

Kulturapfel. Äpfel werden sowohl als Nahrungsmittel im Obstanbau als auch zur Zierde angepflanzt.
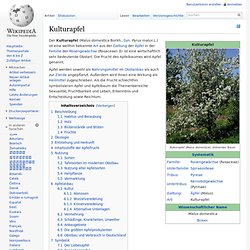
Außerdem wird ihnen eine Wirkung als Heilmittel zugeschrieben. Als die Frucht schlechthin symbolisieren Apfel und Apfelbaum die Themenbereiche Sexualität, Fruchtbarkeit und Leben, Erkenntnis und Entscheidung sowie Reichtum. Beschreibung[Bearbeiten] Malus domestica[1] Habitus und Belaubung[Bearbeiten] Holz[Bearbeiten] Das Holz des Kulturapfels gleicht dem des Holzapfels, hat einen hellrötlichen Splint und einen rotbraunen Kern. Blütenstände und Blüten[Bearbeiten] Blüten der Sorte Holsteiner Cox Einzeln oder in doldigen Schirmrispen stehen die Blüten. Der Apfelbaum blüht im Mai und Juni. Dass 5 % der Blüten bestäubt zu Früchten heranreifen, reicht bei Apfel oder Birne für eine Vollernte, während bei Steinobst der entsprechende Anteil 25 % beträgt.[3] Früchte[Bearbeiten] Ein reifer Apfel Ökologie[Bearbeiten] Entstehung und Herkunft[Bearbeiten] Die ursprüngliche Heimat des Kulturapfels liegt möglicherweise in Asien.
Malus domestica (Apple) (Pyrus malus) Apple. Grown in temperate regions, apples are one of the most widely cultivated tree fruits.
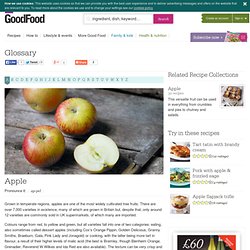
There are over 7,000 varieties in existence, many of which are grown in Britain but, despite that, only around 12 varieties are commonly sold in UK supermarkets, of which many are imported. Colours range from red, to yellow and green, but all varieties fall into one of two categories: eating, also sometimes called dessert apples (including Cox's Orange Pippin, Golden Delicious, Granny Smiths, Braeburn, Gala, Pink Lady and Jonagold) or cooking, with the latter being more tart in flavour, a result of their higher levels of malic acid (the best is Bramley, though Blenheim Orange, Grenadier, Reverend W Wilkes and Ida Red are also available).
The texture can be very crisp and juicy or more yielding, according to variety. All apples are a good source of vitamins A and C, as well as fibre. Availability All year round, though British apples are at their best from September through to November. Choose the best. Apples. What's New and Beneficial About Apples Researchers have long been aware of the potential for apple consumption to support balanced populations of bacteria in our lower digestive tract.
However, two areas of recent research have taken our understanding of apples and gut bacteria to a new level. First, studies have now made it clear that a large percentage of apple polyphenols (some of this fruit's most valuable phytonutrients) can make their way intact through our digestive tract, all the way down to our lower large intestine (colon). This research has proven that apple phytonutrients can be the direct cause of bacterial changes.
Second, studies have now provided us with evidence that apple polyphenols can increase bacterial populations in the broad group of bacteria known as Actinobacteria. Apple, fresh1.00 medium(182.00 grams) NutrientDRI/DV Health Benefits Abundant Phytonutrients from Apples Cardiovascular Benefits from Apples Other Potential Health Benefits from Apples Description History. Apples. Malus domestica. Malus domestica 'Discovery' [edit] Familia: Rosaceae Subfamilia: Amygdaloideae Tribus: Maleae Genus: Malus Sectio: M. sect.
Malus Species: Malus domestica Name[edit] Malus domestica Borkh. Hybrids[edit] M. × adstringens – M. × dawsoniana References[edit] Theoretisches-praktisches Handbuch der Forstbotanik und Forsttechnologie 2:1272. 1803USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program. Apple. The apple tree (Malus domestica) is a deciduous tree in the rose family best known for its sweet, pomaceous fruit, the apple.
It is cultivated worldwide as a fruit tree, and is the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe, and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek and European Christian traditions. Apple trees are large if grown from seed, but small if grafted onto roots (rootstock).
About 69 million tons of apples were grown worldwide in 2010, and China produced almost half of this total. Botanical information Blossoms, fruits, and leaves of the apple tree (Malus domestica) The fruit matures in late summer or autumn, and varieties exist with a wide range of sizes. Wild ancestors Genome History Cultural aspects Storage.