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems, such as bone, kidney, liver, heart and gonads, have secondary endocrine functions.
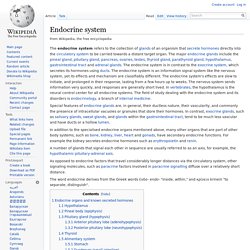
For example the kidney secretes endocrine hormones such as erythropoietin and renin. A number of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis, for example, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. As opposed to endocrine factors that travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system, other signaling molecules, such as paracrine factors involved in paracrine signalling diffuse over a relatively short distance. The word endocrine derives from the Greek words ἐνδο- endo- "inside, within," and κρίνειν krinein "to separate, distinguish". Endocrine organs and known secreted hormones[edit] Endocrine glands in the human head and neck and their hormones Hypothalamus[edit] Pineal body (epiphysis)[edit] Pituitary gland (hypophysis)[edit]
Hypofyse. Mediansnit[1] gennem en (abe)-hypofyse.
Hypofysen (græsk: Hypophysis, eller på latin: Glandula pituitaria[2]) er en overordnet kirtel på størrelse med et solbær placeret under hjernen. Hypofysen står i tæt forbindelse med centre i den primitive hjerne, og disse kan sammen udøve en overordnet kontrol på mange af kroppens andre organer. Hormonudskillelsen styres ved hjælp af Feedback-systemer. Anatomi[redigér | redigér wikikode] Makroskopisk[redigér | redigér wikikode] Om organet: Hypofysen måler 1,5x1,0x0,5 cm og vejer ca 0,5 g, dog stiger vægten under graviditet.
Relationer:Hypofysen befinder sig i "Den Tyrkiske Sadel" (sella turcica eller fossa hypophysialis), som er en lille udhulning i kilebenet (os sphenoidale). Blodforsyning: Blodet til hypofysen kommer fra to sæt arterier, der begge kommer fra a. carotis interna. Mikroskopisk[redigér | redigér wikikode] Pars distalis[redigér | redigér wikikode] Neurohypofysen[redigér | redigér wikikode] Pars intermedia[redigér | redigér wikikode]