

Paws.kettering.edu/~dludwigs/Phys114/Phys114-Eqs.pdf.
Pearson Education. IB Physics : Magnetic Flux. 12.2 Alternating Current. 12.2.1 Describe the emf induced in a coil rotating within a uniform magnetic field.

As the handle is turned, AB moves up through the field. As it cuts the field a current will be induced. Using Fleming's right hand rule --> direction of current is from A to B. Direction of motion of the right hand side (CD) is opposite so current is opposite. Result is a clockwise current through the resistor.After turning half a revolution, side CD will now be moving up the field. A coil of wire rotates in the magnetic field due to an external force.
Sides AB + CD will experience a force opposing the motion. The work done rotating the coil generates electrical energy. 12.2.3 Describe the effect on the induced emf of changing the generator frequency.If the speed of rotation is changed it will affect:* Time period (distance between peaks)* EMF (amplitude of peaks)For example, if the speed is doubled therefore, the time period will be halved and the EMF (amplitude) will be doubled. w= 2π x 50 = 100π rad s-1. Alternating Current - IB Physics Stuff. 11.3.1 Describe the e.m.f. induced in a coil rotating within a uniform magnetic field. 11.3.2 Explain the operation of a basic alternating current (ac) generator.
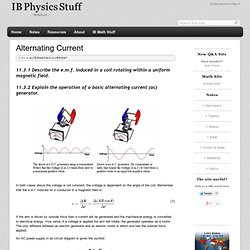
In both cases above the voltage is not constant, the voltage is dependent on the angle of the coil. Remember that the e.m.f. induced on a conductor in a magnetic field is: If the arm is driven by outside force then a current will be generated and the mechanical energy is converted to electrical energy. Vice versa, if a voltage is applied the arm will rotate, the generator operates as a motor. An AC power supply in an circuit diagram is given the symbol: Topic 12: Electromagnetic Induction. Induced EMF: Faraday and Lenz's Laws Induced EMF is the phenomenon of generating electricity from movement in a magnetic field.

Task: Use the apparatus set up for you to make as many observations as you can. Conclusion: When a conductor moves with respect to a magnetic field (or visa versa) an electric current is induced. We need to think of magnetic field lines as magnetic flux (flux meaning something that flows). Magnetic Flux. 'A Universe From Nothing' by Lawrence Krauss, AAI 2009. Fundamentals of Physics I. About the Course This course provides a thorough introduction to the principles and methods of physics for students who have good preparation in physics and mathematics. Emphasis is placed on problem solving and quantitative reasoning. This course covers Newtonian mechanics, special relativity, gravitation, thermodynamics, and waves.
View class sessions » Course Structure This Yale College course, taught on campus twice per week for 75 minutes, was recorded for Open Yale Courses in Fall 2006. The Open Yale Courses Book Series For more information about Professor Shankar's book based on the lectures from this course, Fundamentals of Physics: Mechanics, Relativity, and Thermodynamics, click here. Course Materials Download all course pages [zip - 10MB] Video and audio elements from this course are also available on: Earl Haig Secondary School - Physics Review Lessons.