

How Boolean Logic Works" Simple Gates" There are three, five or seven simple gates that you need to learn about, depending on how you want to count them (you will see why in a moment).
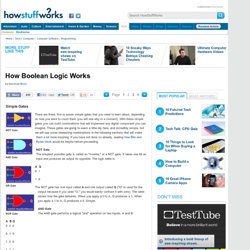
With these simple gates you can build combinations that will implement any digital component you can imagine. These gates are going to seem a little dry here, and incredibly simple, but we will see some interesting combinations in the following sections that will make them a lot more inspiring. Boolean algebra. Boolean algebra was introduced by George Boole in his first book The Mathematical Analysis of Logic (1847), and set forth more fully in his An Investigation of the Laws of Thought (1854).[1] According to Huntington the term "Boolean algebra" was first suggested by Sheffer in 1913.[2] Boolean algebra has been fundamental in the development of digital electronics, and is provided for in all modern programming languages.
It is also used in set theory and statistics.[3] History[edit] In the 1930s, while studying switching circuits, Claude Shannon observed that one could also apply the rules of Boole's algebra in this setting, and he introduced switching algebra as a way to analyze and design circuits by algebraic means in terms of logic gates.