

85% of British power can be via renewables by 2030, says Greenpeace. Britain can produce 85% of its power via renewable energy by 2030 provided it undergoes significant changes in energy production and use, according to a new study by Greenpeace.

The study attempts to counter the argument that only fossil fuels and nuclear power can keep the lights on for the next few decades. It foresees wind leaping from today’s level of 13 gigawatts (GW) of wind farms in operation – enough to power around 10 million homes – to a level of 77GW in 2030, with solar rising from just more than 5GW to 28GW. However, the renewables drive would need to be accompanied by a 60% reduction in demand for domestic heating through a home insulation programme and other initiatives, according to the report by energy system analysts, Demand Energy Equality.
Pylons to be removed in four protected areas - BBC News. Image copyright PA Electricity pylons are to be removed in four areas of England and Wales to reduce their visual impact on the landscape.
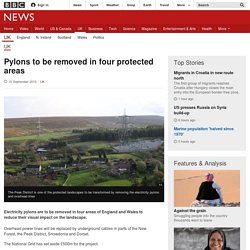
Overhead power lines will be replaced by underground cables in parts of the New Forest, the Peak District, Snowdonia and Dorset. The National Grid has set aside £500m for the project. Environmentalist Chris Baines, who helped select the locations, said it had been a "difficult decision". The four schemes have been prioritised out of 12 sections of electricity lines in eight national parks and areas of outstanding natural beauty (AONB) across England and Wales which were considered to have the most significant impact on beauty spots. The four stretches of lines which have been prioritised are in: Dorset AONB, near Winterbourne AbbasNew Forest National Park, near HalePeak District National Park, near Dunford BridgeSnowdonia National Park, near Porthmadog He said all the locations on the original shortlist would remain under consideration for future work.
Australian climate policy paralysis has to end, business roundtable says. An unprecedented alliance of business, welfare and environmental groups and trade unions is demanding an end to Australia’s decade of political paralysis and division on climate policy, insisting the Abbott government make credible emission reduction commitments and the major parties agree on how the pledges should be implemented.

In an attempt to reset the bitter political debate on climate policy, the powerful lineup of interest groups has reached a historic agreement on “principles” that should guide Australia’s climate policy. The principles do not explicitly mention the Abbott government’s Direct Action climate plan or the former Labor government’s emissions trading scheme, but they include objectives Direct Action fails to meet in its current form – including being “internationally linked”, being “capable of achieving deep reductions” and achieving greenhouse reductions “across all sections of the economy”.
Smart meter scheme could be IT disaster, says IoD - BBC News. The government's smart meter scheme could be an "IT disaster", the Institute of Directors (IoD) has said.
The risks involved with "the largest UK government-run IT project in history" were "staggering", a report said. It recommended that the government drastically scale back the programme or abandon it altogether. Smart Energy GB, the independent body set up to publicise smart meters, said the IoD wanted to take the UK "back to an analogue dark age". Energy-saving digital smart meters, designed to replace existing analogue gas and electricity meters, should help householders to monitor their energy-use far more accurately, and energy companies to do away with estimated bills. 'Technological innovation' Renewable energy in the United States. Sources of total United States renewable energy, 2012 (US EIA) US renewable electricity generated in 2012, by source (US EIA) Renewable energy in the United States accounted for 12.9 percent of the domestically produced electricity in 2013,[1] and 11.2 percent of total energy generation.[2] As of 2014, more than 143,000 people work in the solar industry and 43 states deploy net metering, where energy utilities buy back excess power generated by solar arrays.[3]
Black Saturday fires: Australia court backs record payout. 23 December 2014Last updated at 02:39 ET A total of 173 people died in the Black Saturday fires in Victoria, Australia An Australian court has approved a record payout of almost A$500m (£260m; $406m) for those who survived - or lost family members to - one of the country's worst bushfires.
The payout - the largest class action settlement in Australia - was over the deadliest of the Black Saturday fires, which killed 172 people in 2009. Thousands sued a power company and others for negligence over the fire. The settlement does not include any admissions of liability. Black Saturday fires: Australia court backs record payout. Lignite. Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft brown combustible sedimentary rock that is formed from naturally compressed peat.
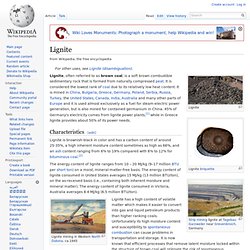
It is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat content. It is mined in China, Bulgaria, Greece, Germany, Poland, Serbia, Russia, Turkey, the United States, Canada, India, Australia and many other parts of Europe and it is used almost exclusively as a fuel for steam-electric power generation, but is also mined for contained germanium in China. 45% of Germany's electricity comes from lignite power plants,[1] while in Greece lignite provides about 50% of its power needs. Characteristics[edit] Lignite is brownish-black in color and has a carbon content of around 25-35%, a high inherent moisture content sometimes as high as 66%, and an ash content ranging from 6% to 19% compared with 6% to 12% for bituminous coal.[2] Uses[edit] Geology[edit]
Gas trading hub. Biofuel. Scrapping RET 'could save households $65 a year but lose the nation $10bn' European Renewable Energy Council. Home.