Primary biliary cirrhosis. Primary biliary cirrhosis, often abbreviated PBC, is an autoimmune disease of the liver[1][2] marked by the slow progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, with the intralobular ducts (Canals of Hering) affected early in the disease.[3] When these ducts are damaged, bile builds up in the liver (cholestasis) and over time damages the tissue.
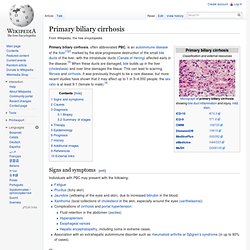
This can lead to scarring, fibrosis and cirrhosis. It was previously thought to be a rare disease, but more recent studies have shown that it may affect up to 1 in 3–4,000 people; the sex ratio is at least 9:1 (female to male).[4] Signs and symptoms[edit] Individuals with PBC may present with the following: Causes[edit] Generalisierte Angststörung.
Generalized anxiety disorder. Causes[edit] Genetics[edit] Generalized anxiety disorder may be hereditary with it running in families.[9] Genetics seem to play a role in this; those with genetic predisposition are more likely to develop GAD, usually in response to a life stressor.[10] Substance induced[edit] Long-term use of benzodiazepines can worsen underlying anxiety,[11][12] with evidence that reduction of benzodiazepines can lead to a lessening of anxiety symptoms.[13] Similarly, long-term alcohol use is associated with anxiety disorders,[14] with evidence that prolonged abstinence can result in a disappearance of anxiety symptoms.[15] However, it can take up to 2 years for anxiety symptoms to return to baseline in about a quarter of people recovering from alcoholism.[16]