

Top Ten Moderator Skills (for 2010) Salmon Five Stage Model Accessible Version. Gilly Salmon's.

Top 5 Tips To Effectively Use Humor in eLearning. In this article, I will give you the insight and advice you need to effectively use humor in your eLearning deliverables.
This article offers a variety of tips on how to use humor in your eLearning courses or online training events, without stepping on any toes or compromising your learning goals. As any experienced eLearning professional will surely attest, when using humor in eLearning there are certain unspoken rules that one must follow. After all, what one learner may find hilarious, another might find offensive. For this very reason, I've decided to share a variety of tips that can help you to effectively use humor in your eLearning courses or online training events, so that you can successfully walk the fine line between entertaining and educational. Research your audience to assess culture, experience, and personality. PodOmatic. Russell Stannard "Simple ICT Tools" 4 Steps to Constructively Align your Course. Step 1: Define the intended outcomes (The Objectives) The first step of constructive alignment is to define what the students must learn and the depth of understanding required for each topic.

It is important that the student does not only acquire knowledge of the subject, but can also put this knowledge to use. Biggs claims that in order to really understand something, a student must begin to see the world differently and, in turn, behave differently towards the world (Biggs, 2002). Constructive Alignment - and why it is important to the learning process. What is Constructive Alignment?

Constructive Alignment, a term coined by John Biggs (Biggs, 1999) is one of the most influential ideas in higher education. Selecting Technologies. This page helps you choose among various technologies (not just LMSs) using two approaches: examples of learning outcomes, the kinds of learning activities that could achieve those outcomes, and how those activities could be supported by various learning technologies examples of the tools you may be interested in using and the types of activities and learning outcomes that are likely to be relevant.
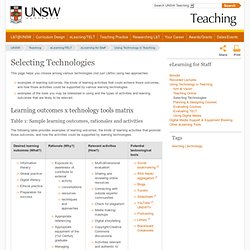
Table 1: Sample learning outcomes, rationales and activities The following table provides examples of learning outcomes, the kinds of learning activities that promote those outcomes, and how the activities could be supported by learning technologies. Choosing the Best Technology. UAF eLearning Instructor Training Online Grow Skills Share your resources or thoughts with us.
Use #iTeach as your tag! Choosing the Best Technology Print Friendly. Constructing Learning Outcomes. Learning outcomes explicitly state what we want students to know, understand, or be able to do as a result of completing their chosen course.

Learning Outcomes Should : 1) Represent real goals Paul Ramsden suggests that, rather than describing facts or procedures, we should describe concepts that students need to understand as well as relations between those concepts. Says Ramsden, if learning outcomes "concentrate largely on procedures and facts, students will inevitably receive the message that higher order outcomes (including both an understanding of key concepts and the development of complex skills such as a systematic approach to experimentation or historical argument) are less important than an ability to categorise and reproduce disconnected pieces of knowledge. "(Learning to Teach in Higher Education, Routledge, London, 1992, p.133) How To Use Social Media In Education (Part 2 of 2) (this is a continuation from yesterday’s article about barriers to using social media in education) The first step towards applying social media into education starts with empowering teachers by giving them freedom to use social media to engage with students and giving them the freedom to come-up with innovative ways of teaching using technology.
On the contrary, let’s talk about few practical ways on how many educators apply social media to flip the conventional teaching model and make classroom & home work experience meaningful to for the students. YouTube The average teacher impacts about 3,000 students in his or her lifetime. Imagine what could happen when you inspire 3,000 individuals or perhaps 300,000 students. Ask your students what they would prefer – Lectures of their teachers teaching them in the real classroom, or Videos of the same lectures on their computers, Macs, iPads or Smartphone devices. Facebook Twitter Twitter Tips Instagram When kids are engaged, they learn better. Mobile Learning: Cell Phones meet the English Classroom. Illinois Online Network: Educational Resources. Welcome to the Rubric for Online Instruction (ROI) - Rubric for Online Instruction.
California State University, Chico's first strategic priority is "...to develop high-quality learning environments both inside and outside the classroom.
" The Rubric for Online Instruction (ROI) is a tool that can be used to create or evaluate the design of a fully online or blended course. The rubric is designed to answer the question, "What does high-quality online instruction look like? " The ROI can be applied to any course with online elements. It represents a developmental process for online course design rather than a guide to make curriculum or technology choices. The ROI was constructed to promote course assessment based on University expectations, to guide course redesign using instructional design principles, and to recognize instructors who have developed expertise in online instruction. The ROI was developed by a consortium of CSU, Chico educators who wished to build and share a tool to assist in the design and evaluation of online or blended courses.
Education 3.0 and the Pedagogy (Andragogy, Heutagogy) of Mobile Learning. The evolution of the web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 and now to Web 3.0 can be used a metaphor of how education should also be evolving, as a movement based on the evolution from Education 1.0 to Education 3.0.
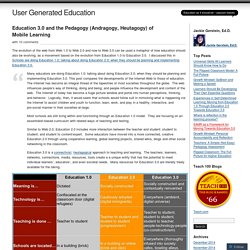
I discussed this in Schools are doing Education 1.0; talking about doing Education 2.0; when they should be planning and implementing Education 3.0. Many educators are doing Education 1.0; talking about doing Education 2.0; when they should be planning and implementing Education 3.0. This post compares the developments of the Internet-Web to those of education. The Internet has become an integral thread of the tapestries of most societies throughout the globe. The web influences people’s way of thinking, doing and being; and people influence the development and content of the web. Source: