

Deutsche Diabetes Gesellschaft: Home. International Diabetes Federation. Life for a Child News The Programme Saving the lives of children in developing countries Donate Give the gift of life to a child Partners Helping Life for a Child save lives Education Resources For children and adolescents Life for a Child film series Showcasing the work of the Programme YouTube Channel.
International Diabetes Federation. Latest Issue March 2014 Voice Box The Diabetes Voice Inbox Readership survey Take a minute to fill in our survey Subscribe Now Receive all issues free of charge Currently in DRCP The latest from IDF's Official Journal On the bookshelf.
International Diabetes Federation. World Diabetes Day. Logo for World Diabetes Day World Diabetes Day is the primary global awareness campaign of the diabetes world and is held on November 14 of each year.
It was introduced in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation and the World Health Organization in response to the alarming rise of diabetes around the world. World Diabetes Day is a campaign that features a new theme chosen by the International Diabetes Federation each year to address issues facing the global diabetes community. While the campaigns last the whole year, the day itself marks the birthday of Frederick Banting who, along with Charles Best, first conceived the idea which led to the discovery of insulin in 1922. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice - Home. Diabetes Atlas. Deutscher Diabetiker Bund, Landesverband Hessen e. V.
Deutsche Diabetes-Gesellschaft. DiabetesDE – Deutsche Diabetes-Hilfe. Logo der Organisation Die gemeinnützige Organisation diabetesDE – Deutsche Diabetes-Hilfe vereint als Dachverband Menschen mit Diabetes und Berufsgruppen, die sich mit Diabetes beschäftigen.
Dazu gehören Ärzte und Wissenschaftler, Diabetesberater, Psychologen und Podologen. International Diabetes Federation. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) is a worldwide alliance of over 230 national diabetes associations in more than 160 countries, who have come together to enhance the lives of people with diabetes everywhere.
The Federation is committed to raising global awareness of diabetes, promoting appropriate diabetes care and prevention, and encouraging activities towards finding a cure for the different types of diabetes. The Federation has been leading the global diabetes community since 1950. It is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. IDF is divided into seven regions, with the aim of strengthening the work of national diabetes associations and enhancing the collaboration between them. Diabetes renalis. Als Diabetes renalis wird eine Funktionsstörung der Niere bezeichnet, die durch eine dauerhafte Ausscheidung von Glucose im Urin (Glucosurie) bei normaler Glucosetoleranz und nicht erhöhtem Blutzuckerspiegel gekennzeichnet ist.
Synonyme Namen sind Diabetes innocens, Diabetes innocuus, Nierendiabetes, Nierenharnruhr, Normoglykämische Glucosurie oder Primäre renale Glucosurie. Das Symptombild des Diabetes renalis wurde erstmals 1895 beschrieben. Der Schweizer Kinderarzt Guido Fanconi prägte 1931 die Bezeichnung Familiäre renale Glucosurie. Neben dem angeborenen Diabetes renalis gibt es darüber hinaus auch erworbene und vorübergehende Formen.
Da diese Störung im Regelfall nahezu symptomlos und damit für die Patienten beschwerdefrei bleibt und keine Spätfolgen bekannt sind, ist eine Therapie im Regelfall nicht notwendig. Renal glycosuria. Diagnosis[edit] A doctor normally can diagnose renal glycosuria when a routine urine test (Urinalysis) detects glucose in the urine, while a blood test indicates that the blood glucose level is normal.
Presentation[edit] In most affected individuals, the condition causes no apparent symptoms (asymptomatic) or serious effects. When renal glycosuria occurs as an isolated finding with otherwise normal kidney function, the condition is thought to be inherited as an autosomal recessive trait[citation needed]. Genetics[edit] It is associated with SLC5A2, coding the sodium glucose cotransporter 2. Synonyms[edit] Benign glycosuriaFamilial renal glycosuriaNondiabetic glycosuriaPrimary renal glycosuriaDiabetes renalisRenal diabetesDiabetes innocence. Diabetes renalis. Diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a condition characterized by excessive thirst and excretion of large amounts of severely diluted urine, with reduction of fluid intake having no effect on the concentration of the urine.
There are different types of DI, each with a different set of causes. The most common type in humans is the neurological form, called Central DI (CDI), which involves a deficiency of arginine vasopressin (AVP), also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH). The second common type of DI is nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI), which is due to kidney or nephron dysfunction caused by an insensitivity of the kidneys or nephrons to ADH. DI can also be gestational, or present as an iatrogenic artifact of alcohol or some types of drug abuse. DI should not be confused with nocturia. Diabetes insipidus. Gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes (or gestational diabetes mellitus, GDM) is a condition in which women without previously diagnosed diabetes exhibit high blood glucose levels during pregnancy (especially during their third trimester).
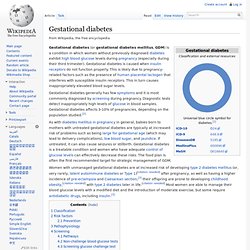
Gestational diabetes is caused when insulin receptors do not function properly. This is likely due to pregnancy-related factors such as the presence of human placental lactogen that interferes with susceptible insulin receptors. This in turn causes inappropriately elevated blood sugar levels. As with diabetes mellitus in pregnancy in general, babies born to mothers with untreated gestational diabetes are typically at increased risk of problems such as being large for gestational age (which may lead to delivery complications), low blood sugar, and jaundice.
If untreated, it can also cause seizures or stillbirth. Classification[edit] Schwangerschaftsdiabetes. Der Schwangerschaftsdiabetes, auch als Gestationsdiabetes, GDM oder Typ-4-Diabetes bezeichnet, ist definiert als eine erstmals in der Schwangerschaft diagnostizierte Glucose-Toleranzstörung.
In seltenen Fällen kann es sich um einen neu aufgetretenen Diabetes -Typ 1 oder -Typ 2 handeln. Beim typischen Gestationsdiabetes tritt nach der Geburt bei den meisten Frauen wieder ein normaler Zuckerstoffwechsel auf.[1] Der Gestationsdiabetes zählt insgesamt zu den häufigsten schwangerschaftsbegleitenden Erkrankungen. Diabetes mellitus. Type 1 DM results from the pancreas' failure to produce enough insulin. This form was previously referred to as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or "juvenile diabetes". The cause is unknown.[3]Type 2 DM begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly.[3] As the disease progresses a lack of insulin may also develop.[6] This form was previously referred to as "non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes". The primary cause is excessive body weight and not enough exercise.[3]Gestational diabetes, is the third main form and occurs when pregnant women without a previous history of diabetes develop a high blood sugar level.[3] Prevention and treatment involve a healthy diet, physical exercise, not using tobacco and being a normal body weight.
Blood pressure control and proper foot care are also important for people with the disease. Signs and symptoms. Diabetes mellitus. Der Diabetes mellitus (DM) („honigsüßer Durchfluss“, griechisch διαβήτης, von altgriechisch διαβαίνειν diabainein, „hindurchgehen“, „hindurchfließen“ und lateinisch mellitus „honigsüß“), umgangssprachlich kurz: Diabetes oder Zuckerkrankheit ist die Bezeichnung für eine Gruppe von Stoffwechselkrankheiten. Das Wort beschreibt deren Hauptsymptom, die Ausscheidung von Zucker im Urin.
In der Antike wurde die Diagnose durch eine Geschmacksprobe des Urins gestellt, denn der Harn von Personen mit Diabetes weist bei erhöhtem Blutzuckerspiegel einen süßlichen Geschmack auf. Diabetes mellitus.