

Oldest stone tools pre-date earliest humans - BBC News. The world's oldest stone tools have been discovered, scientists report.
Skeletal remains of 24,000-year-old boy raise new questions about first Americans. Results from a DNA study of a young boy's skeletal remains believed to be 24,000 years old could turn the archaeological world upside down -- it's been demonstrated that nearly 30 percent of modern Native American's ancestry came from this youngster's gene pool, suggesting First Americans came directly from Siberia, according to a research team that includes a Texas A&M University professor.

Kelly Graf, assistant professor in the Center for the Study of First Americans and Department of Anthropology at Texas A&M, is part of an international team spearheaded by Eske Willerslev and Maanasa Raghaven from the Centre for GeoGenetics at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark and additional researchers from Sweden, Russia, United Kingdom, University of Chicago and University of California-Berkeley. Their work, funded by the Danish National Science Foundation, Lundbeck Foundation, and the National Science Foundation, is published in the current issue of Nature magazine. Neanderthal Viruses Found In Human DNA Prompt Scientists To Explore Links To Cancer And AIDS.
Ancient viruses inherited from Neanderthals have been found in modern human DNA.
Scientists are investigating possible links between the "endogenous retroviruses", which are hard-wired into DNA, and modern diseases such as AIDS and cancer. Researchers compared DNA from Neanderthals and another group of ancient humans called Denisovans with that obtained from cancer patients. Dinosaur Brain Structure Modeled From Birds & Alligators In New Study.
SAN DIEGO — Fossils have painted an often colorful and sometimes feathery picture of what dinosaurs looked like in their heyday, but almost nothing is known about the brains of man's favorite Jurassic beasts.
Drawing from the brain structures of crocodiles and birds, new research provides some clues about the structure of the dinosaur brain. "No one has ever found a preserved dinosaur brain," said Erich Jarvis, a neurobiologist at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who presented the research with a colleague Tuesday (Nov. 12) here at the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience. Dinosaur Extinction Event Research Helps Explain Why Some Species Survived. When an asteroid or comet slammed into Earth about 66 million years ago, most of our planet’s species were wiped out in a mass extinction—including entire groups such as the nonavian dinosaurs, marine reptiles such as mosasaurs, and their flying kin the pterosaurs.
But not all ecosystems suffered equally, and the dramatic difference in survival rates between marine species and freshwater ones has been particularly puzzling. Battle for the Americas. One More Homo Species? 3D-comparative analysis confirms status of Homo floresiensis as fossil human species. Ever since the discovery of the remains in 2003, scientists have been debating whether Homo floresiensis represents a distinct Homo species, possibly originating from a dwarfed island Homo erectus population, or a pathological modern human.
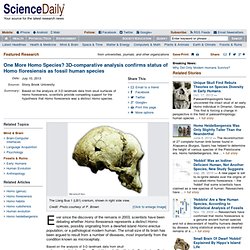
Sabretooth killing power depended on thick neck. 2 July 2013Last updated at 11:13 ET By Melissa Hogenboom Science reporter, BBC News This marsupial pouched killer (pictured in an artist's interpretation) had bigger canines than those of other similar-sized sabretooth beasts Scientists have analysed how an extinct sabretooth animal with huge canines dispatched its prey, finding that strong neck muscles were vital for securing a kill.
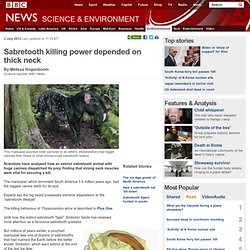
The marsupial, which terrorised South America 3.5 million years ago, had the biggest canine teeth for its size. Did Humans Eat Neanderthals? Evidence For Scientists' Shocking Claim Said Lacking. By: Charles Choi, LiveScience Contributor Published: 06/04/2013 12:14 PM EDT on LiveScience No clear evidence suggests modern humans ate Neanderthals, much less that they did so enough to drive Neanderthals to extinction, despite recent claims from scientists in Spain.
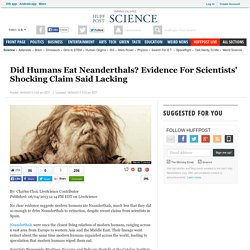
Neanderthals were once the closest living relatives of modern humans, ranging across a vast area from Europe to western Asia and the Middle East. Their lineage went extinct about the same time modern humans expanded across the world, leading to speculation that modern humans wiped them out. Eight Bronze Age Boats Unearthed In Britain Go On Display (PHOTOS) Eight Bronze Age boats go on display this week in England after extremely meticulous preservation efforts.
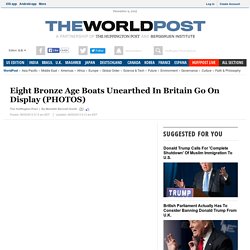
The fleet of wooden boats -- which included one vessel that could still float -- was discovered between 2011 and 2012 at Must Farm in what was once a river bed outside the city of Peterborough, according to the Guardian. Archeologists working with the Cambridge Archaeological Unit are still waiting on the results of carbon 14 dating, but they believe some of the boats date all the way back to 1,600 B.C. Dinosaur Embryos Discovered In Egg Clutch In Portugal Called Most Primitive Ever Found.
By: Stephanie Pappas, LiveScience Senior Writer Published: 05/30/2013 09:02 AM EDT on LiveScience A dinosaur nest discovery has revealed the most primitive known dinosaur embryos, which are among the oldest ever found.
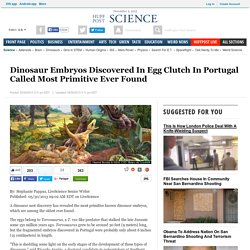
The eggs belong to Torvosaurus, a T. rex-like predator that stalked the late Jurassic some 150 million years ago. Babies Learn To Talk & Birds Learn To Sing In Similar Ways, Finch Study Shows. By Karen Ravn Babies learn to babble before they learn to talk, at first simply repeating individual syllables (as in ba-ba-ba), and later stringing various syllables together (as in ba-da-goo). Songbirds exhibit similar patterns during song-learning, and the capacity for this sort of syllable sequencing is widely believed to be innate and to emerge full-blown — a theory that is challenged by a paper published on Nature's website today1.
How the turtle got its unique hard shell. 31 May 2013 Last updated at 08:08 GMT By Melissa Hogenboom Science reporter, BBC News The sea turtle's unique shell evolved many millions of years ago How the turtle shell evolved has puzzled scientists for years, but new research sheds light on how their hard shells were formed. Scientists say the ancient fossil skeleton of an extinct South African reptile has helped bridge a 30 to 55-million-year gap. This ancestor of the modern turtle, Eunotosaurus , is thought to be around 260 million years old. Archaeopteryx restored in fossil reshuffle. 29 May 2013 Last updated at 13:12 ET By Jonathan Amos Science correspondent, BBC News Features seen in the bones of Aurornis tell scientists they are looking at the beginning of the bird line What may be the earliest creature yet discovered on the evolutionary line to birds has been unearthed in China.
Dog’s tooth accessories were all the rage in Stone Age Europe. Archaeologists excavating a Stone Age burial ground near Leipzig, Germany, have uncovered the world’s oldest purse. The very rare discovery is believed to be up to 4,500 years old and is decorated with over 100 tightly packed canine teeth. Susanne Friederich, of the Sachsen-Anhalt State Archaeology and Preservation Office, believes the teeth formed the decorative outer flap of the purse. She told the National Geographic , “Over the years the leather or fabric disappeared, and all that’s left is the teeth. New evidence suggests Europeans reached America by boat up to 26,000 years ago. A remarkable series of several dozen European-style stone tools, dating back between 19,000 and 26,000 years, have been discovered at 6 locations along the US east coast. Three of the sites are on the Delmarva Peninsular in Maryland, one is in Pennsylvania and another in Virginia. A sixth was discovered by fishermen on the seabed 60 miles from the Virginian coast on what, in prehistoric times, would have been dry land.
The new discoveries are being heralded as “among the most important archaeological breakthroughs for several decades”. Neanderthal Breastfeeding Habits Revealed By Analysis Of Prehistoric Tooth. Humans' Spear Use Dates Back 90,000 Years, Bone Study Suggests. Dinosaur Ancestors Flourished After Mass Extinction, Fossil Study Suggests. Team reconstructs 'human ancestor' 12 April 2013Last updated at 05:36 ET The researchers were able reconstruct the species using bones from three different individuals. Fragments of ancient continent buried under Indian Ocean. 24 February 2013Last updated at 19:13 ET By Rebecca Morelle Science reporter, BBC World Service. HIV 'may have an ancient origin' 25 January 2013Last updated at 02:53 ET By Helen Briggs BBC News. Darwin Was Wrong About Dating. A history lesson from genes: Using DNA to tell us how populations change.
When Charles Darwin first sketched how species evolved by natural selection, he drew what looked like a tree. The diagram started at a central point with a common ancestor, then the lines spread apart as organisms evolved and separated into distinct species. Prehistoric ghosts revealing new details: Synchrotron helps identify previously unseen anatomy preserved in fossils. 'Marine' Fossils May Instead Represent Early Land Dwellers. Scientists 'surprised' to discover very early ancestors survived on tropical plants, new study suggests. Researchers involved in a new study led by Oxford University have found that between three million and 3.5 million years ago, the diet of our very early ancestors in central Africa is likely to have consisted mainly of tropical grasses and sedges.
The findings are published in the early online edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Tracing humanity's African ancestry may mean rewriting 'out of Africa' dates. New way to look at dawn of life: Focus shifts from 'hardware' to 'software' Reconstruction of prehistoric DNA refutes criticism on theory of evolution. Origin Of Life: New Study Spotlights Not Chemistry But How Living Things Store, Process Information. Feathered Non-Avian Dinosaurs from North America Provide Insight into Wing Origins.