

Technology Strategy. IPD. Collaborative software. Collaborative software or groupware is an application software designed to help people involved in a common task to achieve goals.
One of the earliest definitions of collaborative software is 'intentional group processes plus software to support them.'[1] The design information technology, seems to have several definitions. Understanding the differences in human interactions is necessary to ensure that appropriate technologies are employed to meet interaction needs. Collaborative software is a broad concept that overlaps considerably with Computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW).
The use of collaborative software in the work space creates a collaborative working environment (CWE). Origins[edit] Online collaborative gaming software began between early networked computer users. Parallel to development of MUDs were applications for online chat, video sharing and voice over IP. Philosophical underpinnings[edit] Technology has long been used to bring people together. Autodesk - AutoCAD WS. 15 Free Online Collaboration Tools. We rarely learn in isolation.

The vast majority of our learning is social, and whether we are aware of it or not, most of that social learning occurs when we are collaborating with others. Because of what the Internet makes possible, we no longer have to be in the same room with others to collaborate effectively. There are free tools for online conferencing, collaborative writing and editing, file sharing, private communication, and desktop sharing – and countless other activities. Here are 15 free online collaboration tools and apps to try today: Keep and Share – Keep and Share is a group file sharing system. Wridea – Wridea makes it easy to collaborate and share ideas with colleagues, team members, and fellow learners. Writeboard – Whiteboard is free collaborative writing software.
Twiddla – Twiddla works very well for online meetings or co-browsing. Spicebird – This open source platform is an all-in-one suite of communication tools for people who want to collaborate online. Shop drawing. A shop drawing showing different perspective views of a post and beam building.
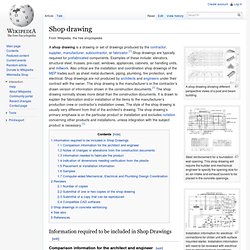
Steel reinforcement for a foundation wall opening. This shop drawing will require the builder and mechanical engineer to specify the opening size for an air-intake and exhaust louvers to be placed in the concrete openings. Installation information for electrical connections for chiller unit with surface mounted starter. Installation information will need to be reviewed with electrical and plumbing trades to coordinate third-party service connections. Information required to be included in Shop Drawings[edit] Submittals (construction) A wall mock-up.
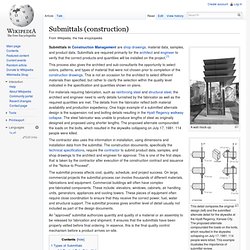
This detail compares the original design (left) and the submitted alternate detail for the skywalks at the Hyatt Regency, Kansas City. The proposed alternate compounded the loads on the bolts, which resulted in the skywalks collapsing on July 17, 1981. 114 people were killed. This example illustrates the importance of submittal review. Submittals in Construction Management are shop drawings, material data, samples, and product data. Submittals are required primarily for the architect and engineer to verify that the correct products and quantities will be installed on the project.[1] This process also gives the architect and sub-consultants the opportunity to select colors, patterns, and types of material that were not chosen prior to completion of the construction drawings.
The contractor also uses this information in installation, using dimensions and installation data from the submittal. The submittal process affects cost, quality, schedule, and project success. Request for information. A request for information (RFI) is a standard business process whose purpose is to collect written information about the capabilities of various suppliers.

Normally it follows a format that can be used for comparative purposes. An RFI is primarily used to gather information to help make a decision on what steps to take next. RFIs are therefore seldom the final stage and are instead often used in combination with the following: request for proposal (RFP), request for tender (RFT), and request for quotation (RFQ). In addition to gathering basic information, an RFI is often used as a solicitation sent to a broad base of potential suppliers for the purpose of conditioning suppliers' minds, developing strategy, building a database, and preparing for an RFP, RFT, or RFQ.[1] See also[edit] References[edit]