

Robert Fisher Teaching Thinking homepage. Robert Fisher A version of this paper is to be published in Arthur J, Grainger T & Wray D (eds) (in press) Learning to teach in primary school, Routledge Falmer ‘We need to think better if we are to become better people.’

Paul, aged 10 Introduction In recent years there has been growing interest across the world in ways of developing children’s thinking and learning skills (Fisher 2005). Objectives The aims of this chapter are to enable you to: inform your understanding of ‘thinking skills’ and their role in learning understand some key principles that emerge from research into teaching thinking know the main approaches to developing children’s thinking see how you might integrate a ‘thinking skills’ approach into classroom teaching What are thinking skills?
Thinking skills are not mysterious entities existing somewhere in the mind. A skill is commonly defined as a practical ability in doing something or succeeding in a task. Bloom’s Taxonomy (Source: Bloom & Krathwohl 1956) Bloom’s Thinking Skills ≠ Apps. I’ve been researching Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy of Cognitive Tasks, and I’ve been seeing a number of guides attempt to match iPad apps with each level in Bloom’s hierarchy.
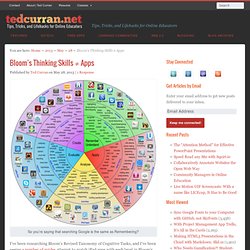
These app guides seem built on a false assumption that using a certain app will reliably stimulate a certain mode of thinking. I think equating apps with Bloom’s thinking tasks create the false impression that if you have all the right apps, your students can just click their way to critical thinking. Thinking Skills for Rich Tasks. The Problem Solving Process Seven Structured Thinking Skills for MathematicsAnd Any Other Rich Task Activity Expectations: The Student will: Describe seven key structured thinking skills and explain how these skills are used to apply and enhance the problem-solving process.

Identify important prerequisites to becoming a good thinker. Synthesize (ie “output”) Portfolio entries connecting Thinking Skills, the Learning Process and the Mathematics Problem-Solving Process. Assignment: This is individual work. Mark: ___ / 15 Due Date: Today or Homework Tonight Special Insight: What is the single biggest difference between life and your personal computer? This Sub-Module is Important Because: To keep or advance in a job you must be able to think clearly -- to propose better ways of doing something; to save your employer money; to be able to use new tools quickly… and so on… Other Resources / Instruction Aids to Use -- Files Will be In Pickup Folder: Collaboration - Lower and higher order thinking skills. A thinking skill is a mental process.
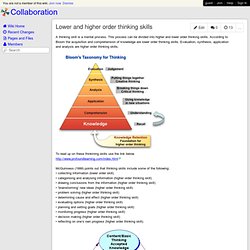
This process can be divided into higher and lower order thinking skills. According to Bloom the acquisition and comprehension of knowledge are lower order thinking skills. Evaluation, synthesis, application and analysis are higher order thinking skills. To read up on these thinkining skills use the link below. Thinking Skills - Bloom's Taxonomy. Thinking Skills - National Curriculum (UK) Problem-solving skills for kids. Self-assembly If you have ever tried your hand at DIY you may well have fallen foul of “self assembly syndrome”.

That build-it-yourself furniture looks so easy to put together on the instruction sheet - but how many times have you found yourself with vital pieces missing, or, more worrying still, with some pieces left over. A similar thing happens when you are trying to repair an item which has many parts which all depend on each other.
Examples like these make an excellent starting point for helping children recognise how problems, like everyday items, are invariably made up of smaller component parts. If you feel brave enough, you might be prepared to allow your child, under supervision, to experiment by taking apart various simple household items. I’ll do as I’m told Ask your child to write down as accurately as they can all the steps necessary to perform a simple task with which they are familiar (such as making a cup of tea). Thinking Hats. Thinking Skills. What do we mean by "Thinking Skills"?

Thinking skills are the mental processes that we apply when we seek to make sense of experience. Thinking skills enable us to integrate each new experience into the schema that we are constructing of "how things are". It is apparent that better thinking will help us to learn more from our experience and to make better use of our intelligence. It has always been the central aim of education to improve the quality of thinking because better thinking will not only enable us to become more successful at learning but will also equip us for life, enabling us to realise our own potential and to contribute to the development of society.
Why do we need to develop thinking skills? When I was at school (in the 1950's and 1960's) students were largely considered to be "clever" if they demonstrated the ability to commit to memory huge amounts of data and to recall that data on the appropriate occasion.