

Earth. Earth is the third planet from the Sun.
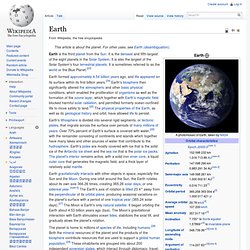
It is the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets. It is sometimes referred to as the world or the Blue Planet.[23] Earth formed approximately 4.54 billion years ago, and life appeared on its surface within its first billion years.[24] Earth's biosphere then significantly altered the atmospheric and other basic physical conditions, which enabled the proliferation of organisms as well as the formation of the ozone layer, which together with Earth's magnetic field blocked harmful solar radiation, and permitted formerly ocean-confined life to move safely to land.[25] The physical properties of the Earth, as well as its geological history and orbit, have allowed life to persist.
Name and etymology In general English usage, the name earth can be capitalized or spelled in lowercase interchangeably, either when used absolutely or prefixed with "the" (i.e. Heat. Earth's Magnetosphere. Earth's magnetic field. Computer simulation of the Earth's field in a period of normal polarity between reversals.[1] The lines represent magnetic field lines, blue when the field points towards the center and yellow when away.
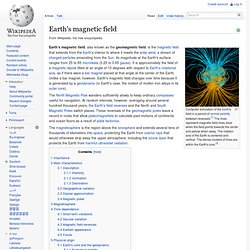
The rotation axis of the Earth is centered and vertical. The dense clusters of lines are within the Earth's core.[2] The North Magnetic Pole wanders sufficiently slowly to keep ordinary compasses useful for navigation. At random intervals, however, averaging around several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that allow paleomagnetists to calculate past motions of continents and ocean floors as a result of plate tectonics. Importance[edit] Earth's Magnetosphere. A magnetosphere is the area of space near an astronomical object in which charged particles are controlled by that object's magnetic field.[1][2] Near the surface of the object, the magnetic field lines resemble those of a magnetic dipole.
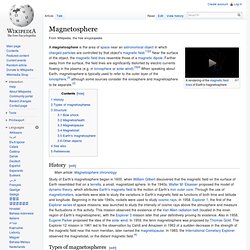
Farther away from the surface, the field lines are significantly distorted by electric currents flowing in the plasma (e.g. in ionosphere or solar wind).[3][4] When speaking about Earth, magnetosphere is typically used to refer to the outer layer of the ionosphere,[3] although some sources consider the ionosphere and magnetosphere to be separate.[2] History[edit] Types of magnetospheres[edit] The structure and behavior of magnetospheres is dependent on several variables: the type of astronomical object, the nature of sources of plasma and momentum, the period of the object's spin, the nature of the axis whereabout the object spins, the axis of the magnetic dipole, and the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the flow of solar wind. Structure[edit] Magnetosphere. A magnetosphere is the area of space near an astronomical object in which charged particles are controlled by that object's magnetic field.[1][2] Near the surface of the object, the magnetic field lines resemble those of a magnetic dipole.
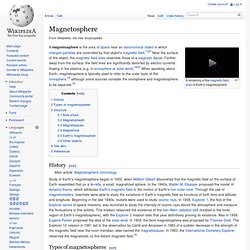
Farther away from the surface, the field lines are significantly distorted by electric currents flowing in the plasma (e.g. in ionosphere or solar wind).[3][4] When speaking about Earth, magnetosphere is typically used to refer to the outer layer of the ionosphere,[3] although some sources consider the ionosphere and magnetosphere to be separate.[2] History[edit] Mars Express - Earth’s magnetic field provides vital protection.
Earth’s magnetic field provides vital protection Propagation of a solar wind stream 8 March 2012 A chance alignment of planets during a passing gust of the solar wind has allowed scientists to compare the protective effects of Earth’s magnetic field with that of Mars’ naked atmosphere.
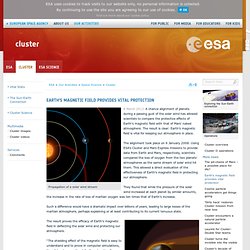
The result is clear: Earth’s magnetic field is vital for keeping our atmosphere in place. The alignment took place on 6 January 2008. They found that while the pressure of the solar wind increased at each planet by similar amounts, the increase in the rate of loss of martian oxygen was ten times that of Earth’s increase.
Such a difference would have a dramatic impact over billions of years, leading to large losses of the martian atmosphere, perhaps explaining or at least contributing to its current tenuous state. Magnetosphere.jpg (JPEG Image, 453x360 pixels)