

Homeostasis. IB Chemistry Review: Option D: Drugs and Medicines (HL) IB Biology Evolution. IB Bio Evolution flashcards. Ib bio hl paper 2 past papers - 6 ebooks - free download. Bio 2: Past IB Questions flashcards. Www.xtremepapers.com/papers/AQA/Human Biology/2005 Jun/AQA-BYA5-W-QP-JUN05.pdf. 172 Questions on Respiration. Respiration - Biology Innovation. Respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place with in the cells of organisms.
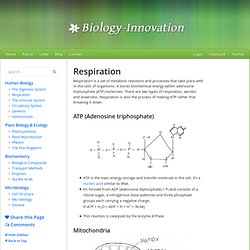
It stores biochemical energy within adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules. There are two types of respiration, aerobic and anaerobic. Respiration is also the process of making ATP rather that breaking it down. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) ATP is the main energy storage and transfer molecule in the cell. Li>ATP + H2O = ADP + Pι + H+ = 30.6Kj This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme ATPase Mitochondria The diagram above shows the usual mitochondria which would be found in a eukaryotic cell. 1.
The conversion to phosphorylated is simply to make it more reactive and the conversion to sugar phosphate easier. This is the first stage of three in respiration and takes place within the cytoplasm of the cell.Glycolysis is the same process for aerobic and anaerobic respiration.In this process the cell gains a net of 2 ATP molecules. 2. 3. 3. Anaerobic Respiration The Respiring of Fats and Proteins. IB Biology Notes - Cell Respiration HL. Oxidation involves the loss of electrons from an element, whereas reduction involves the gain of electrons and that oxidation frequently involves gaining oxygen or losing hydrogen, whereas reduction frequently involves losing oxygen or gaining hydrogen.
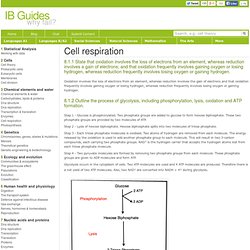
Step 1 - Glucose is phosphorylated. Two phosphate groups are added to glucose to form hexose biphosphate. These two phosphate groups are provided by two molecules of ATP. Step 2 - Lysis of hexose biphosphate. Hexose biphosphate splits into two molecules of triose phosphate. Step 3 - Each triose phosphate molecules is oxidised. Step 4 - Two pyruvate molecules are formed by removing two phosphate groups from each molecule. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. Figure 8.1.1 - Steps in glycolysis Figure 8.1.2 - Labelled diagram of a mitochondrion Aerobic Respiration Glycolysis can take place without oxygen. Occ.ibo.org/ibis/documents/dp/gr4/biology/d_4_biolo_gui_0903_1. IB Biology. IB Biology Review Guide A Free Online Study Guide The initial list of links are appropriate for those currently on IB Biology courses.
However there is a new syllabus with first teaching in August 2014 (first exam 2016). Therefore the content of the syllabus (below) as listed after the resources link are now nothing more than a historical record of the pre-2009 syllabus. Authorised copies of the IB Syllabus can be obtained from the International Baccalaureate or viewed here on the web. Resources for current students of IB Biology: Click4biology by John BurrellOpen Door by Paul Billieti-Biology by Stephen Taylor[1] by Stephanie Castle is a Youtube series of screen and videocasts[2]for students in a hurry[3] also by Stephen Taylor and for assistance with the Internal Assessment go to Lab Banks again by Stephen Taylor.
Very Old Syllabus Introduction to the Guide How to use this Guide Study Guide Core (SL/HL) Chapter 1 ~ Topic 1 Cells Chapter 2 ~ The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 ~ Genetics Types of Defense. Www.courseworkbank.info/courseworkbank.info.php?f=R0NTRS9CaW9sb2d5L0FuIGV4cGVyaW1lbnQgdG8gZGV0ZXJtaW5lIHRoZSBlZmZlY3Qgb2YgbGlnaHQgaW50ZW5zaXR5IG9uIHBob3Rvc3ludGhlc2lzLnBkZg==