

Electricity and Electric Circuits. Voltage, Current and Resistance. Series and Parallel Circuits. Series Circuits. Resistors & Calculator. Favorited Favorite 4 Take a Stance, The Resist Stance Resistors - the most ubiquitous of electronic components.
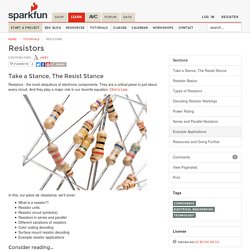
They are a critical piece in just about every circuit. And they play a major role in our favorite equation, Ohm’s Law. In this, our pièce de résistance, we’ll cover: What is a resistor?! Consider reading… Some of the concepts in this tutorial build on previous electronics knowledge. Resistor Basics Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistor units The electrical resistance of a resistor is measured in ohms. As SI units go, larger or smaller values of ohms can be matched with a prefix like kilo-, mega-, or giga-, to make large values easier to read. Schematic symbol All resistors have two terminals, one connection on each end of the resistor. Two common resistor schematic symbols. Types of Resistors Termination and mounting Power Rating.
How to Solder - Through-hole Soldering. Introduction Soldering is one of the most fundamental skills needed to dabble in the world of electronics. The two go together like peas and carrots. And, although it is possible to learn about and build electronics without needing to pick up a soldering iron, you’ll soon discover that a whole new world is opened with this one simple skill. We here at SparkFun believe that soldering should be a skill in everyone’s arsenal. In a world of increasing technological surroundings, we believe it is important that people everywhere be able to not only understand the technologies they use everyday but also be able to build, alter, and fix them as well. In this tutorial we will go over the basics of through-hole soldering – also known as plated through-hole soldering (PTH), discuss the tools needed, go over techniques for proper soldering, and show you where you can go from there. Suggested Reading As stated earlier, you can learn about and build electronics without touching a soldering iron.
Light-emitting Diodes (LEDs) Favorited Favorite 2 The Basics LEDs are all around us: In our phones, our cars and even our homes.

Any time something electronic lights up, there’s a good chance that an LED is behind it. They come in a huge variety of sizes, shapes, and colors, but no matter what they look like they have one thing in common: they’re the bacon of electronics. They’re widely purported to make any project better and they’re often added to unlikely things (to everyone’s delight). Unlike bacon, however, they’re no good once you’ve cooked them. LEDs (that’s “ell-ee-dees”) are a particular type of diode that convert electrical energy into light. In short, LEDs are like tiny lightbulbs. Are you getting the craving yet? Suggested Reading Here are some other topics that will be discussed in this tutorial. How to Use Them So you’ve come to the sensible conclusion that you need to put LEDs on everything. 1) Polarity Matters In electronics, polarity indicates whether a circuit component is symmetric or not. LED Current. Voltage Dividers. Introduction A voltage divider is a simple circuit which turns a large voltage into a smaller one.

Using just two series resistors and an input voltage, we can create an output voltage that is a fraction of the input. Voltage dividers are one of the most fundamental circuits in electronics. If learning Ohm’s law was like being introduced to the ABC’s, learning about voltage dividers would be like learning how to spell cat. Covered in this Tutorial What a voltage divider circuit looks like.How the output voltage depends on the input voltage and divider resistors.How voltage dividers behave in the real-world.Real-life voltage divider applications. Suggested Reading This tutorial builds on basic electronics knowledge.
Analog to Digital Conversion. The Analog World Microcontrollers are capable of detecting binary signals: is the button pressed or not? These are digital signals. When a microcontroller is powered from five volts, it understands zero volts (0V) as a binary 0 and a five volts (5V) as a binary 1. The world however is not so simple and likes to use shades of gray. What if the signal is 2.72V? Here are some topics and concepts you may want to know before reading this tutorial: What is the ADC? An Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) is a very useful feature that converts an analog voltage on a pin to a digital number. Not every pin on a microcontroller has the ability to do analog to digital conversions. ADCs can vary greatly between microcontroller. The way an ADC works is fairly complex.