

Milankovitch cycles. Is the calculated daily-averaged insolation at the top of the atmosphere, on the day of the summer solstice at 65 N latitude.— Benthic forams and — Vostok ice core show two distinct proxies for past global sealevel and temperature, from ocean sediment and Antarctic ice respectively.
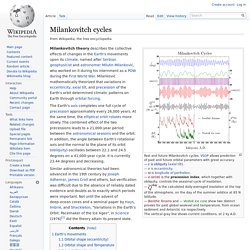
The vertical gray line shows current conditions, at 2 ky A.D. The Earth's axis completes one full cycle of precession approximately every 26,000 years. At the same time, the elliptical orbit rotates more slowly. The combined effect of the two precessions leads to a 21,000-year period between the astronomical seasons and the orbit. In addition, the angle between Earth's rotational axis and the normal to the plane of its orbit (obliquity) oscillates between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees on a 41,000-year cycle.
Earth’s movements[edit] Orbital shape (eccentricity)[edit] Circular orbit, no eccentricity. Orbit with 0.5 eccentricity. Orbital shape and Temperature[edit] Axial tilt (obliquity)[edit] Axial precession[edit] Is Global Warming Part of Earth's Natural Cycle: MIT Team Says "Yes" -A Galaxy Insight. A team of MIT scientists recorded a nearly simultaneous world-wide increase in methane levels -the first increase in ten years.

What baffles the team is that this data contradicts theories stating humans are the primary source of increase in greenhouse gas. It takes about one full year for gases generated in the highly industrial northern hemisphere to cycle through and reach the southern hemisphere. Since all worldwide levels rose simultaneously throughout the same year, however, it is probable that this may be part of a natural cycle - and not the direct result of man's contributions. MIT's Matthew Rigby and Ronald Prinn, the TEPCO Professor of Atmospheric Chemistry in MIT's Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Science, state that this imbalance has resulted in several million metric tons of additional methane in the atmosphere. Methane accounts for roughly one-fifth of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, though its effect is 25x greater than that of carbon dioxide. New Evidence: Earth's Natural Cooling Cycle.
New evidence from deep-sea cores shows that the earth's climate cools significantly and abruptly in a naturally occurring 1,000- to 3,000-year cycle, a scientist at Columbia's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory reported recently.

The evidence shows that abrupt coolings occurred not only during the ice ages, but also during the current warmer period--long after most ice sheets disappeared and conditions on earth more closely resembled today's. Regularly spaced layers of rocky fragments in ocean sediments revealed the rapid cooling cycle, the most recent yet discovered.
The findings were reported at the American Geophysical Union's fall meeting in San Francisco by Gerard Bond, a paleoclimatologist at Lamont-Doherty, Columbia's earth sciences research institute in Palisades, N.Y. The discovery of warming and cooling cycles in the modern era adds a new factor in predicting future global climate change. "If this is indeed a regular climate rhythm, it is still going on today," Bond said.