

Richard Stallman. American free software activist Richard Matthew Stallman (; born March 16, 1953), often known by his initials, rms,[1] and occasionally upper-case RMS, is an American free software movement activist and programmer.
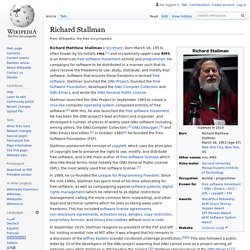
He campaigns for software to be distributed in a manner such that its users receive the freedoms to use, study, distribute, and modify that software. Software that ensures these freedoms is termed free software. Stallman launched the GNU Project, founded the Free Software Foundation, developed the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Emacs, and wrote the GNU General Public License.
Stallman launched the GNU Project in September 1983 to create a Unix-like computer operating system composed entirely of free software.[2] With this, he also launched the free software movement. In 1989, he co-founded the League for Programming Freedom. Early life[edit] Stallman was born March 16, 1953,[12] in New York City, to a family of Jewish heritage. Harvard University and MIT[edit] GNU project[edit] Virtual appliance. A virtual appliance is a pre-configured virtual machine image, ready to run on a hypervisor; virtual appliances are a subset of the broader class of software appliances.
Installation of a software appliance on a virtual machine and packaging that into an image creates a virtual appliance. Like software appliances, virtual appliances are intended to eliminate the installation, configuration and maintenance costs associated with running complex stacks of software. A virtual appliance is not a complete virtual machine platform, but rather a software image containing a software stack designed to run on a virtual machine platform which may be a Type 1 or Type 2 hypervisor.
Like a physical computer, a hypervisor is merely a platform for running an operating system environment and does not provide application software itself. Many virtual appliances provide a Web page user interface to permit their configuration. File formats[edit] Relationship to grid computing[edit] See also[edit] Software as a service. According to a Gartner Group estimate, SaaS sales in 2010 reached $10 billion, and were projected to increase to $12.1bn in 2011, up 20.7% from 2010.[6] Gartner Group estimates that SaaS revenue will be more than double its 2010 numbers by 2015 and reach a projected $21.3bn.

Customer relationship management (CRM) continues to be the largest market for SaaS. SaaS revenue within the CRM market was forecast to reach $3.8bn in 2011, up from $3.2bn in 2010.[7] The term "software as a service" (SaaS) is considered to be part of the nomenclature of cloud computing, along with infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), desktop as a service (DaaS), backend as a service (BaaS), and information technology management as a service (ITMaaS). History[edit]