

National Health Service. The official logo of the NHS in England.

The four publicly funded health care systems in the countries of the United Kingdom are referred to as the National Health Service (NHS). The systems are primarily funded through central taxation. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use for people legally resident in the United Kingdom. The four systems are mostly independent from each other although some functions might be routinely performed on behalf of the UK Department of Health or for one of the other three systems (e.g. Northern Ireland has no high security mental hospitals and thus depends on using hospitals in Great Britain, routinely Carstairs State Mental Hospital in Scotland for male patients and Rampton Secure Hospital in England for female patients);[1] otherwise, they operate under different management, rules, and political authority.
The individual systems are: History[edit] Recent (2010 – present)[edit] Health department. "Health department" can also refer to a university health department.

Health departments around the world[edit] See also[edit] Health minister. Tamiflu. Australia agrees compensation deal for Canberra homes. 27 October 2014Last updated at 23:33 ET About 1,000 homes in Canberra are believed to be affected by asbestos The Australian government has agreed to help compensate people in Canberra whose asbestos-ridden houses will be demolished with a A$1bn (£546m) loan.

The loan to the Australian Capital Territory comes after talks between ACT Chief Minister Katy Gallagher and Federal Employment Minister Eric Abetz. More than 1,000 Canberra homes affected by loose-fill asbestos insulation will be bought and demolished. Ms Gallagher said her government had reached "an in-principle agreement". Category:Health in Australia. Magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to investigate the anatomy and function of the body in both health and disease.
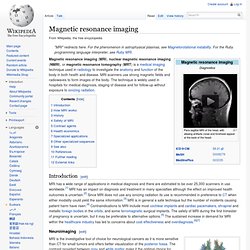
MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields and radiowaves to form images of the body. The technique is widely used in hospitals for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and for follow-up without exposure to ionizing radiation. Introduction[edit] Neuroimaging[edit] MRI image of white matter tracts. MRI is the investigative tool of choice for neurological cancers as it is more sensitive than CT for small tumors and offers better visualization of the posterior fossa.
Cardiovascular[edit] MR angiogram in congenital heart disease Cardiac MRI is complementary to other imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, cardiac CT and nuclear medicine. Proton therapy. Proton therapy is a type of particle therapy which uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often in the treatment of cancer.

The chief advantage of proton therapy is the ability to more precisely localize the radiation dosage when compared with other types of external beam radiotherapy, though it is controversial whether this provides an overall advantage compared to other, less expensive treatments. Description[edit] In a typical treatment plan for proton therapy, the Spread Out Bragg Peak (SOBP, dashed blue line), is the therapeutic radiation distribution. The SOBP is the sum of several individual Bragg peaks (thin blue lines) at staggered depths. The depth-dose plot of an x-ray beam (red line) is provided for comparison. Proton therapy is a type of external beam radiotherapy using ionizing radiation.
To treat tumors at greater depths, the proton accelerator must produce a beam with higher energy, typically given in eV or electron volts. Home. North Metropolitan Health Service, Mental Health. Role and Function North Metropolitan Health Service (NMHS) Mental Health aims to provide best practice, specialised mental health services supported by strategic planning in partnerships with service providers to the people of Western Australia.
NMHS Mental Health is part of North Metropolitan Health Service which includes the Graylands, Sir Charles Gairdner, Osborne Park, Swan District and Kalamunda Hospitals and associated health services, Joondalup Health Campus and NMHS Population and Ambulatory Care Division. NMHS Mental Health is committed to the ongoing development and improvement of mental health services in Western Australia inline with relevant National and State policies, plans and frameworks. Services are delivered through inpatient units, community mental health centres, and day therapy and outreach programs to a catchment area of more than 800,000 people.
NMHS Mental Health services are accessed by referral from a range of health care providers. Governance NMHS Vision Statement. Get The Bigger Picture - Health. Services provided across South Metropolitan Health Service. Our focus at SMHS is improving patient care and population health outcomes for our patients and the community.

To this end, hospitals in the area are undergoing major changes to achieve an integrated approach across professions, sites and services, sharing knowledge and expertise, recognising and building on strengths. Our hospitals will be developing collaborative networks and partnerships, aligning resources, systems and processes across the health service to achieve our goals. Part of the reconfiguration includes changes to how our hospitals deliver their services: PathWest. Healthcare germany. GP groups welcome Budget’s $1.2 billion investment in frontline healthcare. AFTER the disappointment of last year’s Budget, GP and primary health care has enjoyed billion-dollar wins in the Rudd Government’s third Budget.

The Federal Government has set aside $1.2 billion to improve GP and primary health care, including $355.2 million for a widespread rollout of the controversial GP super clinic program. The funding provides for 23 new dedicated GP super clinics plus upgrades to around 425 primary care facilities. Grants to upgrade practices will be worth up to $500,000 per practice. The Government also unveiled the expected new practice nurse incentive payments. All practices will now be eligible for payments of $25,000 per practice nurse, up to a maximum of $125,000. Management of the National Medical Stockpile.