

Www.FungiPhoto.com Mushroom Photo Catalog. California Fungi. Mycology. Mushrooms are a kind of fungal reproductive structure From mycology arose the field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases, and the two disciplines remain closely related because the vast majority of "plant" pathogens are fungi.
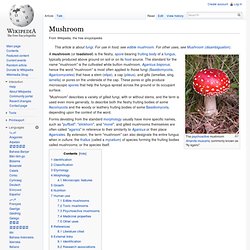
A biologist specializing in mycology is called a mycologist. Historically, mycology was a branch of botany because, although fungi are evolutionarily more closely related to animals than to plants, this was not recognized until a few decades ago. Pioneer mycologists included Elias Magnus Fries, Christian Hendrik Persoon, Anton de Bary, and Lewis David von Schweinitz. Many fungi produce toxins, antibiotics, and other secondary metabolites. Fungi are fundamental for life on earth in their roles as symbionts, e.g. in the form of mycorrhizae, insect symbionts, and lichens. Some fungi can cause disease in humans or other organisms. History[edit] The Middle Ages saw little advancement in the body of knowledge about fungi. Medicinal mycology[edit] See also[edit] Mushroom. "Mushroom" describes a variety of gilled fungi, with or without stems, and the term is used even more generally, to describe both the fleshy fruiting bodies of some Ascomycota and the woody or leathery fruiting bodies of some Basidiomycota, depending upon the context of the word.
Identification[edit] Morphological characteristics of the caps of mushrooms Identifying mushrooms requires a basic understanding of their macroscopic structure. Most are Basidiomycetes and gilled. Their spores, called basidiospores, are produced on the gills and fall in a fine rain of powder from under the caps as a result. While modern identification of mushrooms is quickly becoming molecular, the standard methods for identification are still used by most and have developed into a fine art harking back to medieval times and the Victorian era, combined with microscopic examination. MykoWeb: Mushrooms, Fungi, Mycology. Fungi. Description of Fungi The term fungus has more than one meaning.
It is best limited to members of the kingdom Fungi - in which the normal trophic form is a system of filaments or mycelia and from which spores are occasionally produced. Feeding usually occurs through the mycelia, and the spores usually facilitate distribution and help the fungus colonize new habitats. The true fungi have their evolutionary origins within the chytrids (some taxonomists include these within the fungi). In addition to the true fungi, a number of other evolutionary lineages have produced fungus-like organisms. Trusted. Fungus. Biological kingdom, separate from plants and animals A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls.
Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. Etymology The English word fungus is directly adopted from the Latin fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace and Pliny.[7] This in turn is derived from the Greek word sphongos (σφόγγος "sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds;[8] the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold").[9] Characteristics Shared features: Diversity.