

Global Warming Solutions: Reduce Emissions. Articles. Global Warming News. Mar. 4, 2019 — Researchers have proposed a new idea that may explain why some Antarctic icebergs are tinged emerald green rather than the normal blue, potentially solving a decades-long scientific ... read more Mar. 4, 2019 — Rapid population and economic growth are destroying biodiversity. A growing demand for agricultural products requires ever new cultivated areas.
Even though technological advances are making ... read more Mar. 1, 2019 — A new study shows how information revealed by a new method of analyzing tree rings matches the story told by more high-tech equipment over the short-term. Because trees are long-lived, looking back ... read more New Research from Arctic: Thawing Permafrost Peatlands May Add to Atmospheric CO2 Burden Mar. 1, 2019 — A new study finds that peatlands may strengthen the permafrost-carbon feedback by adding to the atmospheric CO2 burden ... read more Forests, Carbon Sinks Cannot Make Up for Delays in Decarbonizing the Economy, Experts Argue. NASA: Climate Change and Global Warming. Global Warming: 2018 Articles, Facts, Causes & Effects. Climate change.
Global warming. Global mean land-ocean temperature change from 1880 to 2014, relative to the 1951–1980 mean.

The black line is the annual mean and the red line is the 5-year running mean. The green bars show uncertainty estimates. Source: NASA GISS. The map shows the 10-year average (2000–2009) global mean temperature anomaly relative to the 1951–1980 mean. The largest temperature increases are in the Arctic and the Antarctic Peninsula. Fossil fuel related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to five of the IPCC's "SRES" emissions scenarios. Global Warming News, Articles. Study warns of looming potential for runaway global warming. Facts on global warming, climate change and geospatial technologies. Some Facts: The Rising Temperature April 2017 was the second-warmest April in 137 years of modern record-keeping, according to NASA‘s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS).In 2016, Earth’s average surface temperature hit a record level for the third consecutive year since records began in 1880.The global average temperature was about 1.1 degree Celsius (1.98 Fahrenheit) higher than the pre-industrial era.

This is when mankind’s mass burning of coal, and later oil and gas, started hiking levels of heat-trapping CO2 in the atmosphere. The Melting Ice Arctic summer sea ice shrank to 4.14 million square kilometers (1.6 million square miles) in 2016 — the second-lowest after 2012, when it reached 3.39 million km2.The Arctic Ocean could be ice-free in summer as early as 2030.On the other extreme of the world, Antarctica, sea ice last year hit its lowest extent ever recorded by satellites. What Causes Global Warming? What Is Global Warming? The globe is heating up.
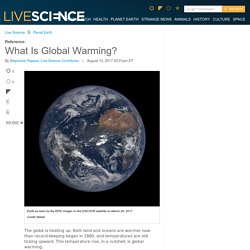
Both land and oceans are warmer now than record-keeping began in 1880, and temperatures are still ticking upward. This temperature rise, in a nutshell, is global warming. Here are the bare numbers, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): Average surface temperatures rose a total of 1.71 degrees Fahrenheit (0.95 degrees Celsius) between 1880 and 2016. The pace of change has been an additional 0.13 degrees F (0.07 degrees C) per decade, with the land surface warming faster than the ocean surface — 0.18 degrees F (0.10 degrees C) versus 0.11 degrees F (0.06 degrees C) per decade, respectively. The Paris Agreement, ratified by 159 nations as of the summer 2017, aims to halt that warming at 2.7 degrees F (1.5 degrees C) above Earth's average temperature during preindustrial times — a goal most scientists and policy makers agree will be a challenge to meet.
The main driver of today's warming is the combustion of fossil fuels. Global Warming 101 - Definition, Facts, Causes and Effects of Global Warming. Jump to Section Q: What is global warming? A: Here's a simple definition of global warming. (And yes, it's really happening.) What is global warming, facts and information? Glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, cloud forests are dying, and wildlife is scrambling to keep pace. It has become clear that humans have caused most of the past century's warming by releasing heat-trapping gases as we power our modern lives. Called greenhouse gases, their levels are higher now than at any time in the last 800,000 years. We often call the result global warming, but it is causing a set of changes to the Earth's climate, or long-term weather patterns, that varies from place to place. While many people think of global warming and climate change as synonyms, scientists use “climate change” when describing the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems—in part because some areas actually get cooler in the short term.
Global Warming. This page contains archived content and is no longer being updated.
At the time of publication, it represented the best available science. Throughout its long history, Earth has warmed and cooled time and again. Climate has changed when the planet received more or less sunlight due to subtle shifts in its orbit, as the atmosphere or surface changed, or when the Sun’s energy varied. But in the past century, another force has started to influence Earth’s climate: humanity. Global Warming and Its Effects. Effects of global warming. Describes the effects created by global warming A 2014 summary of climate change impacts Seven of these indicators would be expected to increase in a warming world and observations show that they are, in fact, increasing.
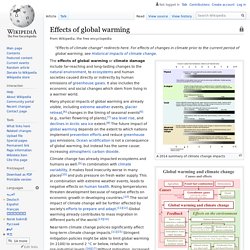
Three would be expected to decrease and they are, in fact, decreasing.[5] The effects of global warming or climate damage include far-reaching and long-lasting changes to the natural environment, to ecosystems and human societies caused directly or indirectly by human emissions of greenhouse gases. It also includes the economic and social changes which stem from living in a warmer world.
Climate change has already impacted ecosystems and humans as well.[9] In combination with climate variability, it makes food insecurity worse in many places[10] and puts pressure on fresh water supply. Effects. › en español Global climate change has already had observable effects on the environment.
Glaciers have shrunk, ice on rivers and lakes is breaking up earlier, plant and animal ranges have shifted and trees are flowering sooner. Effects that scientists had predicted in the past would result from global climate change are now occurring: loss of sea ice, accelerated sea level rise and longer, more intense heat waves. Taken as a whole, the range of published evidence indicates that the net damage costs of climate change are likely to be significant and to increase over time. Scientists have high confidence that global temperatures will continue to rise for decades to come, largely due to greenhouse gases produced by human activities. According to the IPCC, the extent of climate change effects on individual regions will vary over time and with the ability of different societal and environmental systems to mitigate or adapt to change.
Future Effects Temperatures Will Continue to Rise.