

Magic sand. Trimethylsilanol These properties are achieved by covering ordinary beach sand, which contains tiny particles of pure silica, and exposing them to vapors of trimethylsilanol (CH3)3SiOH, an organosilicon compound.
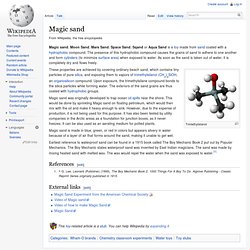
Upon exposure, the trimethylsilane compound bonds to the silica particles while forming water. The exteriors of the sand grains are thus coated with hydrophobic groups. Magic sand was originally developed to trap ocean oil spills near the shore. This would be done by sprinkling Magic sand on floating petroleum, which would then mix with the oil and make it heavy enough to sink. Magic sand is made in blue, green, or red in colors but appears silvery in water because of a layer of air that forms around the sand, making it unable to get wet. Earliest reference to waterproof sand can be found in a 1915 book called The Boy Mechanic Book 2 put out by Popular Mechanics. References[edit] Jump up ^ G. Waste container. Litter bin redirects here.
For a place for pet animals to 'go to the toilet' in, see litter box. A waste container is a container for temporarily storing waste, and is usually made out of metal or plastic. Common terms are dustbin, rubbish bin, litter bin, garbage can, trash can, trash bin, dumpster, waste basket, waste paper basket, waste receptacle, container bin, bin and kitchen bin. The words "rubbish", "basket" and "bin" are more common in British English usage; "trash" and "can" are more common in American English usage.
Immersion diuresis. Immersion diuresis is a type of diuresis caused by immersion of the body in water (or equivalent liquid).
It is mainly caused by lower temperature and by pressure. The temperature component is caused by water drawing heat away from the body and causing vasoconstriction of the cutaneous blood vessels within the body to conserve heat.[1][2][3] The body detects an increase in the blood pressure and inhibits the release of vasopressin (also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH)), causing an increase in the production of urine. The pressure component is caused by the hydrostatic pressure of the water directly increasing blood pressure. Its significance is indicated by the fact that the temperature of the water doesn't substantially affect the rate of diuresis.[4] Partial immersion of only the limbs does not cause increased urination.
See also[edit] Cold-induced diuresis References[edit] Further reading[edit] Sputum culture. In a hospital setting, a sputum culture is most commonly ordered if a patient has a pneumonia.
The Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends that sputum cultures be done in pneumonia requiring hospitalization, while the American College of Chest Physicians does not. One reason for such a discrepancy is that normal, healthy lungs have bacteria, and sputum cultures collect both normal and pathogenic bacteria. Vaginal discharge. Vaginal discharge is a term given to biological fluids contained within or expelled from the vagina.
It can be of various colors, usually whitish, yellowish or greenish. While most discharge is normal and can reflect the various stages of the menstrual cycle, some discharge can be a result of an infection, such as a sexually transmitted disease. The term blennorrhea is often used to designate mucus discharge from the urethra or vagina,[2] while blennorrhagia designates an excess of such discharge,[3] often specifically referring to that seen in gonorrhea. Jump up ^ Vaginal pH Test from Point of Care Testing, July 2009, at: University of California, San Francisco – Department of Laboratory Medicine.
Cloth menstrual pad. Cloth menstrual pads are a reusable alternative to disposable sanitary napkins. They receive praise for being environmentally friendly, cost-cutting, as well as having purported health benefits. Bog body. Tollund Man lived in the 4th century BCE, and is one of the best studied examples of a bog body. A bog body (Moorleiche in German) is a human cadaver that has been naturally mummified within a peat bog. Palustrine. Palustrine comes from the Latin word palus or marsh.
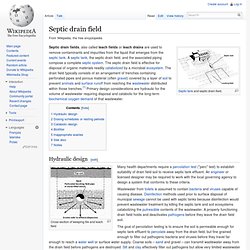
Septic drain field. Septic drain fields, also called leach fields or leach drains are used to remove contaminants and impurities from the liquid that emerges from the septic tank.
Blackwater (waste) Blackwater is a term dating to at least the 1970s[1] used to describe wastewater containing fecal matter and urine.
It is also known as foul water, or sewage. It is distinct from greywater or sullage, the residues of washing processes. Water coming from domestic equipment other than toilets (e.g., bathtubs, showers, sinks, washing machines) is called greywater and it is preferred to be kept separate from blackwater (which comes from toilets) to reduce the amount of water that gets heavily polluted. Separation of blackwater and greywater nowadays happens with all ecological buildings. Especially in autonomous buildings, the separation is always present. Blackwater contains pathogens that must decompose before they can be released safely into the environment.
Intertidal wetland. An intertidal wetland is an area along a shoreline that is exposed to air at low tide and submerged at high tide.
This type of wetland is defined by an intertidal zone and includes its own intertidal ecosystems. Description[edit] The main types of intertidal wetlands are mudflats (e.g., mangrove swamps) and salt marshes. The mangrove swamps are encountered along tropical shores and are characterized by tree vegetation, while salt marshes are mostly found in temperate zones and are mostly grass ecosystems.[1] Elastin. Epithelium. Epithelial layers are avascular, so they must receive nourishment via diffusion of substances from the underlying connective tissue, through the basement membrane.[2][3] Epithelia can also be organised into clusters of cells that function as exocrine and endocrine glands.
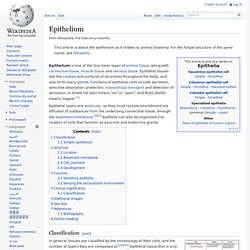
Classification[edit] Summary showing different epithelial cells/tissues and their characteristics.