

International Carnivorous Plant Society.
Cannabis Cultivation. Synsepalum dulcificum. The berry itself has a low sugar content[7] and a mildly sweet tang. It contains a glycoprotein molecule, with some trailing carbohydrate chains, called miraculin.[8][9] When the fleshy part of the fruit is eaten, this molecule binds to the tongue's taste buds, causing sour foods to taste sweet.
At neutral pH, miraculin binds and blocks the receptors, but at low pH (resulting from ingestion of sour foods) miraculin binds protons and becomes able to activate the sweet receptors, resulting in the perception of sweet taste.[10] This effect lasts until the protein is washed away by saliva (up to about 60 minutes).[11] The names miracle fruit and miracle berry are shared by Gymnema sylvestre and Thaumatococcus daniellii,[2] which are two other species of plant used to alter the perceived sweetness of foods. Hort 231: Comparisons of maple leaves, buds, and fruit (samaras) Adventures in Field Botany / Illustrated-Glossary. Leaf Morphology: Phyllode/ Cladode: modifyed stems that act as leaves.
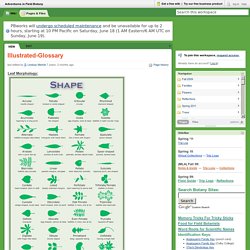
Ensiform: leaves sharp edges, taper into a slender point (fern) Stellate: hairs come up like fingers. Looks like cluster of hair. Peltate: "petiole joins to the center" in leaves. Best Dorm Room Plants - Plants for College Dorm Rooms. Growing and caring for Bonsai trees - Bonsai Empire.