

Kanban: Is it in the cards? (Page 1 of 7)People often ask, “Why should I use kanban?”
Or “Why switch from scrum to kanban?” These questions show that we need to communicate better what kanban is and why many people are starting to use it. Kanban is a lean method that takes our current process and enhances it to provide better predictability and risk management. It can take an agile (or waterfall) method that has stalled and bring it back to life, creating a custom solution based on the unique needs of the organization.
It creates a culture of continuous improvement so that we get better at scheduling and delivering our work while our workers are happier in their jobs. Kanban is lean. Let’s consider a typical development scenario: A batch of work items, such as features, is planned for completion at the end of a 2-week iteration time box. Then the work begins and reality sets in. What could help this situation? Kanban does not replace the current development process; it is overlaid on top of it. Kanban Applied to Software Development: from Agile to Lean. Abstract A Kanban1 is a physical card used in Toyota Production System (TPS) to support non-centralized "pull" production control.

It has spread to the manufacturing industry all over the world as a tool of Lean Manufacturing. Now in Agile software development the visualization of projects, such as posting task cards on a wall, is a commonly seen practice, which is sometimes called "Software Kanban", or "Task Kanban". Now we even see some product maintenance teams utilizing Kanban systems in a waterfall-like process model.
So what is Kanban? In this article, I first explain what a Kanban system is in the context of Lean manufacturing, especially in TPS, and gather insights from the practices and principles in that mature industry, identifying concepts that can be applied to software development. What is Kanban in TPS? Figure 1 Kanban and Pull Production Figure 1 is an abstract model of a Kanban system. So here are two types of Kanban working together in Figure 1: Visualizing Agile Projects using Kanban Boards. In Agile projects, it's a common practice to visualize and share project status in “big visible charts” on a wall of the project room.
Lean systems also use such devices. "Kanban," in Japanese means, loosely translated, 'card or sign'. In a Lean production system, Kanban is a method which uses standard units or lot sizes with a single card attached to each. A new card is "pulled" into the system only when the work represented by an "in progress" card is completed.. In this paper, I explore visualization methods found widely in agile projects these days, and then propose using Kanban Boards to organize three viewpoints (Time, Task, and Team) so that the whole team understands the current status of the project and can work in an autonomous, motivated and collaborative manner.
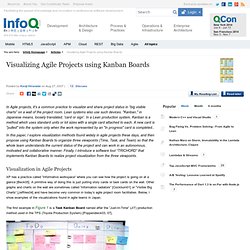
Visualization in Agile Projects XP has a practice called “informative workspace” where you can see how the project is going on at a glance [Beck05]. Figure 1: Task Kanban Board Figure 2: Feature Kanban Board 1. 2.