

Partial least squares regression. Partial least squares regression (PLS regression) is a statistical method that bears some relation to principal components regression; instead of finding hyperplanes of minimum variance between the response and independent variables, it finds a linear regression model by projecting the predicted variables and the observable variables to a new space.
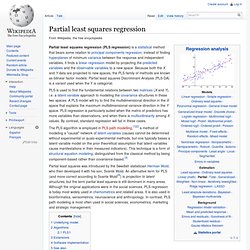
Because both the X and Y data are projected to new spaces, the PLS family of methods are known as bilinear factor models. Partial least squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) is a variant used when the Y is categorial. The PLS algorithm is employed in PLS path modelling,[1][2] a method of modeling a "causal" network of latent variables (causes cannot be determined without experimental or quasi-experimental methods, but one typically bases a latent variable model on the prior theoretical assumption that latent variables cause manifestations in their measured indicators). Underlying model[edit] where is an matrix of predictors, and are .
As . . 5 for. Análisis de componentes principales. ACP de una distribución normal multivariante centrada en (1,3) con desviación estándar 3 en la dirección aproximada (0,878, 0,478) y desviación estándar 1 en la dirección perpendicular a la anterior. Los vectores muestran los autovectores de la matriz de correlación escalados mediante la raíz cuadrada del correspondiente autovalor, y desplazados para que su origen coincidan con la media estadística.
En estadística , el (en español , en inglés, ) es una técnica utilizada para reducir la dimensionalidad de un conjunto de datos. Intuitivamente la técnica sirve para hallar las causas de la variabilidad de un conjunto de datos y ordenarlas por importancia. Técnicamente, el ACP busca la proyección según la cual los datos queden mejor representados en términos de mínimos cuadrados. El ACP se emplea sobre todo en análisis exploratorio de datos y para construir modelos predictivos. . [ editar ] Fundamento [ editar ] Matemáticas del ACP Existen dos formas básicas de aplicar el ACP: Non-negative matrix factorization. Illustration of approximate non-negative matrix factorization: the matrix V is represented by the two smaller matrices W and H, which, when multiplied, approximately reconstruct V.
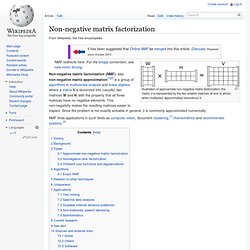
NMF redirects here. For the bridge convention, see new minor forcing. NMF finds applications in such fields as computer vision, document clustering,[1] chemometrics and recommender systems.[3] History[edit] In chemometrics non-negative matrix factorization has a long history under the name "self modeling curve resolution".[4] In this framework the vectors in the right matrix are continuous curves rather than discrete vectors.
Background[edit] Let matrix be the product of the matrices and such that: Matrix multiplication can be implemented as linear combinations of column vectors in with coefficients supplied by cell values in . Can be computed as follows: where: is the number of columns in is the column vector of the product matrix is the cell value in the. Latent Dirichlet allocation. In natural language processing, latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) is a generative model that allows sets of observations to be explained by unobserved groups that explain why some parts of the data are similar.
For example, if observations are words collected into documents, it posits that each document is a mixture of a small number of topics and that each word's creation is attributable to one of the document's topics. LDA is an example of a topic model and was first presented as a graphical model for topic discovery by David Blei, Andrew Ng, and Michael Jordan in 2003.[1] Topics in LDA[edit] In LDA, each document may be viewed as a mixture of various topics. This is similar to probabilistic latent semantic analysis (pLSA), except that in LDA the topic distribution is assumed to have a Dirichlet prior. For example, an LDA model might have topics that can be classified as CAT_related and DOG_related. Each document is assumed to be characterized by a particular set of topics.
Model[edit]