

Ultrasonic Testing. Ultrasonic Testing (Internationa Atomic Energy Agency) Training Guidelines for non destructive testing (Internationa Atomic Energy Agency) ISO Standards - ISO/TC 135/SC 3 - Ultrasonic testing. EN ISO 12718. ISO Standards - ISO/TC 135/SC 4 - Eddy current methods. 1 s2 0 S0963869509001698 main.
1_12_16.pdf. RPV Specimen Removal, Radiation Tolerant Manipulator. Diakont produces complete systems for Reactor Pressure Vessel inspection and in-situ repairInspections are completed using either visual or laser-holographicEntire operations are automated, for completion at high speed and with minimal critical path impactRPV repairs are completed through grinding Laser-holographic visual testing for crack detection The STS-K-78P is a unique, radiation-resistant television system that provides controlled surface scanning at high speed and measures deviations with metrological-certified accuracy.
The system is designed for automated pre-operational and operational control of the base metal, weld coatings, and welds inside PWR, BWR, and VVER reactors. The system meets the visual inspection criteria VT-1, PNAE G-7-016-RD-89, and EA-0079-2005. STS-K-78P systems have discovered dozens of RPV defects that inspectors determined would not have been detected by other means. Specifications: Automated RPV Defect Repair Grinding RPV Specimen Sample Removal Manipulator. Innovative Robotics and Ultrasonic Technology at the Examination of Reactor Pressure Vessels in BWR and PWR Nuclear Power Stations. NDT.net - October 1998, Vol.3 No.10 Introduction Inservice inspections on the reactor pressure vessels of nuclear power plants not only demand high standards of technology and quality but increasingly require that more emphasis be placed on economics.

The aim is to cut down on the time required for inspections thereby shortening nuclear power plant outages and to cut the cost of performing such inspections. This demands continual innovation both in the field of ultrasonic examination technology as well as regarding manipulators and robotics. The development of the SAPHIR ultrasonic examination equipment has made a considerable contribution towards achieving these goals. Ultrasonic examination technology using SAPHIR Non-destructive inspections on reactor pressure vessels are characterized by the following criteria: : Ultrasonic testing. An example of Ultrasonic Testing (UT) on blade roots of a V2500IAEaircraftengine.Step 1: The UT probe is placed on the root of the blades to be inspected with the help of a special borescope tool (video probe).Step 2: Instrument settings are input.Step 3: The probe is scanned over the blade root.
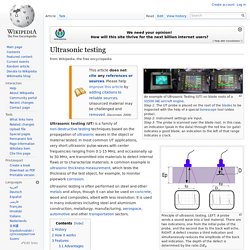
In this case, an indication (peak in the data) through the red line (or gate) indicates a good blade; an indication to the left of that range indicates a crack. Principle of ultrasonic testing. LEFT: A probe sends a sound wave into a test material. There are two indications, one from the initial pulse of the probe, and the second due to the back wall echo. RIGHT: A defect creates a third indication and simultaneously reduces the amplitude of the back wall indication. Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. History[edit] On May 27, 1940, U.S. researcher Dr. James F. How it works[edit] Eddy current. By Lenz's law, an eddy current creates a magnetic field that opposes the magnetic field that created it, and thus eddy currents react back on the source of the magnetic field.
For example, a nearby conductive surface will exert a drag force on a moving magnet that opposes its motion, due to eddy currents induced in the surface by the moving magnetic field. This effect is employed in eddy current brakes which are used to stop rotating power tools quickly when they are turned off. The current flowing through the resistance of the conductor also dissipates energy as heat in the material. Thus eddy currents are a source of energy loss in alternating current (AC) inductors, transformers, electric motors and generators, and other AC machinery, requiring special construction such as laminated magnetic cores to minimize them. Origin of term[edit] History[edit] French physicist Léon Foucault (1819–1868) is credited with having discovered eddy currents. Explanation[edit] where Skin effect[edit]