

What is a Magnet? What makes a magnet? Magnetic Fields & Magnetic Force. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined electromagnetic force.

It refers to physical phenomena arising from the force caused by magnets, objects that produce fields that attract or repel other objects. A magnetic field exerts a force on particles in the field due to the Lorentz force, according to Georgia State University's HyperPhysics website. The motion of electrically charged particles gives rise to magnetism.
The force acting on an electrically charged particle in a magnetic field depends on the magnitude of the charge, the velocity of the particle, and the strength of the magnetic field. All materials experience magnetism, some more strongly than others. How the King of Snakes Makes a Meal Out of Rival Serpents | Video The kingsnake triumphs over larger, rival serpents by squeezing them to death with its powerful constriction. Magnetic fields are generated by rotating electric charges, according to HyperPhysics. The Earth itself is a giant magnet. Additional resources. Magnetism. A magnetic quadrupole Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that includes forces exerted by magnets on other magnets. It has its origin in electric currents and the fundamental magnetic moments of elementary particles.
These give rise to a magnetic field that acts on other currents and moments. All materials are influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The strongest effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. The magnetic state (or phase) of a material depends on temperature (and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field) so that a material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism depending on its temperature, etc. History[edit] In ancient China, the earliest literary reference to magnetism lies in a 4th-century BC book named after its author, The Master of Demon Valley (鬼谷子): "The lodestone makes iron come or it attracts it Michael Faraday, 1842. Magnetism. ONDES & MAGNETISME - Pearltrees voisins (sources) Electricity and Magnetism. K&J Magnetics - Magnetic Field Visualization. MAGCRAFT&174; Brand Neodymium Rare Earth Magnets. Lévitation Magnétique.
For years, NASA has been researching the possibility of using the high speeds of maglev transportation to fling spacecraft into low Earth orbit.

"It would really open up space to human exploration and commercialization," Powell says. "It's something we can't do now because it's too expensive. " Powell and his colleagues have proposed two generations of space launching technology. The first is a cargo-only launch track that could be built into a mountainside to reach a height of 20,000 feet.
Magnets could allow a spacecraft traveling along the track to reach speeds around 18,000 miles per hour—enough to fly into space. And that's just the first generation. Levitation. Magnetic Child Discovered In Croatia 2011 Mystery History TV. Ami G Show - Ivkovic Bogdan - Cudo od deteta - RTV Pink (Magneto) Magneto Boy. Magnetic. Electricity,Magnetism and Optics by Professor Walter Lewin - Free Physics Video Lectures. Électro-magnétisme. Relativity of Electric and Magnetic Fields. Previous home next Michael Fowler, University of Virginia A Magnetic Puzzle… Suppose we have an infinitely long straight wire, having a charge density of electrons of coulombs per meter, all moving at speed to the right (recall typical speeds are centimeters per minute) and a neutralizing fixed background of positive charge, also of course coulombs per meter.
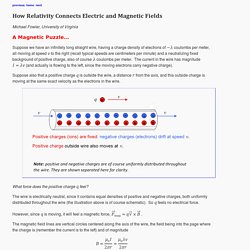
The current in the wire has magnitude (and actually is flowing to the left, since the moving electrons carry negative charge). Suppose also that a positive charge is outside the wire, a distance from the axis, and this outside charge is moving at the same exact velocity as the electrons in the wire. What force does the positive charge feel? The wire is electrically neutral, since it contains equal densities of positive and negative charges, both uniformly distributed throughout the wire (the illustration above is of course schematic). However, since is moving, it will feel a magnetic force, Magnetic Motor.