

7.2 MENDEL'S GENETICS, LINKAGE, AND THE MOUSE. 7.2.1 Historical overview By the time the chemical nature of the gene was uncovered, genetics was already a mature science.

In fact, Mendel's formulation of the basic principles of heredity was not even dependent on an understanding of the fact that genes existed within chromosomes. Rather, the existence of genes was inferred solely from the expression in offspring of visible traits at predicted frequencies based on the traits present in the parental and grandparental generations. Today, of course, the field of genetics encompasses a broad spectrum of inquiry from molecular studies on gene regulation to analyses of allele frequencies in natural populations, with many subfields in between. To distinguish the original version of genetics — that of Mendel and his followers — from the various related fields that developed later, several terms have been coined including "formal" genetics, "transmission" genetics, or "classical" genetics. 7.2.2 Linkage and recombination.
Maternal Inheritance and Maternal Effects. The classic study of maternal inheritance was performed by Correns on the four o'clock plant.
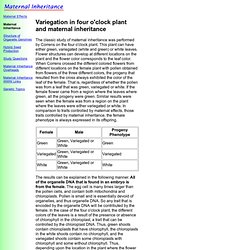
This plant can have either green, variegated (white and green) or white leaves. Flower structures can develop at different locations on the plant and the flower color corresponds to the leaf color. When Correns crossed the different colored flowers from different locations on the female plant with pollen obtained from flowers of the three different colors, the progeny that resulted from the cross always exhibited the color of the leaf of the female. That is, regardless of whether the pollen was from a leaf that was green, variegated or white. If the female flower came from a region where the leaves where green, all the progeny were green. The results can be explained in the following manner. Copyright © 1997. Maternal Inheritance and Maternal Effects.
The embryo is formed when a female gamete unites with a male gamete.

In the vast majority of species, the female gamete is physically larger than the male gamete and provides the cytoplasm for the developing embryo. Within this cytoplasm are factors that were released by the nuclear genes of the female. Those factors may have specific effects upon the developing embryo. The female cytoplasm also contributes the mitochondria for all species as well as the chloroplast for plant species. These two organelles contain DNA and control certain traits in the offspring. The classic phenotype which exhibits maternal effects is coiling direction of snail shells. These results at first glance appear to be at odds with Mendel's laws.
How can this result be explained? Right-coiled shell: s+s+ Left-coiled shell: ss The next observation is that the phenotype of the F1 generation is always that of the female parent. Copyright © 1998. Introduction to Linkage Mapping. Example 1: Two Point Cross How do you tell your genes are linked?

How do you identify the parental linkage? How do you calculate linkage map distance? Mating: AaBb x aabb Where: A = Long antennae a = Short antennae B = Green eyebrows, and b = Blue eyebrows. How do you tell your genes are linked? If the genes were independent, using standard genetic techniques you would predict that your offspring would have the phenotypic ratio: 1 Long Green : 1 Long Blue : 1 Short Green : 1 Short Blue Given 2000 offspring, that would mean 500 of each of these phenotypic classes. Say you make this mating, and your actual results look like this: Long Green - 850 Long Blue - 150 Short Green - 150 Short Blue - 850 Obviously not 500 of each, and not close enough to be explained by chance variation.
What are the parental linkages? The only parent that matters for figuring things out in this cross is the AaBb parent. There are two ways these alleles could be linked in this parent. How do you calculate linkage map distance?