

General Relativity Equations. Fundamental Concepts of General Relativity. General Relativity Phenomena. Spacetime. Schwarzschild Radius. Speed of Light. General relativity. General relativity, or the general theory of relativity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916[1] and the current description of gravitation in modern physics.
General relativity generalizes special relativity and Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time, or spacetime. In particular, the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of partial differential equations. Some predictions of general relativity differ significantly from those of classical physics, especially concerning the passage of time, the geometry of space, the motion of bodies in free fall, and the propagation of light. Einstein's theory has important astrophysical implications. History[edit] Allgemeine Relativitätstheorie. Die allgemeine Relativitätstheorie erweitert die spezielle Relativitätstheorie und geht für hinreichend kleine Gebiete der Raumzeit in diese über.
Außerdem kann sie als eine Erweiterung des newtonschen Gravitationsgesetzes verstanden werden, weil sie dieses im Grenzfall von hinreichend kleinen Massendichten und Geschwindigkeiten liefert. Die allgemeine Relativitätstheorie wurde vielfach experimentell bestätigt (siehe Tests der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie), so dass sie als Gravitationstheorie allgemein anerkannt ist. Insbesondere hat sie sich bisher in der von Einstein formulierten Form gegen alle später vorgeschlagenen Alternativen durchsetzen können. Offene Fragen betreffen vor allem die Beziehung zur Quantenmechanik.
Einführung[Bearbeiten] Grundlegend für die allgemeine Relativitätstheorie ist eine Wechselwirkung zwischen allen Typen physikalischer Systeme, die Energie und Impuls tragen können („Materie“), und der Raumzeit mit zwei Eigenschaften: Einstein's Theory of General Relativity: A Simplified Explanation. In 1905, Albert Einstein determined that the laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers, and that the speed of light in a vacuum was independent of the motion of all observers.

This was the theory of special relativity. It introduced a new framework for all of physics and proposed new concepts of space and time. Einstein then spent 10 years trying to include acceleration in the theory and published his theory of general relativity in 1915. In it, he determined that massive objects cause a distortion in space-time, which is felt as gravity. Two objects exert a force of attraction on one another known as "gravity. " Albert Einstein, in his theory of special relativity, determined that the laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers, and he showed that the speed of light within a vacuum is the same no matter the speed at which an observer travels. "As the planet rotates, the honey around it would swirl, and it's the same with space and time. Einstein's Gravity Theory Passes Toughest Test Yet. An extreme pair of superdense stars orbiting each other has put Einstein's general theory of relativity to its toughest test yet, and the crazy-haired physicist still comes out on top.

About 7,000 light-years from Earth, an exceptionally massive neutron star that spins around 25 times a second is orbited by a compact, white dwarf star. The gravity of this system is so intense that it offers an unprecedented testing ground for theories of gravity. Scientists know general relativity, proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915, isn't the complete story.
NASA Gravity Probe Confirms Two Einstein Theories. A NASA probe orbiting Earth has confirmed two key predictions of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which describes how gravity causes masses to warp space-time around them.
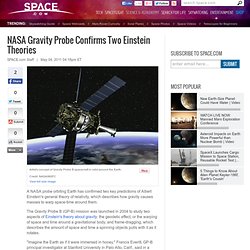
The Gravity Probe B (GP-B) mission was launched in 2004 to study two aspects of Einstein's theory about gravity: the geodetic effect, or the warping of space and time around a gravitational body, and frame-dragging, which describes the amount of space and time a spinning objects pulls with it as it rotates. "Imagine the Earth as if it were immersed in honey," Francis Everitt, GP-B principal investigator at Stanford University in Palo Alto, Calif., said in a statement. "As the planet rotates, the honey around it would swirl, and it's the same with space and time. GP-B confirmed two of the most profound predictions of Einstein's universe, having far-reaching implications across astrophysics research. " [6 Weird Facts About Gravity] A long time coming Gravity Probe B's wide reach.