

Probability distribution. In applied probability, a probability distribution can be specified in a number of different ways, often chosen for mathematical convenience: A probability distribution can either be univariate or multivariate.
A univariate distribution gives the probabilities of a single random variable taking on various alternative values; a multivariate distribution (a joint probability distribution) gives the probabilities of a random vector—a set of two or more random variables—taking on various combinations of values.
Distribution Measures. Negative binomial distribution. In probability theory and statistics, the negative binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of independent and identically distributed Bernoulli trials before a specified (non-random) number of failures (denoted r) occurs.
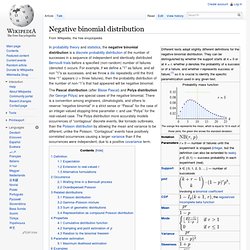
For example, if we define a "1" as failure, and all non "1"s as successes. and we throw a die repeatedly until the third time “1” appears (r = three failures), then the probability distribution of the number of non-“1”s that had appeared will be negative binomial. The Pascal distribution (after Blaise Pascal) and Polya distribution (for George Pólya) are special cases of the negative binomial.
There is a convention among engineers, climatologists, and others to reserve “negative binomial” in a strict sense or “Pascal” for the case of an integer-valued stopping-time parameter r, and use “Polya” for the real-valued case. Definition[edit] The probability mass function of the negative binomial distribution is.