

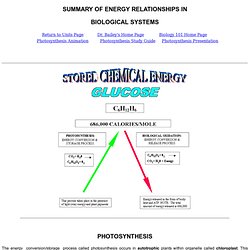
Bio 231 Cell Biology Laboratory Home Page. MBY2604.swf (application/x-shockwave-flash Object) Photosynthesis diagram. Photosynthesis Study Goals. Biological Oxidation / Cell Respiration. SUMMARY OF ENERGY RELATIONSHIPS IN. The energy conversion/storage process called photosynthesis occurs in autotrophic plants within organelle called chloroplast.
This organelle is double membrane bound structure; necessary pigments are concentrated within inner membrane of chloroplast. FUNCTIONAL PARTS OF CHLOROPLAST: (see text, pg. 108-109, Fig. 7.2) Inner membrane represented as a series of staked membranes = GRANUM (GRANA = plural). Each GRANUM is made up of a number of individual membrane units called a THYLAKOID.
The portion of photosynthesis which is called the LIGHT REACTION (LIGHT DEPENDENT Rx--requires light energy in order to occur) takes place in the Grana. The clear, non-membrane areas of chloroplast = STROMA. Photosynthesis is responsive to certain wave lengths of light energy (see Fig. 7.3, 7.4 & 7.5, Pg. 110-111 in text). In addition to Chlorophyll a, there are a number of other pigments concentrated within the membranes of the grana. Chap 4 Sec 3 Cellular Respiration. Concept Map on Cellular Respiration. Introduction to Cellular Respiration. Introduction: Once the energy that was in sunlight is transformed into chemical energy, often by photosynthesis, the organism has to now convert the chemical energy into a usable form.

It may seem a bit odd for there still to be more steps. After all, when you eat a candy bar isn't the sugar in the candy bar "burnt" by the body to provide energy? Well the answer is yes and no. First of all when we burn something normally in the air we combine that substance with oxygen releasing energy from the substance. What goes on in living things is not really like burning because the molecules from which we harvest energy give up their energy in a controlled fashion rather than all at once as what happens in a fire. The Point of Cellular Respiration The point of cellular respiration is to harvest electrons from organic compounds such as glucose and use that energy to make a molecule called ATP.
Courseware Animations. Cellular Processes. WIT Home Page. Metabolism Problem Set. CELLULAR METABOLISM AND FERMENTATION. Cellular Respiration. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation 2D says, “We Monarchs need lots of energy to live our lives.

As adult butterflies, we siphon nectar from flowers. That is high in sugar, which our mitochondria ‘burn for fuel,’ via the process of cellular respiration, so our bodies can use the energy for other things, including flying all the way to Mexico to spend the winter. While we are ‘cold-blooded,’ you might actually see us using cellular respiration to warm up before we begin to fly. To you humans, that might look like we’re ‘shivering,’ but by rapidly twitching our flight muscles, thereby stimulating the mitochondria to do cellular respiration, we’re able to warm up those muscles to prepare for flight.”
Background Information: AMP may be joined to another phosphate group by dehydration synthesis to form adenosine diphosphate or “ADP.” The bonds that hold the last two phosphate groups, especially the last one, onto the molecule are “high-energy” bonds. Glycolysis: Glucose (C6H12O6) 4 H+ + 4 e– Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water.
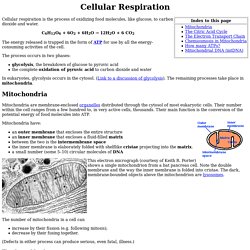
The energy released is trapped in the form of ATP for use by all the energy-consuming activities of the cell. The process occurs in two phases: glycolysis, the breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid the complete oxidation of pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water In eukaryotes, glycolysis occurs in the cytosol. (Link to a discussion of glycolysis). The remaining processes take place in mitochondria. Mitochondria Mitochondria are membrane-enclosed organelles distributed through the cytosol of most eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria have: an outer membrane that encloses the entire structure an inner membrane that encloses a fluid-filled matrixbetween the two is the intermembrane spacethe inner membrane is elaborately folded with shelflike cristae projecting into the matrix. a small number (some 5–10) circular molecules of DNA This electron micrograph (courtesy of Keith R.