

Test Variant Torpedo. Offshore Patrol Vessel. Planet-class research ship. The Type 751 Planet of the German Navy is the most modern naval research ship within NATO.[1] It was built as SWATH design in order to reduce the hull volume and to increase the ship's stability - particularly in high seas and at high speed.
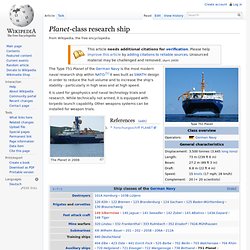
It is used for geophysics and naval technology trials and research. While technically not armed, it is equipped with torpedo launch capability. Other weapons systems can be installed for weapon trials. Research vessel. History[edit] The research ship had origins in the early voyages of exploration.
By the time of James Cook's Endeavour, the essentials of what today we would call a research ship are clearly apparent. In 1766, the Royal Society hired Cook to travel to the Pacific Ocean to observe and record the transit of Venus across the Sun.[1] The Endeavour was a sturdy boat, well designed and equipped for the ordeals she would face, and fitted out with facilities for her "research personnel", Joseph Banks. And, as is common with contemporary research vessels, Endeavour carried out more than one kind of research, including comprehensive hydrographic survey work.
The names of early research vessels have been used to name later research vessels, as well as Space Shuttles. Modern types[edit] ↑ Danish fisheries research vessel, FRV Dana ↑ German naval research vessel Planet Hydrographic survey[edit] A hydrographic survey ship is a vessel designed to conduct hydrographic research and survey. HMAS Jervis Bay. Two ships of the Royal Australian Navy have been named HMAS Jervis Bay, for Jervis Bay on the south coast of New South Wales.
Battle honours[edit] One battle honour has been awarded to ships named HMAS Jervis Bay:[1][2] East Timor 1999–2000. HMAS Jervis Bay. Canberra-class landing helicopter dock. Planning and selection[edit] Design and capabilities[edit] Each ship is fitted with a Saab 9LV Mark 4 combat management system.[5] The sensor suite includes a Sea Giraffe 3D surveillance radar, and a Vampir NG infrared search and track system.[5] For self-defence, the LHDs will be fitted with four Rafael Typhoon 25 mm remote weapons systems (one in each corner of the flight deck),[18] six 12.7 mm machine guns, an AN/SLQ-25 Nixie towed torpedo decoy, and a Nulka missile decoy.[16] Defence against aircraft and larger targets is to be provided by escort vessels and air support from the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).[18] The ships' companies will consist of 358 personnel; 293 RAN, 62 Australian Army, and 3 RAAF.[19]
Perisher submarine command training. Hyuga class helicopter destroyer. Ticonderoga-class cruiser. History[edit] Shoot down of Iran Air Flight 655[edit] Interception of United States satellite USA-193[edit] Possible early retirement[edit] Due to Budget Control Act of 2011 requirements to cut the Defense Budget for FY2013 and subsequent years, plans are being considered to decommission some of the Ticonderoga-class cruisers.[7] For the U.S.
Defense 2013 Budget Proposal, the U.S. Because of these retirements, the U.S. By October 2012, the U.S. Rigid-hulled inflatable boat. RNLI inshore rescue boat during Falmouth Lifeboat Day, August 2006 Uses include work boats (supporting shore facilities or larger ships) in trades that operate on the water, as well as use as lifeboats and military craft, where they are used in patrol roles and to transport troops between vessels or ashore.
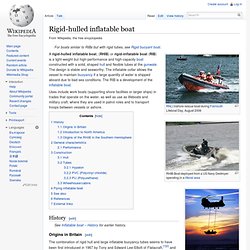
History[edit] See Inflatable boat – History for earlier history. Origins in Britain[edit] In 1964, Rear-Admiral Desmond J. By 1966 the students had built a further five rigid inflatable boats – Aphrodite (15 ft), Triton (16 ft) and X1–X3. By that time Des Hoare had concluded that for the conditions under which they operated a boat of around 18 feet long was optimum which led to X4 (launched 1966), X5 and X6 (launched 1967), and X7 to X8 (launched 1968). All the above boats’ hulls were built from plywood. HMAS Penguin. Three ships and two shore installations of the Royal Australian Navy have been named HMAS Penguin after the aquatic, flightless bird: Three other bases were established as subordinate to the Garden Island base.
These were also given the name HMAS Penguin, but with a Roman numeral suffix added: LCM-1E. The LCM-1E is a class of amphibious mechanized landing craft manufactured by Navantia at their factory in San Fernando.
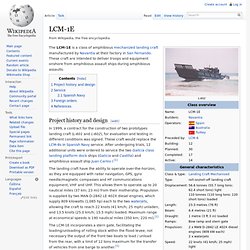
These craft are intended to deliver troops and equipment onshore from amphibious assault ships during amphibious assaults. Project history and design[edit] The landing craft have the ability to operate over-the-horizon, as they are equipped with radar navigation, GPS, gyro needle/magnetic compasses and HF communications equipment, VHF and UHF. This allows them to operate up to 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi) from their mothership. Propulsion is supplied by two MAN D-2842 LE 402X diesel engines, which supply 809 kilowatts (1,085 hp) each to the two waterjets, allowing the craft to reach 22 knots (41 km/h; 25 mph) unladen, and 13.5 knots (25.0 km/h; 15.5 mph) loaded. Hobart-class destroyer. The Hobart class is a ship class of three air warfare destroyers (AWDs) being built for the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).
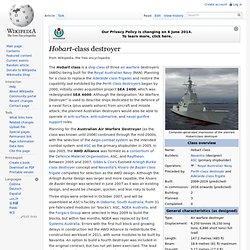
Planning for a class to replace the Adelaide class frigates and restore the capability last exhibited by the Perth class destroyers began by 2000, initially under acquisition project SEA 1400, which was redesignated SEA 4000. Although the designation "Air Warfare Destroyer" is used to describe ships dedicated to the defence of a naval force (plus assets ashore) from aircraft and missile attack, the planned Australian destroyers would also be able to operate in anti-surface, anti-submarine, and naval gunfire support roles. Incat. Incat is a manufacturer of large HSC catamarans, based in the Derwent Park suburb of Hobart, Tasmania, Australia founded by Robert Clifford.
The company builds large commercial and military vessels that use aluminium construction, wave-piercing and water-jet technology. Vessels have been constructed up to 112 metres in length and cruise at 40 knots (75 km/h). Deliveries[edit] Incat's HSV-X1 near Crete Incat's Hobart Shipyard (to the right) Ton-class minesweeper. Meko 360. The MEKO 360 is a class of five destroyers built in Germany for the Argentine and Nigerian Navies. The 360 was the first ship of the MEKO family of vessels built by Blohm und Voss. Variants[edit] Four vessels of a second variant, the MEKO 360H2, were constructed for Argentina. They were locally named the Almirante Brown class, and currently serve as the main strength in their Navy. Although considered by its builders to be a frigate, the Almirante Brown vessels have been classed in Argentina (and in Jane's Fighting Ships) as destroyers. Brandenburg-class frigate. Currently the F123 class is being upgraded under the auspices of the Fähigkeitsanpassung FüWES (FAF) project.
The primary component being upgraded under this program is the Combat Management System, for which a version of the Thales Nederland TACTICOS system will be used. The ships will also receive an IFF upgrade, to the EADS MSSR 2000 I secondary radar system. However, its primary radars, specifically its long-range 2D search radar, the Thales Nederland LW08, and its medium-range 3D surveillance radar, the Thales Nederland SMART-S, are to remain. Sachsen-class frigate. The F124 Sachsen class is Germany's latest class of highly advanced air-defense frigates.
The design of the Sachsen class frigate is based on that of the F123 Brandenburg class but with enhanced stealth features intended to deceive any opponent's radar and acoustic sensors and incorporate also the advanced multifunction radar APAR as well as the SMART-L long-range radar which is claimed to be capable of detecting stealth aircraft and stealth missiles. Although designated as frigates, they are in capability and size comparable to destroyers. At €2.1 billion for only three ships, this was one of the most expensive ship building programs of the German Navy. They are similar to the Dutch De Zeven Provinciën-class frigates. In June 1996 the German government contracted for three ships with an option on a fourth that was provisionally to have been named as the Thüringen, but the option for this fourth ship was not taken up. MEKO 200. The MEKO 200 is a frigate design by the Blohm + Voss shipyard of Germany, as part of the MEKO family of warships. Variants[edit] Anzac class (MEKO 200)[edit]
Karel Doorman-class frigate. The Karel Doorman class is a class of eight multi-purpose frigates of the Royal Netherlands Navy. The class is also known as the "Multi-purpose" or M class. The ships are named after famous Dutch naval officers, the lead ship being named after Karel Doorman. Kortenaer-class frigate. Bremen-class frigate. F125-class frigate. FREMM European Multimission Frigate, France / Italy. The FREMM European multimission frigate is a joint programme between France and Italy.
HMAS Coonawarra. HMAS Coonawarra is a Royal Australian Navy base located in Darwin, Northern Territory and is home to twelve fleet units of the Royal Australian Navy. Seahorse Mercator. Design and construction[edit] Huon-class minehunter. HMAS Waterhen. There have been one ship and one shore establishment in the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) named HMAS Waterhen. Clearance Diving Team. Cyclone-class patrol ship. Taiwan launches first 'carrier killer' stealth missile corvette. Patrol Boat (PB) List of warship classes of the Royal Australian Navy.
List of active Royal Australian Navy ships. Australian Navy Cadets. Recruit training. Attack-class patrol boat. Fremantle-class patrol boat. Ton-class minesweeper. Leeuwin-class survey vessel. Paluma-class survey motor launch. Bay-class minehunter. Huon-class minehunter. Planned Australian offshore combatant vessel. Protector-class inshore patrol vessel. Armidale-class patrol boat. Pacific-class patrol boat. HMAS Harman. Visby-class corvette. Berlin-class replenishment ship. CB90-class fast assault craft. A26 submarine. Air-independent propulsion. Gotland-class submarine. Deep-submergence rescue vehicle. LCVP (United States) Type 21 frigate. Westland Lynx. List of active Royal Australian Navy ships. HMAS Adelaide. Royal Australian Navy Submarine Service. Procurement programme of the Royal Australian Navy. Carrier air wing. RIM-116 Rolling Airframe Missile. Italian aircraft carrier Cavour (550) Independence-class littoral combat ship. Littoral combat ship. Freedom-class littoral combat ship.
FREMM multipurpose frigate. Horizon-class frigate. Harpoon (missile) Grumman S-2 Tracker. Sikorsky SH-60 Seahawk. 725 Squadron RAN. Adelaide-class frigate. 816 Squadron RAN. 724 Squadron RAN. 805 Squadron RAN. HMAS Albatross. HMAS Melbourne. List of Douglas A-4 Skyhawk operators. Douglas A-4 Skyhawk. Amphibious assault ship. Amphibious transport dock. Austin-class amphibious transport dock.
Whidbey Island-class dock landing ship. Tarawa-class amphibious assault ship. Arleigh Burke-class destroyer. Virginia-class submarine. Virginia Class. Mobile Landing Platform (MLP) Ship. Naval Technology. Corvette. RV Triton. Patrol boat. Frigate. S-80-class submarine. Sōryū-class submarine. Oberon-class submarine.