

Classification of Alzheimer’s illness by Using Random Forest – Keen Advance Institute of Research. Article: Classification of Alzheimer’s illness by Using Random Forest Abstract Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that leads to the loss of memory and cognition function.

Using neuroimaging and biological data from Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Intuitive (ADNI), previous researchers presented the classifications of the application framework. They applied Random Forest (RF) classifier to distinguish between multiple patients and they recommended bagging without replacement techniques for handling imbalanced data. They used RF algorithm for diagnosing based on the combination of all information for comparisons between AD and Normal Control (NC), as well as between Multi Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and NC patients.
In this work, we built our own algorithm named New Random Forest (NRF) to improve the classification accuracies by running efficiently of the large dataset as it is able to handle thousands of input variables without deletion also. A. A. II. Random Forest ensembles for detection and prediction of Alzheimer's disease with a good between-cohort robustness. Random forest-based similarity measures for multi-modal classification of Alzheimer's disease. Efficacy and Safety Trial of Verubecestat (MK-8931) in Participants With Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease (MK-8931-019) This study is ongoing, but not recruiting participants.
Sponsor: Information provided by (Responsible Party): Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: First received: September 25, 2013 Last updated: April 11, 2017. Merck Announces EPOCH Study of Verubecestat for the Treatment of People with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease to Stop for Lack of Efficacy. KENILWORTH, N.J.

--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Merck (NYSE: MRK), known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, today announced that it will be stopping protocol 017, also known as the EPOCH study, a Phase 2/3 study evaluating verubecestat, an investigational small molecule inhibitor of the beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), in people with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Merck is stopping the study following the recommendation of the external Data Monitoring Committee (eDMC), which assessed overall benefit/risk during a recent interim safety analysis, and determined that there was “virtually no chance of finding a positive clinical effect.”
The eDMC noted that safety signals observed in the study “are not sufficient to warrant stopping study 017,” and recommended that protocol 019, also known as APECS, which is evaluating verubecestat in people with prodromal Alzheimer’s disease, continue unchanged. About the EPOCH Study. Lilly Announces Top-Line Results of Solanezumab Phase 3 Clinical Trial (NYSE:LLY)
, /CNW/ -- (: LLY) today announced that solanezumab did not meet the primary endpoint in the EXPEDITION3 clinical trial, a phase 3 study of solanezumab in people with mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Patients treated with solanezumab did not experience a statistically significant slowing in cognitive decline compared to patients treated with placebo (p=.095), as measured by the ADAS-Cog14 (Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive subscale). While the study results, including many secondary clinical endpoints, directionally favored solanezumab, the magnitudes of treatment differences were small. There were no new safety signals identified in the study. Lilly will not pursue regulatory submissions for solanezumab for the treatment of mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. Lilly will work with investigators to appropriately conclude the open-label extensions for EXPEDITION, EXPEDITION2 and EXPEDITION3. Solanezumab. In Phase 1, single doses of 0.5, 1.5, 4.0, or 10.0 mg/kg of solanezumab were well-tolerated in healthy volunteers and 19 patients with mild to moderate AD.
MRI showed no evidence of inflammation, vasogenic edema, or microhemorrhage. A multiple-dose study in Japan delivered a 400 mg dose to 33 patients with mild to moderate AD intravenously every one, four, or eight weeks, also without serious adverse events related to solanezumab. Pharmacodynamic biomarker studies found changes in plasma and CSFAβ40, Aβ42, plasma pyro-Glu Aβ, and plasma and CSF N-terminally truncated Aβ, but not CSF total tau and phosphorylated tau. In Phase 2, trials administering 100 to 1,600 mg per month of solanezumab for 12 weeks, and monitoring for safety and biomarker effects for one year, confirmed the antibody's safety and tolerability. Merck: Clinical Trials. Computer-assisted measurement of retinal vessel diameters in the Beaver Dam Eye Study: methodology, correlation between eyes, and effect of refract... Association of retinal vessel caliber to optic disc and cup diameters.
The International Society of Hypertension. Featured ISH 2018 Scientific MeetingSeptember 19th 2018 to September 23rd 2018Beijing, ChinaSave the date and plan to join us in Beijing for the 2018 ISH Scientific MeetingMore Inter-American Society of Hypertension / Argentinian Society of Hypertension Mendoza, Argentina Inter-American Society of Hypertension (IASH) XXI Scientific Sessions in conjunction with the XXIV Congress of the Argentinian Society of Hypertension (SAHA) More April 20th 2017 to April 24th 2017 ISN World Congress of Nephrology Centro Banamex, Mexico City, Mexico An international nephrology meeting focusing on diabetes and kidney disease.

More April 21st 2017 to April 25th 2017. Retina World Congress. European Society of Retina Specialists. The Eyes Have It: Anatomy of the Visual System. Simple Anatomy of the Retina by Helga Kolb. Helga Kolb 1.
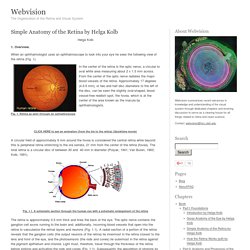
Overview. When an ophthalmologist uses an ophthalmoscope to look into your eye he sees the following view of the retina (Fig. 1). In the center of the retina is the optic nerve, a circular to oval white area measuring about 2 x 1.5 mm across. From the center of the optic nerve radiates the major blood vessels of the retina. Fig. 1. CLICK HERE to see an animation (from the iris to the retina) (Quicktime movie) A circular field of approximately 6 mm around the fovea is considered the central retina while beyond this is peripheral retina stretching to the ora serrata, 21 mm from the center of the retina (fovea). Fig. 1.1. The retina is approximately 0.5 mm thick and lines the back of the eye. A simplistic wiring diagram of the retina emphasizes only the sensory photoreceptors and the ganglion cells with a few interneurons connecting the two cell types such as seen in Figure 2.
Fig. 2. 2. Central retina is cone-dominated retina whereas peripheral retina is rod-dominated. 3. 4. Fundus photography. The models and technology of fundus photography has advanced and evolved rapidly over the last century.[2] Since the equipments are sophisticated and challenging to manufacture to clinical standards, only a few manufacturers/brands are available in the market: Topcon, Zeiss, Canon, Nidek, Kowa, CSO and CenterVue are some example of fundus camera manufacturers.[3] History[edit] The concept of fundus photography was first introduced in the mid-1800s, after the introduction of photography in 1839.
The goal of photographing the human ocular fundus was slowly but surely becoming more achievable. In 1851, Hermann von Helmholtz introduced the Ophthalmoscope, and James Clerk Maxwell presented a colour photography method in 1861. In the early 1860s, Henry Noyes and Abner Mulholland Rosebrugh both assembled fundus cameras and tried fundus photography on animals. There has been some controversy regarding the first ever successful human fundus photo. Hypertension Research - Arterial stiffness estimation in healthy subjects: a validation of oscillometric (Arteriograph) and tonometric (SphygmoCor) techniques. Basics of Scientific Literature Analysis, Part 4: Network analysis/visualization with Gephi. Basics of Scientific Literature Analysis, Part 2: How to Analyse. Kingston University London. Retinal Microvascular Changes and Risk of Stroke. The Singapore Malay Eye Study + Author Affiliations Correspondence to Carol Y.

Cheung, PhD, Singapore Eye Research Institute, Singapore National Eye Centre, 11 Third Hospital Ave, Singapore 168751. E-mail carol.cheung.y.l@seri.com.sg Abstract Background and Purpose—To examine the relationship between retinal microvascular measures and incident stroke in an Asian Malay population. Methods—We conducted a prospective, population-based cohort study of Asian Malay persons 40 to 80 years at baseline. Results—A total of 3189 participants were free of prevalent stroke at baseline. Conclusions—Retinal microvascular changes are related to an increased risk of stroke in Asian Malay, consistent with data from white populations.