

Troubleshooting Database Links. Each Oracle DBA knowns this story of course ... sorry, but not every Oracle user is a DBA.

One early morning your management staff complains about missing sales data, which must be ready for the daily trend analysis. What's happen ... nobody changed the calculation procedure during the night ... here it is ... the database link is down. Why ... well the remote DBA changed all passwords. This is only one of the famous database link trobleshooting stories. Read the following article and you have less annoyance with database links. Oracle enforces the requirement that the database.domain portion of the database link name must match the complete global name of the remote database by setting GLOBAL_NAMES to TRUE in the initialization parameter file initSID.ora. Example: Local DB is 'SOL3' (Oracle 8.1.6), remote DB is 'SOL1' (Oracle 7.3.4) # Parameter file initSOL3.ora for Database SOL3 # ### Global Naming ### ------------- # Enforce that a dblink has same name as the DB it connects to Example.
Oracle Database Links DB Link. If the REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE parameter is not specified, either in the init.ora parameter file or using the ALTER SESSION or ALTER SYSTEM DDL statements, then timestamp is the default value. Therefore, unless you explicitly use the REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE parameter, or the appropriate DDL statement, your server is operating using the timestamp dependency model.
When you use REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE=SIGNATURE: If you change the default value of a parameter of a remote procedure, then the local procedure calling the remote procedure is not invalidated. If the call to the remote procedure does not supply the parameter, then the default value is used. In this case, because invalidation/recompilation does not automatically occur, the old default value is used.
Dependency Resolution When REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE = TIMESTAMP (the default value), dependencies among program units are handled by comparing timestamps at runtime. In the timestamp dependency mode, signatures are not compared. Oracle database link. Wyobraźmy sobie sytuację w której mamy dwie bazy.
Niech to będą baza A i baza B. Będąc zalogowani do bazy A potrzebujemy jednak czasami zrobić jakiegoś selekta (i nie tylko) na tabelach z bazy B. Tutaj z pomocą przychodzi nam mechanizm Oracle database link. Powiązanie z bazą danych (ang. database link) – jest to zapisana w bazie danych ścieżka sieciowa do odległej bazy danych. Istnieje kilka rodzajów data linków ( szczegóły w dokumentacji ): Connected User Link Current User Link Fixed User Link Shared Link Public Link Jak stworzyć link bazodanowy? Do tego musimy stworzyć użytkownika na bazie produkcyjnej. Składnia tworzenia powiązania z bazą danych (powiązania bazodanowego) jest następująca: CREATE DATABASE LINK nazwa_linku CONNECT TO użytkownik IDENTIFIED BY hasło USING 'nazwa_usługi'; Tworzymy link: CREATE DATABASE LINK B CONNECT TO użytkownik IDENTIFIED BY hasło USING 'B'; Sprawdzamy czy link istnieje: select * from user_db_links Pierwszy selekcik: Zamykanie linku: Kasowanie linku:
DROP DATABASE LINK. Purpose Use the DROP DATABASE LINK statement to remove a database link from the database.
Prerequisites A private database link must be in your own schema. To drop a PUBLIC database link, you must have the DROP PUBLIC DATABASE LINK system privilege. Syntax. Database Links. The central concept in distributed database systems is a database link .
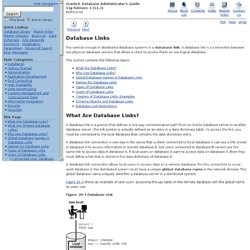
A database link is a connection between two physical database servers that allows a client to access them as one logical database. This section contains the following topics: What Are Database Links? A database link is a pointer that defines a one-way communication path from an Oracle Database server to another database server. The link pointer is actually defined as an entry in a data dictionary table. A database link connection is one-way in the sense that a client connected to local database A can use a link stored in database A to access information in remote database B, but users connected to database B cannot use the same link to access data in database A. A database link connection allows local users to access data on a remote database. Figure 29-3 shows an example of user scott accessing the emp table on the remote database with the global name hq.acme.com :