

ECS 40 Homework 1: Postfix Calculator. Due: Thursday, January 19 at 2200 hours.

Check out: git clone metastasis@cancer.cs.ucdavis.edu:user/{username}/1/1 Hand out: Reference program: postfix (SHA-1: 955dc54f30c2e85215122ade7c75f8001d2f768a). Example input: postfix.test. Note: the reference program runs on only x86-64 Linux, where the command uname -m should output x86_64. Only some CSIF machines are x86-64. Check in: Makefile and all the necessary source files (do NOT check in executable or object files!). Reverse Polish notation. During the 1970s and 1980s, RPN was known to many calculator users, as it was used in some handheld calculators of the time designed for advanced users: for example, the HP-10C series and Sinclair Scientific calculators.
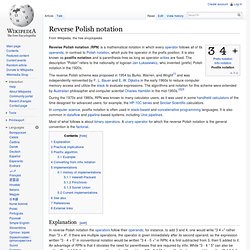
Most of what follows is about binary operators. A unary operator for which the reverse Polish notation is the general convention is the factorial. Explanation[edit] Postfix Calculator. Postfix Evaluation. Linked list. A linked list whose nodes contain two fields: an integer value and a link to the next node.
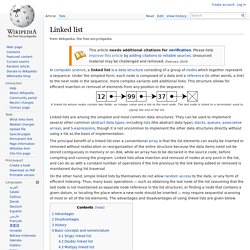
The last node is linked to a terminator used to signify the end of the list. The principal benefit of a linked list over a conventional array is that the list elements can easily be inserted or removed without reallocation or reorganization of the entire structure because the data items need not be stored contiguously in memory or on disk, while an array has to be declared in the source code, before compiling and running the program.
Linked lists allow insertion and removal of nodes at any point in the list, and can do so with a constant number of operations if the link previous to the link being added or removed is maintained during list traversal. On the other hand, simple linked lists by themselves do not allow random access to the data, or any form of efficient indexing. Advantages[edit] Disadvantages[edit] History[edit] Basic concepts and nomenclature[edit] Singly linked list[edit] Stack (abstract data type) Simple representation of a stack A stack may be implemented to have a bounded capacity.
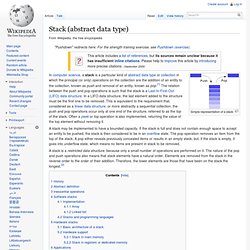
If the stack is full and does not contain enough space to accept an entity to be pushed, the stack is then considered to be in an overflow state. The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack. A pop either reveals previously concealed items or results in an empty stack, but, if the stack is empty, it goes into underflow state, which means no items are present in stack to be removed. Classes (I) Classes are an expanded concept of data structures: like data structures, they can contain data members, but they can also contain functions as members.
An object. Introduction to C++ Classes. Contents An Example C++ Class C++ classes are similar to Java classes in many ways, but there are also important differences.

C++ classes. Differences between struct and classes in C++[edit] In C++, a structure is a class defined with the struct keyword.[1] Its members and base classes are public by default.
A class defined with the class keyword has private members and base classes by default. Object-Oriented C++ Class Design - CProgramming.com. Understanding Interfaces When you're designing a class in C++, the first thing you should decide is the public interface for the class.
The public interface determines how your class will be used by other programmers (or you), and once designed and implemented it should generally stay pretty constant. You may decide to add to the interface, but once you've started using the class, it will be hard to remove functions from the public interface (unless they aren't used and weren't necessary in the first place). But that doesn't mean that you should include more functionality in your class than necessary just so that you can later decide what to remove from the interface. If you do this, you'll just make the class harder to use.
At the same time, just because adding methods to the public interface (probably) won't break anything that doesn't mean that you should start off with a tiny interface. The public interface, then, should remain as constant as possible. Friendship and inheritance. Friend functions In principle, private and protected members of a class cannot be accessed from outside the same class in which they are declared.
However, this rule does not apply to "friends". Friends. Classes (II) [NOTE: This chapter requires proper understanding of dynamically allocated memory] Special member functions are member functions that are implicitly defined as member of classes under certain circumstances.
There are six: Let's examine each of these: Default constructor. Arrays. An array is a series of elements of the same type placed in contiguous memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to a unique identifier. That means that, for example, five values of type int can be declared as an array without having to declare 5 different variables (each with its own identifier).
Instead, using an array, the five int values are stored in contiguous memory locations, and all five can be accessed using the same identifier, with the proper index. For example, an array containing 5 integer values of type int called foo could be represented as: where each blank panel represents an element of the array. In this case, these are values of type int. Like a regular variable, an array must be declared before it is used. Therefore, the foo array, with five elements of type int, can be declared as: Initializing arrays By default, regular arrays of local scope (for example, those declared within a function) are left uninitialized.
Control Structures. A simple C++ statement is each of the individual instructions of a program, like the variable declarations and expressions seen in previous sections. They always end with a semicolon (;), and are executed in the same order in which they appear in a program. But programs are not limited to a linear sequence of statements. During its process, a program may repeat segments of code, or take decisions and bifurcate. For that purpose, C++ provides flow control statements that serve to specify what has to be done by our program, when, and under which circumstances. Many of the flow control statements explained in this section require a generic (sub)statement as part of its syntax. . { statement1; statement2; statement3; } The entire block is considered a single statement (composed itself of multiple substatements). C++ Operators. Logical OR Operator:
Logical-or-expression || logical-and-expression The logical OR operator (||) returns the boolean value true if either or both operands is true and returns false otherwise. The operands are implicitly converted to type bool prior to evaluation, and the result is of type bool. Logical OR has left-to-right associativity. Delete an array element. Istream. Public member function Get characters Extracts characters from the stream, as unformatted input: (1) single character Extracts a single character from the stream. The character is either returned (first signature), or set as the value of its argument (second signature). Using cin.get, cin.getline, & cin.ignore. Using >>, cin.get, cin.getline, and cin.ignore. Getline. Istream. Public member function Peek next character.
Istream. Fgets. How to use EOF in C. In article Malcolm McLean >the function fgetc() will return an integer, not a character as you may haveimagined, in the range 0-255 except some very odd systems that don't use 8bit bytes. Ios. Atoi. Function int atoi (const char * str); C Strings in C and C. How to concatenate two integer values. Infix, Postfix and Prefix. UP Infix, Postfix and Prefix notations are three different but equivalent ways of writing expressions.