

Memento mori. Earthly Vanity and Divine Salvation by Hans Memling.
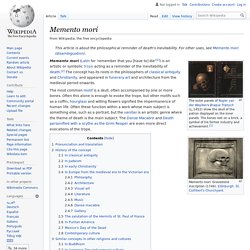
This triptych contrasts earthly beauty and luxury with the prospect of death and hell. The outer panels of Rogier van der Weyden's Braque Triptych shows the skull of the patron displayed in the inner panels. Japanese Zen Buddhist Philosophy. 1.

The Meaning of the Term Zen The designation of this school of the Buddha-Way as Zen, which means sitting meditation, is derived from a transliteration of the Chinese word Chán. Because the Chinese term is in turn a transliteration of the Sanskrit term dhyāna, however, Zen owes its historical origin to early Indian Buddhism, where a deepened state of meditation, called samādhi, was singled out as one of the three components of study a Buddhist was required to master, the other two being an observation of ethical precepts (sīla) and an embodiment of nondiscriminatory wisdom (prajñā).
Meditation was picked as the name for this school because the historical Buddha achieved enlightenment (nirvāna) through the practice of meditation. In the context of Zen Buddhism, the perfection of nondiscriminatory wisdom (Jpn.: hannya haramitsu; Skrt.: prajñāpāramitā) designates practical, experiential knowledge. Laughter is the Best Medicine: The Health Benefits of Humor and Laughter. Value Theory. 1.

Basic Questions The theory of value begins with a subject matter. It is hard to specify in some general way exactly what counts, but it certainly includes what we are talking about when we say any of the following sorts of things: Well-Being. 1.
The Concept Popular use of the term ‘well-being’ usually relates to health. A doctor’s surgery may run a ‘Women’s Well-being Clinic’, for example. Philosophical use is broader, but related, and amounts to the notion of how well a person’s life is going for that person. The Meaning of Life. 1.
The Meaning of “Meaning” One part of the field of life's meaning consists of the systematic attempt to clarify what people mean when they ask in virtue of what life has meaning. This section addresses different accounts of the sense of talk of “life's meaning” (and of “significance,” “importance,” and other synonyms). A large majority of those writing on life's meaning deem talk of it centrally to indicate a positive final value that an individual's life can exhibit. That is, comparatively few believe either that a meaningful life is a merely neutral quality, or that what is of key interest is the meaning of the human species or universe as a whole (for discussions focused on the latter, see Edwards 1972; Munitz 1986; Seachris 2009). Jean-Paul Sartre. 1.

Philosophical Development Sartre was born in Paris where he spent most of his life. Friedrich Nietzsche. 1.
Life: 1844–1900 In the small German village of Röcken bei Lützen, located in a rural farmland area southwest of Leipzig, Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche was born at approximately 10:00 a.m. on October 15, 1844. The date coincided with the 49th birthday of the Prussian King, Friedrich Wilhelm IV, after whom Nietzsche was named, and who had been responsible for Nietzsche's father's appointment as Röcken's town minister. COMMENTARY: THE IMPACT OF NIETZSCHE ON FREUD : The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. What Is the Unconscious? By Kendra Cherry Definition: In Freud's psychoanalytic theory of personality, the unconscious mind is a reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that outside of our conscious awareness.

Most of the contents of the unconscious are unacceptable or unpleasant, such as feelings of pain, anxiety, or conflict. According to Freud, the unconscious continues to influence our behavior and experience, even though we are unaware of these underlying influences. Reevaluating 'Dr. Fox Effect,' Study Finds Students Can Spot a Nonsensical Lesson - Inside School Research. A pair of Israeli researchers have re-opened the question of "what does the Fox say?
" In an article published earlier this year in the peer-reviewed Journal of Educational Psychology, Eyal Peer and Elisha Babad reached new conclusions when they recreated an old but famous psychological experiment known as "the Dr. Fox lecture. " Affective blindsight. Capgras Syndrome - Delusions and The Brain. This movie clip shows exerts from TV shows and movies displaying the severity of Capgras Syndrome.
Capgras syndrome is defined as "the belief that someone emotionally close to you- in many cases, this is your spouse, sometimes also other family members- have vanished and been replaced by a stranger” 2. This is a serious delusional disorder, typically caused by trauma to the brain. Without treatment, patients with this disorder can be extremely dangerous. As seen in the movie clip, it is crucial that these patients receive treatment so they do not hurt anyone.
Capgras syndrome can be tested by the skin conductive response (SCR), which is used to detect responses in the autonomic nervous system. How Sleep Deprivation Fries Your Hormones, Your Immune System, and Your Brain. “I can sleep when I’m dead!” “The early bird gets the worm.” Ever said either of those things to yourself? Or do you no longer have to say these things to yourself because you run on four to five hours of sleep pretty much every night? You’re used to it. What is Serotonin? What Does Serotonin Do? Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) is a chemical found in the human body. It carries signals along and between nerves - a neurotransmitter. It is mainly found in the brain, bowels and blood platelets. Serotonin is thought to be especially active in constricting smooth muscles, transmitting impulses between nerve cells, regulating cyclic body processes and contributing to wellbeing and happiness.1 Serotonin is regarded by some researchers as a chemical that is responsible for maintaining mood balance, and that a deficit of serotonin leads to depression.
The word serotonin comes from its discovery when it was isolated in 1948 by Maurice M. What is serotonin? What does serotonin do? Amygdala. Figure 1: Location of amygdala in the brain (reproduced from Wikipedia under GFDL). The amygdaloid region of the brain (i.e. the amygdala) is a complex structure involved in a wide range of normal behavioral functions and psychiatric conditions. Not so long ago it was an obscure region of the brain that attracted relatively little scientific interest. Today it is one of the most heavily studied brain areas, and practically a household word. This article will summarize the anatomical organization of the amygdala and its functions. The Amygdala: The Body’s Alarm Circuit. You must make an oral presentation in front of your peers. As you take your place before the group, your heart pounds in your chest, your palms become sweaty, and your knees shake uncontrollably.
In short, you are stricken with fear, a strong emotion caused by the threat of danger or something unwelcome happening. TheDEA.org: Your Brain. Stoicism. 1. Sources of our information on the Stoics Since the Stoics stress the systematic nature of their philosophy, the ideal way to evaluate the Stoics' distinctive ethical views would be to study them within the context of a full exposition of their philosophy. Here, however, we meet with the problem about the sources of our knowledge about Stoicism. We do not possess a single complete work by any of the first three heads of the Stoic school: the ‘founder,’ Zeno of Citium in Cyprus (344–262 BCE), Cleanthes (d. 232 BCE) or Chrysippus (d. ca. 206 BCE). Oxytocin: What Is It? What Does It Do? Neurotransmitters, Depression and Anxiety - Kellevision. Adrenaline Levels and Depression: Epinephrine as an Antidepressant? Emotions, Judgments, and Mattering. What's the Difference Between Emotion, Feeling, Mood?Six Seconds.
Drive theory. What Are Emotions? Anesthesia and hypoxia. Ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Nucleus accumbens : Bipolar Network News. Overview of the Central Nervous System (Gross Anatomy of the Brain) Part 3. Fear Conditioning: How the Brain Learns about Danger - Brain Connection. The Capilano Suspension Bridge experiment - All Men are Liars - Executive Style - <! Quiz: The 36 Questions That Lead to Love. Your Amygdala Doesn't Want You to Find Love. - A Weapon of Mass Seduction. The Amygdala & Emotions. How love grows in your body. Norepinephrine. Epinephrine. Emotion Induction After Direct Intracerebral Stimulations of Human Amygdala. Amygdala. The Amygdala in 5 Minutes. Limbic System: Amygdala (Section 4, Chapter 6) Neuroscience Online: An Electronic Textbook for the Neurosciences. Cortisol: Why “The Stress Hormone” Is Public Enemy No. 1.
Cortisol. Dr. Fox effect. When It Comes to Love, Do You Really Know What You Want? For Couples, Time Can Upend the Laws of Attraction. Obsessed. Is Sex Ever Morally Unacceptable? The Danger of Trying to Possess Who You Love. Why We Want Who We Want.