

Strategic Audit. Author: Jim Riley Last updated: Sunday 23 September, 2012 In our introduction to business strategy, we emphasised the role of the "business environment" in shaping strategic thinking and decision-making.
The external environment in which a business operates can create opportunities which a business can exploit, as well as threats which could damage a business. However, to be in a position to exploit opportunities or respond to threats, a business needs to have the right resources and capabilities in place. An important part of business strategy is concerned with ensuring that these resources and competencies are understood and evaluated - a process that is often known as a "Strategic Audit". The process of conducting a strategic audit can be summarised into the following stages: (1) Resource Audit: The resource audit identifies the resources available to a business.
. (2) Value Chain Analysis: (3) Core Competence Analysis: (4) Performance Analysis (5) Portfolio Analysis: (6) SWOT Analysis: McKinsey Growth Pyramid - Growth Strategy. Author: Jim Riley Last updated: Sunday 23 September, 2012 Introduction This model is similar in some respects to the well-established Ansoff Model.
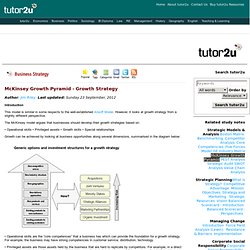
However, it looks at growth strategy from a slightly different perspective. The McKinsey model argues that businesses should develop their growth strategies based on: • Operational skills • Privileged assets • Growth skills • Special relationships Growth can be achieved by looking at business opportunities along several dimensions, summarised in the diagram below: • Operational skills are the “core competences” that a business has which can provide the foundation for a growth strategy. . • Privileged assets are those assets held by the business that are hard to replicate by competitors. . • Growth skills are the skills that businesses need if they are to successfully “manage” a growth strategy. . • Special relationships are those that can open up new options. The model outlines seven ways of achieving growth, which are summarised below: New geographies. Design Your Company, Not Your Product.
When you think of creating a company, all the focus is usually on what you want to make: how the app will work on someone's phone or how attractive your product will look like on store shelves.
There's a new wave of entrepreneurs who believe the real key to long-term success comes from focusing on designing the company--not the product. That means establishing a solid company philosophy, fostering cooperation and friendliness among the staff while still being able to make the key decisions--all steps that help save your office from feeling like just another widget factory. The topic was featured at the first Northside Entrepreneurship Festival in Brooklyn recently on a panel that included Anthony Casalena, CEO of Squarespace, Chris Shiflett, co-founder of the Web conference Brooklyn Beta, and Whitney Hess, the principal consultant at user-experience consultancy Vicarious Partners. 1.
Have a crystal-clear mission statement. Hess said to remember that all businesses exist to solve a problem. SWOT analysis - introduction. Author: Jim Riley Last updated: Sunday 23 September, 2012 SWOT analysis is a method for analysing a business, its resources, and its environment.
SWOT is commonly used as part of strategic planning and looks at: Internal strengths Internal weaknesses Opportunities in the external environment Threats in the external environment SWOT can help management in a business discover: What the business does better than the competition What competitors do better than the business Whether the business is making the most of the opportunities available How a business should respond to changes in its external environment The result of the analysis is a matrix of positive and negative factors for management to address: The key point to remember about SWOT is that: Strengths and weaknesses Are internal to the business Relate to the present situation Opportunities and threats Are external to the business Relate to changes in the environment which will impact the business Using SWOT analysis.