

Les programmes de recherche. Salle de post-amplification du laboratoire des interactions virus-hôtesMaladies infectieuses négligées CAROLIA (FEDER 2012-2015) Mieux comprendre les modalités de circulation et de dispersion du virus de la rage chez les différentes espèces de chauves-souris et caractériser la réponse immunitaire vis-à-vis de l’infection.
GENEVIL (Labex CEBA) Identification de la diversité génétique du virus de Leishmania (Leishmania RNA virus, LRV) infectant le parasite leishmania isolé de patients présentant une leishmaniose en Guyane Française. Étude de l’implication du virus sur l’évolution des lésions cutanées à L.guyanensis. ParisTech : Laboratoire de Physique et mécanique des milieux hétérogènes. Site web L’activité du laboratoire est centrée sur l’hydrodynamique des écoulements complexes (particules, interfaces, instabilités) et les propriétés des milieux hétérogènes (fracturation,..).

Dans cette activité, nous gardons un souci constant d’établir un pont entre en amont des développements théoriques et numériques récents en physique statistique : modèles de marche au hasard, de dynamique de fronts, de transition vers le chaos ; en aval : un intérêt pratique grandissant pour les matériaux hétérogènes et les procédés faisant intervenir des écoulements et des fluides complexes. Ce souci se reflète dans la triple appartenance du laboratoire aux secteurs sciences pour l’ingénieur, sciences physiques et mathématiques et sciences chimiques du CNRS ainsi que dans sa collaboration étroite avec l’industrie. Jernvall Evo-Devo Lab. Mullins Lab. The Canman Lab — Research. Coordination of chromosome segregation with cytokinesis During mitosis, the physical division of one cell into two is called cytokinesis.

Cytokinesis must be tightly coordinated with mitotic chromosome segregation to ensure that each daughter cell receives adequate cytoplasm and a single copy of the genome. This coordination is ensured by a set of proteins required for cytokinesis that localize on the chromosomes during metaphase and transition to the division plane during chromosome segregation, on a structure called the "central spindle". Using the power of genetics and live–cell analysis, we are studying how these central spindle-bound proteins promote efficient division between the separated chromosomes.
Regulation of contractile ring assembly and constriction. Cohen Lab. Magnetic control of coherent electron spin dynamics in room-temperature liquids We are working on a new class of spectroscopies in which the 3-dimensional shape of the electromagnetic field is engineered to induce qualitatively new physical effects in molecules.
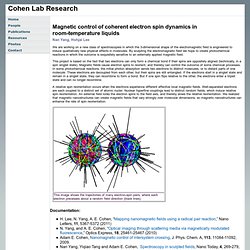
By sculpting the electromagnetic field we hope to create photochemical reactions in which the outcome is exquisitely sensitive to an externally applied magnetic field. This project is based on the fact that two electrons can only form a chemical bond if their spins are oppositely aligned (technically, in a spin singlet state). Magnetic fields cause electron spins to reorient, and thereby can control the outcome of some chemical processes. In some photochemical reactions, the initial photon absorption sends two electrons to distinct molecules, or to distant parts of one molecule. A relative spin reorientation occurs when the electrons experience different effective local magnetic fields.
Szostak Lab: Research. RNA Selections: What Next?
Protocell-related RNA selections (see Szostak et al. 2001 Nature) Aptamer Biology Protocell Related RNA Selections Replicating RNA inside replicating vesicles: a protocell ribozyme,membrane compatibility coordination of replication rates replicase evolution in a protocell. Center for Developmental Biology. Thermal Phenomena in Cells and Biomolecules. Cytoskeletal Dynamics During Cytokinesis. Von Dassow, Bement, Foe, Odell Despite no lack of attention from cell biologists, geneticists, and even theoreticians, animal cell cytokinesis — during which the cell actually pinches in two following chromosome segregation — remains an unsolved mystery.

It is widely accepted that progress of the division furrow is based on the contraction of a bundle of aligned actin filaments and myosins, the contractile ring, which is a remarkably conserved feature of dividing animal cells. Also, classical experiments show that animal cells establish the furrow region in relation to the position and orientation of the microtubule-based mitotic apparatus: cells of various types correct for experimental displacement of the metaphase spindle due to centrifugation, deformation, or micromanipulation, managing still to cleave such that the furrow separates one set of chromosomes and spindle pole from the other set.
LED Pubs. Kenny, N.

J, Dearden, P.K. (2013) "NMDA Receptor Expression and C Terminus Structure in the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis and Long Term Potentiation across the Metazoa" Invertebrate Neuroscience (in press). DOI 10.1007/s10158-013-0154-0 Duncan, E.J. Benton, M.A., Dearden P.K. (2013) "Canonical terminal patterning is an evolutionary novelty" Developmental Biology (in Press) DOI 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.02.010 Duncan, E.J., Leask, M.P., Dearden, P.K. (2013) “The pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) genome encodes two divergent early developmental programs” Developmental Biology (in press) Cameron, R. MPIDR - The maintenance gap: a new theoretical perspective on the evolution of aging. Wensink, M.

J., van Heemst, D., Rozing, M.P., Westendorp, R. G. J. Institut Curie. Mediterranean Institute For Life Sciences. Max Planck Institute for the History of Science. Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics: Home. FR. Landry Laboratory Main/Publications. Research profile on Google Leducq JB*, Charron G*, Samani P, Dubé AK, Sylvester K, James B, Almeida P, Sampaio JP, Hittinger CT, Bell G & CR Landry. 2014.
Local climatic adaptation in a widespread microorganism. PRS B 8;281(1777):20132472. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.2472 Freschi L, Osseni M & Landry CR. 2014. Functional Divergence and Evolutionary Turnover in Mammalian Phosphoproteomes. Systems Biology – HMS. UCSB Santa Barbara. Biography.
Los Alamos National Lab: National Security Science. Laboratoire Matière et Systèmes Complexes - CORNELISSEN Annemiek. TaMaRa's lab. Kewalo Marine Laboratory. Biologie du développement - umr7009 - Les équipes de recherche - Institut de biologie de l'école normale supérieure. Evolution of Nematode Development November 2011: Marie-Anne Felix and her group moved to the Institute of Biology of the Ecole Normale Supérieure. Their new page is on We are studying the development and evolution of a major model system in developmental biology, the vulva of the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans.
We are particularly interested in the developmental robustness of this organ when faced with random noise, environmental variations or mutations, and in its evolution in C. elegans and other closely related nematodes. During vulval formation, a centered pattern of three developmental cell fates is specified within a row of six cells, based on a robust intercellular signaling network that produces an invariant output of fates. The correct fate pattern is required for formation of a normal vulva, and consequently for egg-laying and copulation. CRTD: Home. Hyman Lab. New DRESDEN-concept cultural calendar The MPI-CBG is proud to be part of DRESDEN-concept, a collection of cultural and research institutions in the city.
DRESDEN-concept’s mission “is aimed at the development and use of synergies in research, education, infrastructure, and administration. Partners co-ordinate strategies to support Dresden’s leading areas and identify new emerging scientific areas. The DRESDEN-concept alliance also works on a joint initiative to attract top talents and to convince the best to come to Dresden.” Homepage of Tomas Bohr. TaMaRa's lab. Figure 1. The life cycle of E. coli During cell division, two new poles are formed, one in each of the progeny cells (new poles, shown in blue). The other ends of those cells were formed during a previous division (old poles, shown in red). A. The number of divisions since each pole was formed is indicated by the number inside the pole. Nuclear Pores: Transport and Cell Cycle Nuclear Pore Complexes (NPCs) are elaborate structures embedded in the nuclear envelope and composed of multiple copies of about 30 different proteins termed nucleoporins (Nups) (Figure 1).
Our team aims at characterizing, beyond their well-established function in transport between the cytoplasm and the nucleus, non-conventional functions of NPCs and nucleoporins in nuclear metabolism and during mitosis.To understand these fundamental processes, our projects are mainly focused on an evolutionarily conserved NPC sub-complex, called Nup107-160 in mammalian cells (Figure 1) and Nup84 in the yeast S. cerevisiae. For this purpose, we combine live-cell imaging, genetics and biochemistry. Current Research Topics: The team has been supported by the "Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer since 2006 and is currently supported by the Fondation ARC pour la recherche sur le cancer (ARC Foundation = French Foundation for Cancer Research) IHA. Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research.