

Maple syrup urine disease - PubMed Health. Cri du chat. Cri du chat syndrome, also known as chromosome 5p deletion syndrome, 5p- (said minus) syndrome or Lejeune’s syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder due to a missing part (deletion) of chromosome 5.
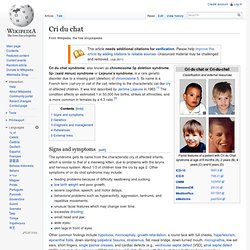
Its name is a French term (cat-cry or call of the cat) referring to the characteristic cat-like cry of affected children. It was first described by Jérôme Lejeune in 1963.[1] The condition affects an estimated 1 in 50,000 live births, strikes all ethnicities, and is more common in females by a 4:3 ratio.[2] Signs and symptoms[edit] The syndrome gets its name from the characteristic cry of affected infants, which is similar to that of a meowing kitten, due to problems with the larynx and nervous system. About 1/3 of children lose the cry by age 2. It has also been observed that people with the condition have difficulties communicating. Affected females reach puberty, develop secondary sex characteristics, and menstruate at the usual time. Cri-du-chat syndrome. Reviewed February 2014 What is cri-du-chat syndrome?

Cri-du-chat (cat's cry) syndrome, also known as 5p- (5p minus) syndrome, is a chromosomal condition that results when a piece of chromosome 5 is missing. Infants with this condition often have a high-pitched cry that sounds like that of a cat. The disorder is characterized by intellectual disability and delayed development, small head size (microcephaly), low birth weight, and weak muscle tone (hypotonia) in infancy. Affected individuals also have distinctive facial features, including widely set eyes (hypertelorism), low-set ears, a small jaw, and a rounded face.
Cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy (CP) is a general term for a group of permanent, non-progressive movement disorders that cause physical disability,[1] mainly in the areas of body movement.[2] There may also be problems with sensation, depth perception, and communication ability.
Difficulty with cognition and epilepsy is found in about one-third of cases. There are a number of subtypes including a type characterized by spasticity, a type characterized by poor co-ordination, and types which feature both symptoms or neither. Cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the motor control centers of the developing brain and can occur during pregnancy, during childbirth, or after birth up to about age three.[3][4] About 2% of all cerebral palsy cases are believed to be due to a genetic cause.[5] Cerebral palsy is not an infectious disease and is not contagious.
Most cases are diagnosed at a young age rather than during adolescence or adulthood. Opisthotonus. Opisthotonus or opisthotonos, from Greek roots, ὄπισθεν, opisthen meaning "behind" and τόνος tonos meaning "tension", is a state of severe hyperextension and spasticity in which an individual's head, neck and spinal column enter into a complete "bridging" or "arching" position.[1] This abnormal posturing is an extrapyramidal effect and is caused by spasm of the axial muscles along the spinal column.
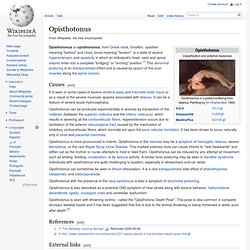
Causes[edit] It is seen in some cases of severe cerebral palsy and traumatic brain injury or as a result of the severe muscular spasms associated with tetanus. It can be a feature of severe acute hydrocephalus. Opisthotonus can be produced experimentally in animals by transection of the midbrain (between the superior colliculus and the inferior colliculus), which results in severing all the corticoreticular fibers. Opisthotonus is more pronounced in infants. Opisthotonus can sometimes be seen in lithium intoxication. References[edit] External links[edit] Opisthotonus at GPnotebook. Hypotonia. Hypotonia (from Ancient Greek ὑπο- hypo-, "under" and τόνος tónos from τείνω teinō, "to stretch") is a state of low muscle tone[1] (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength.
Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength. Recognizing hypotonia, even in early infancy, is usually relatively straightforward, but diagnosing the underlying cause can be difficult and often unsuccessful. The long-term effects of hypotonia on a child's development and later life depend primarily on the severity of the muscle weakness and the nature of the cause.
Some disorders have a specific treatment but the principal treatment for most hypotonia of idiopathic or neurologic cause is physical therapy, occupational therapy for remediation, and/or music therapy. Mennonite. The Mennonites are a Christian group based around the church communities of Anabaptist denominations named after Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland (at that time, a part of the Holy Roman Empire).
Through his writings, Simons articulated and formalized the teachings of earlier Swiss founders. The teachings of the Mennonites were founded on their belief in both the mission and ministry of Jesus Christ, which they held to with great conviction despite persecution by the various Roman Catholic and Protestant states. Rather than fight, the majority survived by fleeing to neighboring states where ruling families were tolerant of their radical belief in believer's baptism. Over the years, Mennonites have become known as one of the historic peace churches because of their commitment to pacifism.[2]