

Telecommunications network. Example of how nodes may be interconnected with links to form a telecommunications network.
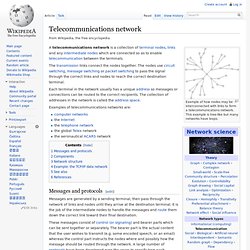
This example is tree-like but many networks have loops. Each terminal in the network usually has a unique address so messages or connections can be routed to the correct recipients. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space. Examples of telecommunications networks are: Messages and protocols[edit] Messages are generated by a sending terminal, then pass through the network of links and nodes until they arrive at the destination terminal.
Components[edit] All telecommunication networks are made up of five basic components that are present in each network environment regardless of type or use. Early networks were built without computers, but late in the 20th century their switching centers were computerized or the networks replaced with computer networks. Network structure[edit] Example: the TCP/IP data network[edit] Computer network. Computer networks differ in the physical media used to transmit their signals, the communications protocols to organize network traffic, the network's size, topology and organizational intent.
In most cases, communications protocols are layered on (i.e. work using) other more specific or more general communications protocols, except for the physical layer that directly deals with the physical media. Computer networks support applications such as access to the World Wide Web, shared use of application and storage servers, printers, and fax machines, and use of email and instant messaging applications. History[edit] Internet. U.S.
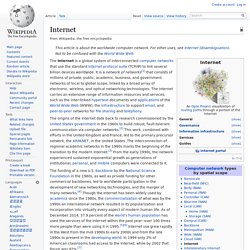
Army soldiers "surfing the Internet" at Forward Operating Base Yusifiyah, Iraq The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link several billion devices worldwide. It is a network of networks[1] that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries an extensive range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), the infrastructure to support email, and peer-to-peer networks for file sharing and telephony.
Most traditional communications media, including telephony and television, are being reshaped or redefined by the Internet, giving birth to new services such as voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and Internet Protocol television (IPTV). Terminology Users. The free encyclopedia. A computer is a program machine that receives input, stores and manipulates data, and provides output in a useful format.
Computer may also refer to: 2600: The Hacker Quarterly. 2600: The Hacker Quarterly is an American publication that specializes in publishing technical information on a variety of subjects including telephone switching systems, Internet protocols and services, as well as general news concerning the computer "underground" and left wing, and sometimes (but not recently), anarchist issues.
Title[edit] The magazine's name comes from the phreaker discovery in the 1960s that the transmission of a 2600 hertz tone (which could be produced perfectly with a plastic toy whistle given away free with Cap'n Crunch cereal—discovered by friends of John Draper) over a long-distance trunk connection gained access to "operator mode" and allowed the user to explore aspects of the telephone system that were not otherwise accessible. The magazine was given its name by David Ruderman, who co-founded the magazine with his college friend, Eric Corley.[2] It was first published in 1984, coinciding with the book of the same name and the break-up of AT&T.
Notes[edit] Wiki. Computer is an IEEE Computer Society practitioner-oriented magazine issued to all members of the society.
It contains peer-reviewed articles, regular columns and interviews on current computing-related issues. The magazine can be categorized somewhere between a trade magazine and a research journal, drawing on elements of both. Computer provides information regarding current research developments, trends, best practices, and changes in the profession. Subscriptions of the magazine are provided free of cost to IEEE Computer Society members. Computer covers all aspects of computer science.