Untitled. Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibition delays recurrence of glioblastoma after radiation by altering myeloid cell recruitment and polarization. Untitled. T: : he tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage : Abstract : Nature. Nature 399, 806-809 (24 June 1999) | doi:10.1038/21690; Received 21 April 1999; Accepted 6 May 1999.

Cell Death and Disease - How cell death shapes cancer. Citation: Cell Death and Disease (2015) 6, e1675; doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.20Published online 5 March 2015 Top of page Facts During cancer development, clonal selection is facilitated by the acquisition of mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressors and by the selection of 'winner' cells.Apoptosis of (pre)-cancerous cells generates vacant niches that potentially become repopulated by more aggressive sub-clones.

Thereby, apoptosis increases proliferative pressure and promotes clonal selection, thus driving tumor evolution.Dying cells can promote cell division of neighboring cells. Susana Godinho - Barts Cancer Institute. Iris View Profile. Professor Walczak Lab Members. Postdoctoral researchers Eva Rieser, PhDEva studies the role of LUBAC in innate immune signalling pathways in vitro and in vivo Email: e.rieser@ucl.ac.uk Silvia von Karstedt, PhDSilvia investigates the cancer biological role of the endogenous TRAIL/TRAIL-receptor system.
Email: s.karstedt@ucl.ac.uk Peter Draber, PhDPeter analyses the biochemistry of LUBAC and linear ubiquitination in various innate and adaptive immune signalling pathways. Email: p.draber@ucl.ac.uk. Cell Death, Cancer and Inflammation. Professor Henning Walczak, PhDScientific Director of the Cancer Research UK-UCL CentreHead of the Department of Cancer BiologyGroup Leader: Cell Death, Cancer and Inflammation Research Group Research focus.
FGF signaling inhibition in ESCs drives rapid genome-wide demethylation to the epigenetic ground state of pluripotency. The Hallmarks of Cancer: Cell. To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription.
Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. Figure 1 Acquired Capabilities of Cancer We suggest that most if not all cancers have acquired the same set of functional capabilities during their development, albeit through various mechanistic strategies. Figure 2 The Emergent Integrated Circuit of the Cell Progress in dissecting signaling pathways has begun to lay out a circuitry that will likely mimic electronic integrated circuits in complexity and finesse, where transistors are replaced by proteins (e.g., kinases and phosphatases) and the electrons by phosphates and lipids, among others. Figure 3 Tumors as Complex Tissues. GetSharedSiteSession?rc=1&redirect= The hallmarks of cancer comprise six biological capabilities acquired during the multistep development of human tumors.
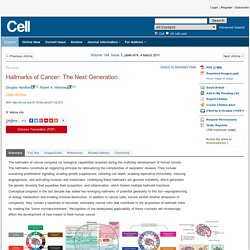
The hallmarks constitute an organizing principle for rationalizing the complexities of neoplastic disease. They include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Underlying these hallmarks are genome instability, which generates the genetic diversity that expedites their acquisition, and inflammation, which fosters multiple hallmark functions.
Conceptual progress in the last decade has added two emerging hallmarks of potential generality to this list—reprogramming of energy metabolism and evading immune destruction. Sinister Self-Sacrifice: The Contribution of Apoptosis to Malignancy. Induction of apoptosis is one of the main defenses of the body against cells that have acquired malicious mutations.
It may seem counter-intuitive then, that massive cell death is observed in many malignant tumors (1, 2). Despite high rates of apoptosis, these tumors continue to grow rapidly. Thus, tumor cell growth must outbalance tumor cell death. Intuitively presumed only to inhibit tumor growth, apoptotic cells may actually promote net tumor growth (3, 4). As long ago as 1956, Revesz showed that cell death can enhance tumor growth (5). Cells undergoing apoptosis are difficult to observe in vivo, as they are rapidly cleared by phagocytosis, most obviously by macrophages.
Loading of nuclear autoantigens prototypically recognized by systemic lupus erythematosus sera into late apoptotic vesicles requires intact microtubules and myosin light chain kinase activity - Zirngibl - 2014 - Clinical & Experimental Immunology. Summary Most cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are characterized by an impaired clearance of apoptotic cells in various tissues.

Non-cleared apoptotic waste is considered an immunogen driving the autoimmune response in patients with SLE. During the execution of apoptosis, membrane blebs are formed and filled with cellular components. Here, we evaluate the cytoskeletal pathway(s) responsible for the loading of SLE prototypic nuclear autoantigens into the apoptotic cell-derived membranous vesicles (ACMV) generated during late phases of apoptosis. HeLa cells expressing a fusion protein of histone H2B with green fluorescent protein (GFP) were irradiated with ultraviolet (UV)-B to induce apoptosis. Cell Death and Differentiation - Modulation of macrophage antitumor potential by apoptotic lymphoma cells.
Cell Death and Differentiation advance online publication 3 February 2017; doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.132 Jorine J L P Voss1, Catriona A Ford1, Sofia Petrova1, Lynsey Melville1, Margaret Paterson1, John D Pound1, Pam Holland1, Bruno Giotti2, Tom C Freeman2 and Christopher D Gregory1.

GetSharedSiteSession?rc=4&redirect= GetSharedSiteSession?rc=4&redirect= Figure 1 Suppression of Apoptosis in Lymphoma Cells Constrains In Vivo Proliferation and Angiogenesis.