

Plant & Animal WebQuest. Plant & Animal WebQuest Introduction Cells, what are they?

What do they do? What are they made of? How do they work? Task Working with a group on this WebQuest, you will first research the various parts of a cell. . * Plant Cell Expert #1 will use and complete the Plant Cell Research Page #1. . * Animal Cell Expert #1 will use and complete the Animal Cell Research Page #1. After you have become an expert you will work in your group to make several creative products based on cells. Process List of things to do: All pages and websites that are needed are found in the Resources section. 1. 2. 3. . * the name of the cell structures and the description of their functions * a picture of the cell part. 4. Resources - Links General Study Tools Resources - Files Work Pages Evaluation You will be evaluated in several ways.
Evaluation Rubric Conclusion Cells are the very building blocks of life. Credits *Helpful website to construct webquest * All websites found in the Resource Section was located by using Google Search. Plant Cell Vs. Animal Cell. The bodies of both plants and animals are made up of cells.
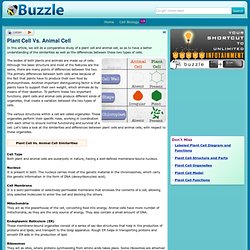
Although the basic structure and most of the features are the same, there are many points of differences between the two. The primary differences between both cells arise because of the fact that plants have to produce their own food by photosynthesis. Another important distinguishing factor is that plants have to support their own weight, which animals do by means of their skeleton. To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells. The various structures within a cell are called organelles. Plant Cell Vs. Cell Type Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic in nature, having a well-defined membrane-bound nucleus.
Nucleus It is present in both. Mitochondria They act as the powerhouse of the cell, converting food into energy. Ribosomes They act as sites, where proteins synthesizing from amino acids takes place. Cell Models: An Interactive Animation. The cells of protozoa, higher plants and animals are highly structured.

These cells tend to be larger than the cells of bacteria, and have developed specialized packaging and transport mechanisms that may be necessary to support their larger size. Use the Interactive animation of plant and animal cells to learn about their respective organelles. : The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. It is enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. Within the nucleus is the DNA responsible for providing the cell with its unique characteristics. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is different from a muscle cell, and a muscle cell is different from a fat cell.
. - microtubules - actin filaments (microfilaments) - intermediate fibers. Inside a Cell. Top 10 Rules of Science Lab Safety. Bugs That Live on You. Microscope. Cheek cell microscope. Big picture. Animal cell. 3D animal cell. Plant cell. 3D plant cell. Discovery Video - Cells. Cells Cells - Parts of the Cell Rap. Introduction to Cells. The wacky history of cell theory - Lauren Royal-Woods. TourOfAnAnimalCell. A REALLY awesome cell animation. Read first. A Tour of the Cell.