

Low-carb and calories. Human adipose tissue One of the most common questions MD and I get via email and snail mail and now through the comment sections of our blogs is about failing to lose weight while following low-carb diets.
Here is an excerpt from an email that we got a few days ago: I’m a 47 year old woman, and I’ve been overweight for the past 20 years or so. I was normal sized most of my life, but after I had my third baby at age 27, I started gaining and haven’t really been able to lose much weight. At least not until I started a low-carb diet about 6 months ago. Fruit vs. sugary drinks - 60 Minutes. How fructose builds belly fat - 60 Minutes. Calories: not all created equal - 60 Minutes. Is sugar toxic? - 60 Minutes. Good Eats S14E01 Porterhouse Rules 3 of 3. Good Eats S14E01 Porterhouse Rules 2 of 3. Good Eats S14E04 Little Big Lunch Eggs Benedict 1 of 3. Hormone-Sensitive Lipase. Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL) is one of the lipases that are manufactured by the pancreas in the human body.
They are enzymes that take active part in several biological activities. Their importance in inflammation, facilitating messaging between the body cells, coordination cell activities, and digestion is undeniable. Different types of lipases such as pancreatic lipase, gastric lipase, lingual lipase, hepatic lipase, lysosomal lipase, and phospholipases are involved in digesting food. These are made and released along with other enzymes and hormones by the pancreas into the stomach, and small intestine of the gastrointestinal tract, to aid the digestion of food. They act on food and convert complex foods into simple forms. Lipid Matabolism. Lipids in the Blood: Lipids ingested as food are digested in the small intestine where bile salts are used to emulsify them and pancreatic lipase hydrolyzes lipids into fatty acids, glycerol, soaps, or mono- and diglycerides.

There is still some dispute about the lipid form that passes through the intestinal wall -- whether as fatty acids or as glycerides. In either case, triglycerides are found in the lymph system and the blood. Since lipids are not soluble in blood, they are transported as lipoproteins after reaction with water-soluble proteins in the blood. Fatty acids are generally transported in this form as well. Glycogen. Schematic two-dimensional cross-sectional view of glycogen: A core protein of glycogenin is surrounded by branches of glucose units.
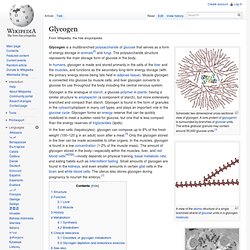
The entire globular granule may contain around 30,000 glucose units.[1] Glycogen (black granules) in spermatozoa of a flatworm; transmission electron microscopy, scale: 0.3 µm Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals[2] and fungi. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and the muscles, and functions as the secondary long-term energy storage (with the primary energy stores being fats held in adipose tissue). What exactly is Fat, and why is it so hard to get rid of? Fat is an enigmatic opponent.

From both the nutrition side and the weight loss side, fat presents a number of challenges. It's high caloric value, ubiquity, and the fact that it usually tastes delicious make it difficult to effectively control dietary intake of fats. At the same time, once your body has stored excess energy as body fat, it is notoriously difficult to get rid of. American Physiological Society > American Physiological Society. What Is The Function Of Fat Cells? Contrary to popular opinion, fat cells in adipose tissue are not simply dormant storage depots, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Alerts.
Fat cells are dynamic and highly active. The fat cells of adipose tissue share an extremely important role in metabolism, according to Sareen Gropper, Jack Smith and James Groff in "Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism. " According to the National Institutes of Health, insulin stimulates fat cells to take in glucose.
Triglycerides can be synthesized in the fat cells from glucose when influenced by insulin. As blood glucose levels decrease, insulin levels fall and the adipose tissue favors the breakdown of triglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol. Fat cells provide triglycerides to fuel much of the body's internal work and physical activity. The body has two types of fat, white and brown adipose tissue, to perform two separate functions. The fat cells continuously break down and rebuild triglycerides as needed. Course D: Diabetes lecture notes - Dr. Afia Ali - Table of Contents. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Is ADHD Caused by Insufficient Dietary Fat? Introduction to How the Atkins Diet Works" Let's face it, you or someone you know has been on a diet at one time or another.
In fact, there's a good chance that many of the folks reading this article are on some kind of diet right now. There are all sorts of diets out there, but most of them have one basic thing in common -- in following the plan, you're required to watch the amount of calories you eat. A majority of diets also require you to avoid high-fat foods. There's one diet out there, though, that doesn't do this. Unlike its fellow regimen, it allows you to eat fairly large amounts of red meat, eggs, cheese, butter and even bacon -- all of which would be considered contraband on other plans.
Obviously there's a considerable amount of controversy over such a program; the Atkins diet, now known as the Atkins Nutritional Approach™, is a frequent topic among the media. What is a Fatty Acid?" A fatty acid is a long hydrocarbon chain capped by a carboxyl group (COOH).
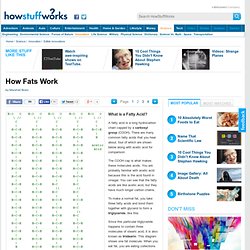
There are many common fatty acids that you hear about, four of which are shown below along with acetic acid for comparison: The COOH cap is what makes these molecules acids. You are probably familiar with acetic acid because this is the acid found in vinegar. You can see that the fatty acids are like acetic acid, but they have much longer carbon chains. To make a normal fat, you take three fatty acids and bond them together with glycerol to form a triglyceride, like this: How Fat Cells Work" A little more than half of the adults in the United States are overweight.

Statistics show that an incredible 65.2 percent of the U.S. population is considered to be "overweight" or "obese. " According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), obesity and overweight status is determined in adults by finding a person's "Body Mass Index" or BMI. BMI is a calculation that takes into consideration both a person's body weight and height to determine whether they are underweight, overweight or at a healthy weight.
Dr Gerber The Science Of Obesity Part 4of4. Dr Gerber The Science Of Obesity Part 3of4. Dr Gerber The Science Of Obesity Part 2of4. Dr Gerber The Science Of Obesity Part 1of4. Sugar Daddy: Taubes tells all. Gary Taubes: What If Fat, Doesn't Make You Fat? A Guide to Ketosis. How To Evaluate Your Blood Sugar & Insulin. How Insulin Gets Glucose Into a Cell. How does Insulin work. Diabetes: Overview. How many calories are in vodka? Good Eats Fan Page. Vodka vs. gin. Dietary fats: Know which types to choose. Dietary fats: Know which types to choose When choosing fats, pick unsaturated fat over saturated or trans fat.

Here's how to know the difference. By Mayo Clinic Staff Most foods contain several different kinds of fat, and some are better for your health than others. You don't need to completely eliminate all fat from your diet. The facts about fat. High-fructose corn syrup: What are the health concerns? High-fructose corn syrup is a common sweetener in sodas and fruit-flavored drinks. As use of high-fructose corn syrup has increased, so have levels of obesity and related health problems, leading some to wonder if there's a connection. Research has shown that high-fructose corn syrup is chemically similar to table sugar.
Controversy exists, however, about whether or not the body handles high-fructose corn syrup differently than table sugar. What is BPA? Should I be worried about it? BPA stands for bisphenol A. Serves up its own ‘Plate’ The Healthy Eating Plate, a visual guide that provides a blueprint for eating a healthy meal, was unveiled today by nutrition experts at Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) in conjunction with colleagues at Harvard Health Publications. Similar to the U.S. government’s MyPlate, the Healthy Eating Plate is simple and easy to understand — and it addresses important deficiencies in the MyPlate icon. “Unfortunately, like the earlier U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) pyramids, MyPlate mixes science with the influence of powerful agricultural interests, which is not the recipe for healthy eating,” said Walter Willett, professor of epidemiology and nutrition and chair of the Department of Nutrition at HSPH.
“The Healthy Eating Plate is based on the best available scientific evidence and provides consumers with the information they need to make choices that can profoundly affect our health and well-being.” “Unfortunately, like the earlier U.S. Popsicles!
WeightWatchers.com. Natural, Healthy, Organic, Gluten-Free Snack Bar. UnitedHealthcare Team - Blog. Tomato vs. Apple - Which is healthier?