

Smart grid. A smart grid is a modernized electrical grid that uses analog[1] or digital information and communications technology to gather and act on information - such as information about the behaviours of suppliers and consumers - in an automated fashion to improve the efficiency, reliability, economics, and sustainability of the production and distribution of electricity.[2] Electronic power conditioning and control of the production and distribution of electricity are important aspects of the smart grid.
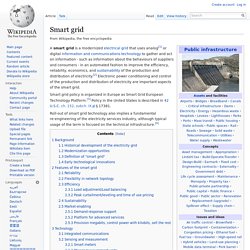
Smart grid policy is organized in Europe as Smart Grid European Technology Platform.[3] Policy in the United States is described in 42 U.S.C. ch. 152, subch. IX § 17381. Roll-out of smart grid technology also implies a fundamental re-engineering of the electricity services industry, although typical usage of the term is focused on the technical infrastructure.[4] Background[edit] Historical development of the electricity grid[edit] Electrical substation. A 50 Hz electrical substation in Melbourne.
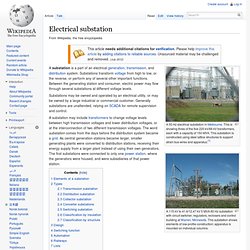
This is showing three of the five 220 kV/66 kV transformers, each with a capacity of 150 MVA. This substation is constructed using steel lattice structures to support strain bus wires and apparatus.[1] A 115 kV to 41.6/12.47 kV 5 MVA 60 Hz substation with circuit switcher, regulators, reclosers and control building at Warren, Minnesota. This substation shows elements of low-profile construction; apparatus is mounted on individual columns. A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substation Automation.