

Pluto’s Planet Status: Use Comparison Chart to Help Students Understand Solar System Objects « seedsofsciencerootsofreading. February 17, 2013 at 3:14 pm On February 18, 1930, Clyde W.
Tombaugh, an assistant at the Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, discovered Pluto. At that time, it was classified as the ninth planet in our Solar System. Then, in 2006, a group of astronomers decided that Pluto should not be classified as a planet. To help students understand the distinction, it is helpful for them to create a comparison chart to see how Pluto is similar to and different from each group of objects in the solar system. Students can research information online or with resources in the classroom or library.
Here’s what the comparison chart might look like, based on research compiled by the students. Based on their research, students may have discovered some key information that would help them differentiate Solar System objects. Rocky planets: Because the outer layers of Earth are composed of rock, Earth is classified as a rocky planet. Comets: Some astronomers have said that Pluto is more like a comet. Teaching Astronomy and Space: Classroom Demonstrations. Seasons Interactive. Astrobiology - Chapter 2 Sample. Videos » here comes science TMBG they might be giants sun hydrogen helium. Kids science: Stars. Science >> Physics >> Astronomy A cluster of stars called the Pleiades.Source: NASA.
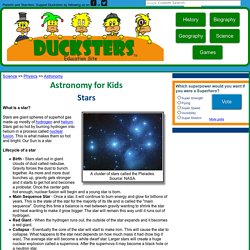
What is a star? Stars are giant spheres of superhot gas made up mostly of hydrogen and helium. Stars get so hot by burning hydrogen into helium in a process called nuclear fusion. This is what makes them so hot and bright. Lifecycle of a star Birth - Stars start out in giant clouds of dust called nebulae. The Horsehead Nebula.Stars form from massive clouds of dust called nebulae.Author: ESA/Hubble [CC 4.0 creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0] Types of Stars There are many different types of stars. Dwarfs - Smaller stars are called dwarf stars. Star Types - Space for Kids! Eagle Nebula (thanks to Don and Elizabeth Van Akker) Stars don't last forever, though they do last for billions of years. And they don't stay the same throughout their existence - they change over time. The earliest beginning of a star is called a nebula. A nebula is a cloud of hydrogen and a few helium atoms hanging in space. Sometimes a nebula just stays at this point, but if the cloud gets thick enough, with enough hydrogen atoms close enough together, it can become a brown dwarf.
Game Descriptions and National Education Standards. SEPUP_Seasons_Interactive. Seasons (Science U) Unless you live near the Earth's equator, you have no doubt noticed that the weather changes during the year: it is hotter during the Summer, colder in Winter, and somewhere in between during Spring and Fall.
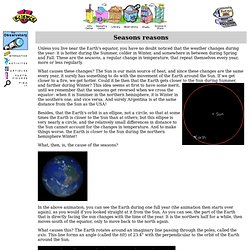
These are the seasons, a regular change in temperature, that repeat themselves every year, more or less regularly. What causes these changes? The Sun is our main source of heat, and since these changes are the same every year, it surely has something to do with the movement of the Earth around the Sun. If we get closer to a fire, we get hotter.
Could it be then that the Earth gets closer to the Sun during Summer, and farther during Winter? This idea seems at first to have some merit, until we remember that the seasons get reversed when we cross the equator: when it is Summer in the northern hemisphere, it is Winter in the southern one, and vice versa. What, then, is, the cause of the seasons? Kinesthetic astronomy.