

Genel bilgi. GIMP. GIMP ( /ɡɪmp/ GHIMP) (GNU Image Manipulation Program) is a free and open-source raster graphics editor[8] used for image retouching and editing, free-form drawing, converting between different image formats, and more specialized tasks.
GIMP is released under GPLv3+ licenses and is available for Linux, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. History[edit] The number of computer architectures and operating systems supported has expanded significantly since its first release. The first release supported UNIX systems, such as Linux, SGI IRIX and HP-UX.[9][14] Since the initial release, GIMP has been ported to many operating systems, including Microsoft Windows and macOS; the original port to the Windows 32-bit platform was started by Finnish programmer Tor M.
Lillqvist (tml) in 1997 and was supported in the GIMP 1.1 release.[14] Following the first release GIMP was quickly adopted and a community of contributors formed. Comparison of raster graphics editors. Comparison of raster graphics editors. Raster graphics editors can be compared by many variables, including availability.
List[edit] General information[edit] Comparison of vector graphics editors. A number of vector graphics editors for various platforms exist.
Potential users of these editors will make a decision based on factors such as the availability for the user's platform, the feature set, usability of the user interface (UI) and the focus of the program. Some programs are more suitable for artistic work while others are better for technical drawings. Another important factor is the application's support of various vector and bitmap image formats for import and export. Some editors in detail[edit] The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of vector graphics editors. General information[edit] Graphic art software. A screenshot of Karbon14 vector graphic software running on an AegeanLinux desktop.
A screenshot of the GIMP 2.2.8 raster graphic software.
Color. Pixel. Camera. Image editing. A colorized version of originally black and white photo, colorized using GIMP This is a photo that has been edited as a Bokeh effect, using a Gaussian blur.
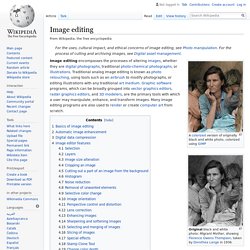
Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs, or editing illustrations with any traditional art medium. Demoscene. Concept[edit] History[edit] The earliest computer programs that have some resemblance to demos and demo effects can be found among the so-called display hacks.
Display hacks predate the demoscene by several decades, with the earliest examples dating back to the early 1950s. Demos in the demoscene sense began as software crackers' "signatures", that is, crack screens and crack intros attached to software whose copy protection was removed. The first crack screens appeared on the Apple II computers in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and they were often nothing but plain text screens crediting the cracker or his group. Graphics display resolution. "WXGA" redirects here.
For the television station, see WXGA-TV. Overview by vertical resolution and aspect ratio[edit] Aspect ratio[edit] Multiple display standards compared. The favored aspect ratio of mass market display industry products has changed gradually from 4:3, then to 16:10, and then to 16:9, and now 21:9. The 4:3 aspect ratio was common in older television cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, which were not easily adaptable to a wider aspect ratio. Also in 2013, displays with 2560×1080 (aspect ratio 64:27 or 2.370, however commonly referred to as "21:9" for easy comparison with 16:9) appeared, which closely approximate the common CinemaScope movie standard aspect ratio of 2.35–2.40.
The computer display industry maintained the 16:10 aspect ratio longer than the entertainment industry, but in the 2005–2010 period, computers were increasingly marketed as dual use products, with uses in the traditional computer applications, but also as means of viewing entertainment content. Graphics. Graphics can be functional or artistic.
Vector graphics. Example showing effect of vector graphics versus raster graphics.
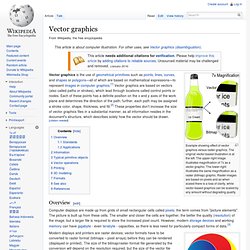
The original vector-based illustration is at the left. The upper-right image illustrates magnification of 7x as a vector graphic. The lower-right illustrates the same magnification as a raster (bitmap) graphic. Raster images are based on pixels and so when scaled there is a loss of clarity, while vector-based graphics can be scaled by any amount without degrading quality. Overview[edit] Computer displays are made up from grids of small rectangular cells called pixels; the term comes from "picture elements". Raster graphics. The smiley face in the top left corner is a bitmap image.
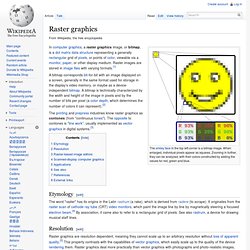
When enlarged, individual pixels appear as squares. Zooming in further, they can be analyzed, with their colors constructed by adding the values for red, green and blue. In computer graphics, a raster graphics image, or bitmap, is a dot matrix data structure representing a generally rectangular grid of pixels, or points of color, viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium. Raster images are stored in image files with varying formats.[1] A bitmap corresponds bit-for-bit with an image displayed on a screen, generally in the same format used for storage in the display's video memory, or maybe as a device-independent bitmap.