

A Planetary System That Never Was Teaches About Those That May Be. Want to stay on top of all the space news?
Follow @universetoday on Twitter While Kepler and similar missions are turning up planets by the fist full, there’s long been many places that astronomers haven’t expected to find planetary systems. The main places include regions where gravitational forces conspire to make the region around potential host stars too unstable to form into planets. And there’s no place in the galaxy with a larger gravitational force than the galactic center where a black hole four and a half million times more massive than the Sun, lurks. But a new study shows evidence that a disk, potentially far enough along to begin forming planets, is in the process of being disrupted. The new study investigates an ionized cloud of gas discovered earlier this year, plummeting in towards the black hole. However, such massive stars are able to determine an age limit for the group, which has been set somewhere between 4-8 million years.
About Jon Voisey. The Cosmic Magnifying Lens. Objects may be closer than they appear; in the distant universe, objects are, in a sense, even farther than they appear The observable universe is one big, giant magnifying lens.
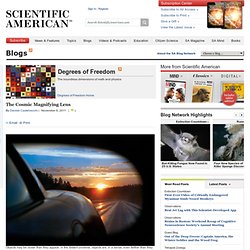
At large distances, objects appear to be larger than their true size, and the farther they are, the bigger they look. The most distant observable objects are so magnified that their images in the sky—if we could see them—would be blown up by a factor of 1,000 or more. If there were a road leading from here to the edge of the universe, you wouldn’t see it getting smaller and smaller and finally converge to a point, the way you see straight roads on earth vanish to a point on the horizon, as in the picture above. Instead, you’d see the two shoulders get closer for a while, reach a minimum width, and then start moving apart again. To get some visual intuition about what happens then, it is helpful to look at the technique that artists have codified as reverse perspective, also known as Byzantine perspective.
Starbursts May Actually Destroy Globular Clusters. Want to stay on top of all the space news?
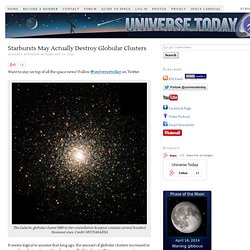
Follow @universetoday on Twitter The Galactic globular cluster M80 in the constellation Scorpius contains several hundred thousand stars. Credit: HST/NASA/ESA It seems logical to assume that long ago, the amount of globular clusters increased in our galaxy during star-making frenzies called ‘starbursts.’ Astrophile: Square galaxy is a rebel - physics-math - 21 March 2012. Astrophile is our weekly column on curious cosmic objects, from the solar system to the far reaches of the multiverse Object type: Dwarf galaxyLocation: Eridanus constellation If a person is square they are a bit dull, but for a galaxy, it is the mark of a true rebel.
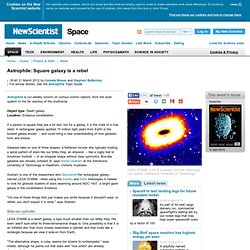
A rectangular galaxy spotted 70 million light years from Earth is the boxiest galaxy known – and could bring a new understanding of how galaxies form and evolve. Galaxies take on one of three shapes: a flattened circular disc typically hosting a spiral pattern of stars like our Milky Way, an ellipsoid – like a rugby ball or American football – or an irregular shape without clear symmetry. Box-like galaxies are virtually unheard of, says Alister Graham at the Swinburne University of Technology in Hawthorn, Victoria, Australia. "It's one of those things that just makes you smile because it shouldn't exist, or rather, you don't expect it to exist," says Graham.
Visible Echoes Reprise 19th Century Spectacle. Fresh Start: Scientists Glimpse Unsullied Traces of the Infant Universe. By peering into the distance with the biggest and best telescopes in the world, astronomers have managed to glimpse exploding stars, galaxies and other glowing cosmic beacons as they appeared just hundreds of millions of years after the big bang.

They are so far away that their light is only now reaching Earth, even though it was emitted more than 13 billion years ago. Astronomers have been able to identify those objects in the early universe because their bright glow has remained visible even after a long, universe-spanning journey. Universe's first stars not so big after all - space - 10 November 2011. The universe's earliest stars may have been less than half as large as previously thought, according to two new simulations.
The findings could resolve one of the universe's oldest mysteries: why some elements are more abundant than our theories suggest they should be. In the first hundreds of millions of years after the big bang, the early universe was composed mainly of atomic hydrogen, helium and tiny amounts of other light elements. Eventually clouds of these gases condensed into the first stars, but without dust, heavy elements, or molecules, these early stars were unable to cool down as quickly as their descendents. In 2008, Christopher McKee of the University of California, Berkeley, and colleagues derived a model suggesting that these early stars would grow to between 100 and 200 times the mass of our sun before the heat they gave off made the surrounding gas too energetic to pull any more gas in and accrete further.
Subsequent simulations bolstered this claim Hot fuss . Baby pulsars spawn universe's most energetic particles - space - 01 February 2012. Talk about enfants terribles.
Baby pulsars may unleash torrents of the highest energy particles known, explaining the provenance of the ultra-high-energy cosmic rays that hit Earth. Charged particles with energies of at least 1019 electronvolts slam into our atmosphere from time to time – since 2008, 5000 have been detected by the Auger observatory in Argentina. Their source has been a mystery. Pulsars – ultradense stars formed during supernova blasts – are one candidate, but it has not been clear if the particles they shed could make it through the dense shroud of stellar shrapnel that surrounds them.
Hubble Spots Mysterious Dark Matter ‘Core’ Want to stay on top of all the space news?
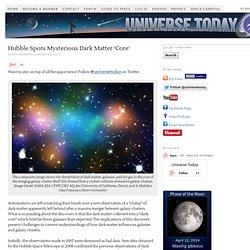
Follow @universetoday on Twitter This composite image shows the distribution of dark matter, galaxies, and hot gas in the core of the merging galaxy cluster Abell 520, formed from a violent collision of massive galaxy clusters. Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CFHT, CXO, M.J. Distant Invisible Galaxy Could be Made Up Entirely of Dark Matter. Want to stay on top of all the space news?
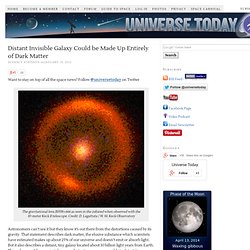
Follow @universetoday on Twitter The gravitational lens B1938+666 as seen in the infrared when observed with the 10-meter Keck II telescope. Credit: D. Lagattuta / W. M. Astronomers can’t see it but they know it’s out there from the distortions caused by its gravity. Astronomers Discover Ancient Planetary System. Want to stay on top of all the space news?
Follow @universetoday on Twitter Artist’s impression of HIP 11952 and its two Jupiter-like planets. Image credit: Timotheos Samartzidis. Astrophile: The planets that formed by cell division - space - 02 April 2012. Read full article Continue reading page |1|2 Objects: Rocky planets KOI 55.01 and KOI 55.02Size: 0.759 and 0.867 times Earth's diameterDistance: 4000 light years from Earth When the sun-like star KIC 05807616 ran out of hydrogen, its planets thought they were done for. The star began puffing off its outer layers, and over the next billion years, ballooned up into a red giant a million times its original volume. When 14 Billion Years Just Isn't Enough Time. Time’s seemingly inexorable march has always provoked interest in, and speculation about, the far future of the cosmos. The usual picture is grim. Five billion years from now the sun will puff itself into a red giant star and swallow the inner solar system before slowly fading to black.
But this temporal frame captures only a tiny portion—in fact, an infinitesimal one—of the entire future. The History of the Universe: From Big Bang to Big Blah. Space::Web Exclusives::February 20, 2012:: ::Email::Print Today's universe may not be as rip-roaring as the primordial cosmos, but remains an action-packed place Image: Our Early Universe: Inflation, or Something Totally Wacky? Want to stay on top of all the space news? Follow @universetoday on Twitter A schematic look at the universe - where it came from and where it is now. Credit: NASA. Naked black-hole hearts live in the fifth dimension - physics-math - 13 January 2012. Read more: "Why physicists can't avoid a creation event" "IT SEEMS very rude to come to someone's party and tell him that he lost a bet again," said cosmologist Luis Lehner of the Perimeter Institute in Ontario, Canada.
Lehner did it anyway. He was speaking at a meeting to celebrate Stephen Hawking's 70th birthday. Goldilocks Black Holes. Big Gulp: Flaring Galaxy Marks the Messy Demise of a Star in a Supermassive Black Hole. Once in a while, a supermassive black hole gets a sumptuous treat. A passing star wanders too close and gets caught in the black hole's gravitational pull, like a fly trapped in a spider's web. X-ray 'Echoes' Probe Habitat of Monster Black Hole. Black Holes are Everywhere. Holes are everywhere, if you look... Black Holes are More Like Venus Fly Traps than Vacuum Cleaners. Early Black Holes were Grazers Rather than Glutonous Eaters. Speca – An Intriguing Look Into The Beginning Of A Black Hole Jet. Two (or three?) black holes in one galactic center.
Title: Chandra high resolution observations of CID-42, a candidate recoiling SMBHAuthors: F. Civano, M. Elvis, G. Black holes as particle detectors. Finding new particles usually requires high energies -- that is why huge accelerators have been built, which can accelerate particles to almost the speed of light. Supernova Explosions, Black Hole Jets Might Cause Galaxies to ‘Age’ Faster. Pulsar heavyweight champ challenges Einstein - space - 16 May 2012. Antimatter-Powered Supernovae. Iron in the Fire: The Little-Star Supernovae That Could. UC Berkeley Press Release. Top 24 Deep Space Pictures of 2011. Stellar Superflares' Trigger Challenged. Some Newfound Planets Are Something Else. Does a galaxy filled with habitable planets mean humanity is doomed?
Diamond planets may not be life's best friend - space - 06 December 2011. Dust rings not 'smoking gun' for planets after all - space - 14 May 2012. Giant Celestial Disk Hard To Explain. Rogue Planets Can Find Homes Around Other Stars. Astrophile: Runaway is star of cosmic whodunnit - physics-math - 15 June 2012. Smallest planet is tinier than Earth - space - 20 December 2011. Planet found at perfect spot for life - in solar system with three suns. Two new Earth-sized exoplanets discovered. Light From a ‘SuperEarth’ Detected for the First Time.
Infographic: The New Planetary Habitability Index. An Abundance of Exoplanets Changes our Universe. Searching for Exoplanet Oceans More Challenging Than First Thought. Alien Planets May Thrive on Many Wavelengths of Light. Hell off Earth: Blustery Exoplanet Charted in 2-D for First Time. New Evidence For Fomalhaut Planets.
Disruptive Planets and their Consequences. Astrophile: Attack of the mystery green blobs - space - 04 November 2011. Astrophile: Wounded galaxy is crux of cosmic whodunnit - space - 09 December 2011. Frantic Comet Massacre Taking Place at Fomalhaut. Astrophile: The case of the disappearing pulsar - space - 21 May 2012. Scientists Discover The Oldest, Largest Body Of Water In Existence. Monster Black Holes Are Most Massive Ever Discovered. 20 million mph winds seen blowing from black hole.
Will This Be The End Of The Earth? 589217_scale_of_universe_enhanced.swf (application/x-shockwave-flash Object) Planck mission steps closer to the cosmic blueprint. “Impossible” Binary Star Systems Found.